Abstract
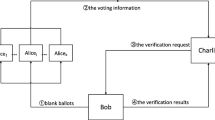
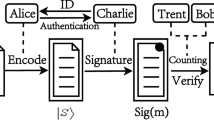
Based on the single-particle states, we propose a novel quantum voting protocol which can select multiple winners from candidates. In this protocol, the voting intentions of voters can be expressed through unitary operation, the voter’s ID information is contained in the ballot, and each ballot is encrypted. In addition, legitimate vote can neither be forged by malicious attackers nor be denied by voters. Considering the influence of the number of candidates and voters on the preparation of quantum states, we propose corresponding grou** strategies, respectively, to reduce the level of d-level single-particle states and the number of quantum states. Security analysis shows that our proposed protocol can resist different types of malicious attacks.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaum, D.L.: Untraceable electronic mail, return addresses, and digital pseudonyms. Commun. ACM 24(2), 84–90 (1981)
Jan, J.K., Tai, C.C.: A secure electronic voting protocol with IC cards. J. Syst. Softw. 39(2), 93–101 (1997)
Ku, W.C., Wang, S.D.: A secure and practical electronic voting scheme. Comput. Commun. 22(3), 279–286 (1999)
Tian, J.H., Zhang, J.Z., Li, Y.P.: A quantum multi-proxy blind signature scheme based on genuine four-qubit Entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(2), 1–8 (2016)
Shao, A.X., Zhang, J.Z., **e, S.C.: A quantum multi-proxy multi-blind-signature scheme based on genuine six-qubit Entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(12), 5216–5224 (2016)
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. Siam Rev. 41(2), 303–332 (1999)
Grover, L.K.: Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a Haystack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79(2), 325–328 (1997)
Grover, L.K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 212–219 (1997)
Britt, B.C.: Modeling viral diffusion using quantum computational network simulation. Quant. Eng. 2(1), 29 (2020)
Shi, Y.P.: A brief introduction to quantum computing and quantum information(I). Math. Model. Appl. 7(2), 1–10 (2018)
Shi, Y.P.: A brief introduction to quantum computing and quantum information(II). Math. Model. Appl. 7(3), 1–11 (2018)
Hillery, M.: Quantum voting and privacy ptotection: first steps. Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2006, 1598 (2006)
Vaccaro, J.A., Spring, J., Chefles, A.: Quantum protocols for anonymous voting and surveying. Phys. Rev. A 75(1), 012333 (2007)
Bonanome, M., Buzek, V., Hillery, M., Ziman, M.: Toward protocols for quantum-ensured privacy and secure voting. Phys. Rev. A 84(2), 290–296 (2011)
Horoshko, D., Kilin, S.: Quantum anonymous voting with anonymity check. Phys. Lett. A 375, 1172–1175 (2011)
Niu, X.F., Zhang, J.Z., **e, S.C., Chen, B.Q.: An improved quantum voting scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57, 3200–3206 (2018)
Wang, S.L., Zhang, S., Wang, Q., Shi, R.H.: Fault-tolerant quantum anonymous voting protocol. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58, 1008–1016 (2019)
Zhang, X., Zhang, J.Z., **e, S.C.: A secure quantum voting scheme based on quantum group blind signature. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 719–729 (2020)
Zhou, B.M., Zhang, K.J., Zhang, X., Wang, Q.L.: The cryptanalysis and improvement of a particular quantum voting model. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 1109–1120 (2020)
Xu, Y.Z., Huang, Y.F., Lu, W., Li, L.Z.: A Quantum Electronic Voting Scheme with d-Level Single Particles. In: Intelligent Computing Methodologies. ICIC. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. pp. 710–715 (2018)
Jiang, D.H., Wang, J., Liang, X.Q., Xu, G.B., Qi, H.F.: Quantum voting scheme based on locally indistinguishable orthogonal product states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 436–444 (2020)
Lin, S., Guo, G.D., Huang, F., Liu, X.F.: Quantum anonymous ranking based on the Chinese remainder theorem. Phys. Rev. A. 93(1), 012318 (2016)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A. 65(3), 032302 (2002)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68(4), 042317 (2003)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad. Phys. Rev. A 69(5), 052319 (2004)
Sun, Z., Qi, R.Y., Lin, Z.H. et al.: Design and implementation of a practical quantum secure direct communication system. In: 2018 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Abu Dhabi National Exhibition Centre (2018)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Public-key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, Ban-galore, India, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3121 (1992)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 661–663 (1991)
Zhang, W., Ding, D.S., Sheng, Y.B., et al.: Quantum secure direct communication with quantum memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118(22), 220501 (2017)
Pu, Y.F., Jiang, N., Chang, W., et al.: Experimental realization of a multiplexed quantum memory with 225 individually accessible memory cells. Nat. Commun. 8, 15359 (2017)
Qi, R.Y., Sun, Z., Lin, Z.S., et al.: Implementation and security analysis of practical quantum secure direct communication. Light Sci. Appl. 8(1), 22 (2019)
Sun, Z., Song, L.Y., Huang, Q., et al.: Towards practical quantum secure direct communication: a quantum-memory-free protocol and code design. IEEE Trans. Commun. 68(9), 5778–5792 (2020)
Pan, D., Li, K.R., Ruan, D., et al.: Single-photon-memory two-step quantum secure direct communication relying on Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pairs. IEEE Access. 8, 121146–121161 (2020)
Djordjevic, I.B., Milenkovic, O., Vasic, B.: Generalized low-density parity-check codes for optical communication systems. Lightw. Technol. 23(5), 1939–1946 (2005)
Yue, G., **, L., Wang, X.: Generalized low-density parity-check codes based on Hadamard constraints. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 53(3), 1058–1079 (2007)
Li, Q., Qu, X., Yin, L., Lu, J.: Generalized low-density parity-check coding scheme with partial-band jamming. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 19(2), 203–210 (2014)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., Gao, F., Sun, Y.: Robust and efficient quantum private comparison of equality with collective detection over collective-noise channels. Sci. China. Phys. Mech. 56(9), 1670–1678 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2019MF023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YR., Jiang, DH., Zhang, YH. et al. A quantum voting protocol using single-particle states. Quantum Inf Process 20, 110 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03048-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03048-6