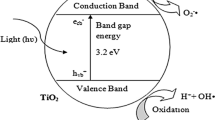
Abstract
Adsorption measurements of CO2 and H2O over TiO2 surfaces in dark and under illumination were carried out to reveal the ensuing bottlenecks of the initial steps of the artificial photosynthesis reaction. When the adsorption isotherms of both CO2 and H2O were measured under illumination, the results were comparable to isotherms measured at higher temperatures in dark. This evidence is interpreted as the presence of hot spots, due to charge carrier recombination reactions. Differential heat of adsorption measurements revealed that H2O adsorption on TiO2 is stronger, and with a higher coverage than that of CO2. Dissociation of water is an energetically uphill reaction, and the local hot spots due to charge carrier recombination in indirect bandgap semiconductors can enhance the reaction probability. At higher temperatures, higher reaction probabilities are expected and estimated by a thermodynamic analysis for water splitting reaction. The potential role of these hot spots during natural and artificial photosynthetic reactions is discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya DP, Camillone N, Sutter P (2011) CO2 adsorption, diffusion, and electron-induced chemistry on rutile TiO2(110): a low-temperature scanning tunneling microscopy study. J Phys Chem C 115(24):12095–12105. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp202476v
Allakhverdiev SI, Kreslavski VD, Klimov VV, Los DA, Carpentier R, Mohanty P (2008) Heat stress: an overview of molecular responses in photosynthesis. Photosynth Res 98(1–3):541–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-008-9331-0
Aschauer U, He Y, Cheng H, Li SC, Diebold U, Selloni A (2010) Influence of subsurface defects on the surface reactivity of TiO2: water on anatase (101). J Phys Chem C 114(2):1278–1284. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp910492b
Bahnemann DW, Hilgendorff M, Memming R (1997) Charge carrier dynamics at TiO2 particles: reactivity of free and trapped holes. J Phys Chem B 101(21):4265–4275. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9639915
Balajka J, Hines MA, DeBenedetti WJI, Komora M, Pavelec J, Schmid M, Diebold U (2018) High-affinity adsorption leads to molecularly ordered interfaces on TiO2 in air and solution. Science 361(6404):786–789. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat6752
Berg IA (2011) Ecological aspects of the distribution of different autotrophic CO2 fixation pathways. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(6):1925–1936. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02473-10
Berger T, Sterrer M, Diwald O, Knözinger E, Panayotov D, Thompson TL, Yates JT (2005) Light-induced charge separation in anatase TiO2 particles. J Phys Chem B 109(13):6061–6068. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0404293
Berger T, Diwald O, Knözinger E, Sterrer M, Yates JT (2006) UV induced local heating effects in TiO2 nanocrystals. Phys Chem Chem Phys 8(15):1822–1826. https://doi.org/10.1039/b517107e
Britt RD, Marchiori DA (2019) Photosystem II, poised for O2 formation. Science 366(6463):305–306. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaz4522
Burghaus U (2014) Surface chemistry of CO2 - adsorption of carbon dioxide on clean surfaces at ultrahigh vacuum. Prog Surf Sci 89(2):161–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progsurf.2014.03.002
Cahill DG, Braun PV, Chen G, Clarke DR, Fan S, Goodson KE, Keblinski P, King WP, Mahan GD, Majumdar A, Maris HJ, Phillpot SR, Pop E, Shi L (2014) Nanoscale thermal transport. II. 2003–2012. Appl Phys Rev 1(1):011305. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4832615
Cai MJ, Li CR, He L (2020) Enhancing photothermal CO2 catalysis by thermal insulating substrates. Rare Met 39(8):881–886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01431-3
Calisan, A., Ogulgonen, C.G., Yilmaz, A., Uner, D., Kincal, S. (2019). Steam methane reforming over structured reactors under concentrated solar irradiation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44: 18682–18693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.04.033
Chen X, Shen S, Guo L, Mao SS (2010) Semiconductor-based photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Chem Rev 110(11):6503–6570. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr1001645
Chen X, Hua C, Zhang H, Ravichandran NK, Minnich AJ (2018) Quasiballistic thermal transport from nanoscale heaters and the role of the spatial frequency. Phys Rev Appl 10(5):054068. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.10.054068
Cheng H, Selloni A (2009) Surface and subsurface oxygen vacancies in anatase TiO2 and differences with rutile. Phys Rev B 79(9):092101. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.79.092101
Chovancek E, Zivcak M, Brestic M, Hussain S, Allakhverdiev SI (2021) The different patterns of post-heat stress responses in wheat genotypes: the role of the transthylakoid proton gradient in efficient recovery of leaf photosynthetic capacity. Photosynth Res 150(1–3):179–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-020-00812-0
Colombo DP, Bowman RM (1996) Does interfacial charge transfer compete with charge carrier recombination? A femtosecond diffuse reflectance investigation of TiO2 nanoparticles. J Phys Chem 100(47):18445–18449. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9610628
Cowan AJ, Tang J, Leng W, Durrant JR, Klug DR (2010) Water splitting by nanocrystalline TiO2 in a complete photoelectrochemical cell exhibits efficiencies limited by charge recombination. J Phys Chem C 114(9):4208–4214. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp909993w
De Angelis F, Di Valentin C, Fantacci S, Vittadini A, Selloni A (2014) Theoretical studies on anatase and less common TiO2 phases: bulk, surfaces, and nanomaterials. Chem Rev 114(19):9708–9753. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr500055q
Di Paola A, Bellardita M, Palmisano L, Barbieriková Z, Brezová V (2014) Influence of crystallinity and OH surface density on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 powders. J Photochem Photobiol A 273:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2013.09.008
Diebold U (2003) The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surf Sci Rep 48(5–8):53–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-5729(02)00100-0
Dilla M, Mateblowski A, Ristig S, Strunk J (2017) Photocatalytic CO2 reduction under continuous flow high-purity conditions: influence of light intensity and H2O concentration. ChemCatChem 9(23):4345–4352. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201701189
Dotan H, Landman A, Sheehan SW, Malviya KD, Shter GE, Grave DA, Arzi Z, Yehudai N, Halabi M, Gal N, Hadari N, Cohen C, Rothschild A, Grader GS (2019) Decoupled hydrogen and oxygen evolution by a two-step electrochemical–chemical cycle for efficient overall water splitting. Nat Energy 4:786–795. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-019-0462-7
Emeline AV, Ryabchuk V, Serpone N (2000) Factors affecting the efficiency of a photocatalyzed process in aqueous metal-oxide dispersions prospect of distinguishing between two kinetic models. J Photochem Photobiol A 133(1–2):89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(00)00225-2
Emeline AV, Ryabchuk VK, Serpone N (2005) Dogmas and misconceptions in heterogeneous photocatalysis Some enlightened reflections. J Phys Chem B 109(39):18515–18521. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0523367
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/238037a0
Fujishima A, Zhang X, Tryk DA (2008) TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf Sci Rep 63(12):515–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SURFREP.2008.10.001
García-Plazaola JI, Esteban R, Fernández-Marín B, Kranner I, Porcar-Castell A (2012) Thermal energy dissipation and xanthophyll cycles beyond the Arabidopsis model. Photosynth Res 113(1–3):89–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-012-9760-7
Gaya UI (2014) Heterogeneous photocatalysis using inorganic semiconductor solids, 1st edn. Springer, Dordrecht
Henderson MA (1996a) An HREELS and TPD study of water on TiO2(110): the extent of molecular versus dissociative adsorption. Surf Sci 355(1–3):151–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(95)01357-1
Henderson MA (1996b) Structural sensitivity in the dissociation of water on TiO2 single-crystal surfaces. Langmuir 12(21):5093–5098. https://doi.org/10.1021/la960360t
Henderson MA (1998) Evidence for bicarbonate formation on vacuum annealed TiO2(11O) resulting from a precursor-mediated interaction between CO2 and H2O. Surf Sci 400(1–3):203–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-6028(97)00863-7
Henderson MA (2011) A surface science perspective on TiO2 photocatalysis. Surf Sci Rep 66(6–7):185–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfrep.2011.01.001
Heo JN, Kim J, Do JY, Park NK, Kang M (2020) Self-assembled electron-rich interface in defected ZnO:rGO-Cu:Cu2O, and effective visible light-induced carbon dioxide photoreduction. Appl Catal B 266(September 2019):118648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118648
Hugenschmidt MB, Gamble L, Campbell CT (1994) The interaction of H2O with a TiO2(110) surface. Surf Sci 302(3):329–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(94)90837-0
Hurum DC, Agrios AG, Gray KA, Rajh T, Thurnauer MC (2003) Explaining the enhanced photocatalytic activity of Degussa P25 mixed-phase TiO2 using EPR. J Phys Chem B 107(19):4545–4549. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0273934
Inoue T, Fujishima A, Konishi S, Honda K (1979) Photoelectrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide in aqueous suspensions of semiconductor powders. Nature 277(5698):637–638. https://doi.org/10.1038/277637a0
Ipek B, Uner D (2012) Artificial Photosynthesis from a Chemical Engineering Perspective. In: Najafpour MM (ed) Artificial Photosynthesis. IntechOpen, London, pp 13–36
Jou JH, Hsieh CY, Tseng JR, Peng SH, Jou YC, Hong JH, Shen SM, Tang MC, Chen PC, Lin CH (2013) Candle light-style organic light-emitting diodes. Adv Func Mater 23(21):2750–2757. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201203209
Jourshabani M, Lee BK, Shariatinia Z (2020) From traditional strategies to Z-scheme configuration in graphitic carbon nitride photocatalysts: recent progress and future challenges. Appl Catal B 276:119157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119157
Kanan MW, Nocera DG (2008) In situ formation of an oxygen-evolving catalyst in neutral water containing phosphate and Co2+. Science 321(5892):1072–1075. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1162018
Kanan MW, Surendranath Y, Nocera DG (2009) Cobalt–phosphate oxygen-evolving compound. Chem Soc Rev 38(1):109–114. https://doi.org/10.1039/b802885k
Landman A, Dotan H, Shter GE, Wullenkord M, Houaijia A, Maljusch A, Grader GS, Rothschild A (2017) Photoelectrochemical water splitting in separate oxygen and hydrogen cells. Nat Mater 16:646–651. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4876
Levchenko AA, Li G, Boerio-Goates J, Woodfield BF, Navrotsky A (2006) TiO2 stability landscape: Polymorphism, surface energy, and bound water energetics. Chem Mater 18(26):6324–6332. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm061183c
Leytner S, Hupp JT (2000) Evaluation of the energetics of electron trap states at the nanocrystalline titanium dioxide/aqueous solution interface via time-resolved photoacoustic spectroscopy. Chem Phys Lett 330(3–4):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(00)01112-X
Lin X, Wang ZT, Lyubinetsky I, Kay BD, Dohnálek Z (2013) Interaction of CO2 with oxygen adatoms on rutile TiO2(110). Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(17):6190–6195. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp44040k
Linsebigler AL, Lu G, Yates JT (1995) Photocatalysis on TiO2 surfaces: principles, mechanisms, and selected results. Chem Rev 95(3):735–758. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00035a013
Litke A, Su Y, Tranca I, Weber T, Hensen EJMM, Hofmann JP (2017) Role of adsorbed water on charge carrier dynamics in photoexcited TiO2. J Phys Chem C 121(13):7514–7524. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b00472
Lu G, Linsebigler A, Yates JT (1994) Ti3+ defect sites on TiO2(110): Production and chemical detection of active sites. J Phys Chem 98(45):11733–11738. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100096a017
Lubitz W, Chrysina M, Cox N (2019) Water oxidation in photosystem II. Photosynth Res 142(1):105–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-019-00648-3
Marinescu C, Sofronia A, Rusti C, Piticescu R, Badilita V, Vasile E, Baies R, Tanasescu S (2011) DSC investigation of nanocrystalline TiO2 powder. J Therm Anal Calorim 103:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-1072-6
Martin ST, Herrmann H, Hoffmann MR (1994) Time-resolved microwave conductivity part 2. Quantum-sized TiO2 and the effect of adsorbates and light intensity on charge-carrier dynamics. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 90(21):3323–3330. https://doi.org/10.1039/FT9949003323
Martra G (2000) Lewis acid and base sites at the surface of microcrystalline TiO2 anatase: relationships between surface morphology and chemical behaviour. Appl Catal A 200(1–2):275–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(00)00641-4
Mendive CB, Hansmann D, Bredow T, Bahnemann D (2011) New insights into the mechanism of TiO2 photocatalysis: thermal processes beyond the electron-hole creation. J Phys Chem C 115(40):19676–19685. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp112243q
Mettan X, Jaćimović J, Barišić OS, Pisoni A, Batistić I, Horváth E, Brown S, Rossi L, Szirmai P, Farkas B, Berger H, Forró L (2019) Tailoring thermal conduction in anatase TiO2. Commun Phys 2:123. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42005-019-0224-7
Mezhenny S, Maksymovych P, Thompson TL, Diwald O, Stahl D, Walck SD, Yates JT (2003) STM studies of defect production on the TiO2(110)-(1 × 1) and TiO2(110)-1 × 2) surfaces induced by UV irradiation. Chem Phys Lett 369(1–2):152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(02)01997-8
Mino L, Cesano F, Scarano D, Spoto G, Martra G (2019) Molecules and heterostructures at TiO2 surface: the cases of H2O, CO2, and organic and inorganic sensitizers. Res Chem Intermed 45:5801–5829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-04003-y
Mohamed HH, Mendive CB, Dillert R, Bahnemann DW (2011) Kinetic and mechanistic investigations of multielectron transfer reactions induced by stored electrons in TiO2 nanoparticles: a stopped flow study. J Phys Chem A 115(11):2139–2147. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp108958w
Murakami Y, Kenji E, Nosaka AY, Nosaka Y (2006) Direct detection of OH radicals diffused to the gas phase from the UV-irradiated photocatalytic TiO2 surfaces by means of laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 110(34):16808–16811. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp063293c
Najafpour MM (2013) An approach for catalyst design in artificial photosynthetic systems: focus on nanosized inorganic cores within proteins. Photosynth Res 117(1–3):197–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-012-9792-z
Najafpour MM, Rahimi F, Sedigh DJ, Carpentier R, Eaton-Rye JJ, Shen JR, Allakhverdiev SI (2013) Gold or silver deposited on layered manganese oxide: a functional model for the water-oxidizing complex in photosystem II. Photosynth Res 117(1–3):423–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9899-x
Nguyen-Phan T-D, Luo S, Liu Z, Gamalski AD, Tao J, Xu W, Stach EA, Polyansky DE, Senanayake SD, Fujita E, Rodriguez JA (2015) Striving toward noble-metal-free photocatalytic water splitting: the hydrogenated-graphene—TiO2 prototype. Chem Mater 27(18):6282–6296. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b02131
Nosaka YA, Fujiwara T, Yagi H, Akutsu H, Nosaka Y (2004) Characteristics of water adsorbed on TiO2 photocatalytic systems with increasing temperature as studied by solid-state 1H NMR spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 108(26):9121–9125. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp037297i
Ohtani B (2013) Titania photocatalysis beyond recombination: a critical review. Catalysts 3(4):942–953. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal3040942
Panarelli EG, Livraghi S, Maurelli S, Polliotto V, Chiesa M, Giamello E (2016) Role of surface water molecules in stabilizing trapped hole centres in titanium dioxide (anatase) as monitored by electron paramagnetic resonance. J Photochem Photobiol A 322–323:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.02.015
Peter LM, Upul Wijayantha KG (2014) Photoelectrochemical water splitting at semiconductor electrodes: fundamental problems and new perspectives. ChemPhysChem 15(10):1983–1995. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201402024
Qian R, Zong H, Schneider J, Zhou G, Zhao T, Li Y, Yang J, Bahnemann DW, Hong Pan J (2018) Charge carrier trap**, recombination and transfer during TiO2 photocatalysis: an overview. Catal Today. 355:78–90 https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CATTOD.2018.10.053
Rabani J, Yamashita K, Ushida K, Stark J, Kira A (1998) Fundamental reactions in illuminated titanium dioxide nanocrystallite layers studied by pulsed laser. J Phys Chem B 102(10):1689–1695. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp973411j
Ras EJ, Louwerse MJ, Mittelmeijer-Hazeleger MC, Rothenberg G (2013) Predicting adsorption on metals: simple yet effective descriptors for surface catalysis. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(12):4436–4443. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp42965b
Rath T, Bloh JZ, Luken A, Ollegott K, Muhler M (2020) Model-based analysis of the photocatalytic HCl oxidation kinetics over TiO2. Ind Eng Chem Res 59(10):4265–4272. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05820
Renz C (1921) Lichtreaktionen der oxyde des titans, cers und der erdsäuren. Helv Chim Acta 4(1):961–968. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.192100401101
Rong W, Kazuhito H, Akira F, Makoto C, Eiichi K, Astushi K, Mitsuhide S, Toshiya W (1997) Light-induced amphiphilic surfaces. Nature 388:431–432. https://doi.org/10.1038/41233
Serpone N (1997) Relative photonic efficiencies and quantum yields in heterogeneous photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol A 104(1–3):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(96)04538-8
Serpone N, Lawless D, Khairutdinov R, Pelizzetti E (1995) Subnanosecond relaxation dynamics in TiO2 colloidal sols (particle sizes Rp = 1.0–1.34 nm). Relevance to heterogeneous photocatalysis. J Phys Chem 99(45):16655–16661. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100045a027
Shirai K, Sugimoto T, Watanabe K, Haruta M, Kurata H, Matsumoto Y (2016) Effect of water adsorption on carrier trap** dynamics at the surface of anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. Nano Lett 16(2):1323–1327. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04724
Shkrob IA, Sauer MC, Gosztola D (2004) Efficient, rapid photooxidation of chemisorbed polyhydroxyl alcohols and carbohydrates by TiO2 nanoparticles in an aqueous solution. J Phys Chem B 108(33):12512–12517. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0477351
Sieland F, Schneider J, Bahnemann DW (2017) Fractal charge carrier kinetics in TiO2. J Phys Chem C 121(43):24282–24291. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b07087
Simon SH (2013) The Oxford solid state basics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Stevanovic A, Büttner M, Zhang Z, Yates JT (2012) Photoluminescence of TiO2: effect of UV light and adsorbed molecules on surface band structure. J Am Chem Soc 134(1):324–332. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja2072737
Suga M, Akita F, Yamashita K, Nakajima Y, Ueno G, Li H, Yamane T, Hirata K, Umena Y, Yonekura S, Yu LJ, Murakami H, Nomura T, Kimura T, Kubo M, Baba S, Kumasaka T, Tono K, Yabashi M, Shen JR (2019) An oxyl/oxo mechanism for oxygen-oxygen coupling in PSII revealed by an x-ray free-electron laser. Science 366(6463):334–338. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aax6998
Szczepankiewicz SH, Moss JA, Hoffmann MR (2002a) Electron traps and the stark effect on hydroxylated titania photocatalysts. J Phys Chem B 106(31):7654–7658. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp020472v
Szczepankiewicz SH, Moss JA, Hoffmann MR (2002b) Slow surface charge trap** kinetics on irradiated TiO2. J Phys Chem B 106(11):2922–2927. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp004244h
Takata T, Jiang J, Sakata Y, Nakabayashi M, Shibata N, Nandal V, Seki K, Hisatomi T, Domen K (2020) Photocatalytic water splitting with a quantum efficiency of almost unity. Nature 581:411–414. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2278-9
Thompson TL, Yates JT (2006) Surface science studies of the photoactivation of TiO2—new photochemical processes. Chem Rev 106(10):4428–4453. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr050172k
Thompson TL, Diwald O, Yates JT (2003) CO2 as a probe for monitoring the surface defects on TiO2(110)-temperature-programmed desorption. J Phys Chem B 107(42):11700–11704. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp030430m
Tilocca A, Selloni A (2003) Reaction pathway and free energy barrier for defect-induced water dissociation on the (101) surface of TiO2-anatase. J Chem Phys 119(14):7445–7450. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1607306
Turchi CS, Ollis DF (1990) Photocatalytic degradation of organic water contaminants: mechanisms involving hydroxyl radical attack. J Catal 122(1):178–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9517(90)90269-P
Uner D, Oymak MM (2012) On the mechanism of photocatalytic CO2 reduction with water in the gas phase. Catal Today 181(1):82–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2011.06.019
Uner D, Tapan NA, Ozen I, Uner M (2003) Oxygen adsorption on Pt/TiO2 catalysts. Appl Catal A 251(2):225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(03)00317-X
Uner D, Bayar I, Tabari T (2015) The influence of relative humidity on photocatalytic oxidation of nitric oxide (NO) over TiO2. Appl Surf Sci 354:260–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.07.045
Vittadini A, Selloni A, Rotzinger FP, Grätzel M (1998) Structure and energetics of water adsorbed at TiO2 anatase (101) and (001) surfaces. Phys Rev Lett 81(14):2954–2957. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.2954
Wang L-Q, Baer DR, Engelhard MH, Shultz AN (1995) The adsorption of liquid and vapor water on TiO2(110) surfaces: the role of defects. Surf Sci 344(3):237–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(95)00859-4
Wang Y, Fu**ami K, Zhang R, Wan C, Wang N, Ba Y, Koumoto K (2010) Interfacial thermal resistance and thermal conductivity in nanograined SrTiO3. Appl Phys Express 3:031101. https://doi.org/10.1143/APEX.3.031101
Wang J, Huang J, **e H, Qu A (2014) Synthesis of g-C3N4/TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic activity for H2 evolution by a simple method. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(12):6354–6363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.02.020
Wang M, **e B, Fu Y, Dong C, Hui L, Guanghui L, Liu H (2015) Effects of different elevated CO2 concentrations on chlorophyll contents, gas exchange, water use efficiency, and PSII activity on C3 and C4 cereal crops in a closed artificial ecosystem. Photosynth Res 126(2–3):351–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-015-0134-9
Wang X, He J, Li J, Lu G, Dong F, Majima T, Zhu M (2020) Immobilizing perovskite CsPbBr 3 nanocrystals on Black phosphorus nanosheets for boosting charge separation and photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Appl Catal B 277(May):119230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119230
Wei Y, Zhou Z, Fang W-H, Long R (2018) Grain boundary facilitates photocatalytic reaction in rutile TiO2 despite fast charge recombination: a time-domain ab initio analysis. J Phys Chem Lett 9(19):5884–5889. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b02761
Wu C-YYC-HH, Tu K-JJ, Deng J-PP, Lo Y-SS, Wu C-YYC-HH (2017) Markedly enhanced surface hydroxyl groups of TiO2 nanoparticles with superior water-dispersibility for photocatalysis. Materials 10(5):566–580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10050566
**ao J, Nishimae S, Vequizo JJM, Nakabayashi M, Hisatomi T, Li H, Lin L, Shibata N, Yamakata A, Inoue Y, Domen K (2022) Enhanced overall water splitting by a zirconium-doped TaON-based photocatalyst. Angew Chem Int Ed 61(17):e202116573. https://doi.org/10.1002/ANIE.202116573
Yamakata A, Ishibashi TA, Onishi H (2001) Time-resolved infrared absorption spectroscopy of photogenerated electrons in platinized TiO2 particles. Chem Phys Lett 333(3–4):271–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(00)01374-9
Yamamoto S, Bluhm H, Andersson K, Ketteler G, Ogasawara H, Salmeron M, Nilsson A (2008) In situ x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy studies of water on metals and oxides at ambient conditions. J Phys 20:184025. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/20/18/184025
Yang CC, Yu YH, Van Der Linden B, Wu JCS, Mul G (2010) Artificial photosynthesis over crystalline TiO2-based catalysts: fact or fiction? J Am Chem Soc 132(24):8398–8406. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja101318k
Zhang Z, Yates JT (2012) Band bending in semiconductors: chemical and physical consequences at surfaces and interfaces. Chem Rev 112(10):5520–5551. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr3000626
Zhang J, Zhou P, Liu J, Yu J (2014) New understanding of the difference of photocatalytic activity among anatase, rutile and brookite TiO2. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16(38):20382–20386. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cp02201g
Zhao Y, Li Z, Li M, Liu J, Liu X, Waterhouse GIN, Wang Y, Zhao J, Gao W, Zhang Z, Long R, Zhang Q, Gu L, Liu X, Wen X, Ma D, Wu LZ, Tung CH, Zhang T (2018) Reductive transformation of layered-double-hydroxide nanosheets to Fe-based heterostructures for efficient visible-light photocatalytic hydrogenation of CO. Adv Mater 30(36):1803127. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201803127
Zhao Y, Gao W, Li S, Williams GR, Mahadi AH, Ma D (2019) Solar-versus thermal-driven catalysis for energy conversion. Joule 3(4):920–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2019.03.003
Zubkoy T, Stahl D, Thompson TL, Panayotov D, Diwald O, Yates JT (2005) Ultraviolet light-induced hydrophilicity effect on TiO2(110) (1×1). Dominant role of the photooxidation of adsorbed hydrocarbons causing wetting by water droplets. J Phys Chem B 109(32):15454–15462. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp058101c
Acknowledgements
The financial support for this project was provided by TUBITAK under grant no 117M040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not declare any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uner, D., Yilmaz, B. Elucidating the role of adsorption during artificial photosynthesis: H2O and CO2 adsorption isotherms over TiO2 reveal thermal effects under UV illumination. Photosynth Res 154, 353–367 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-022-00924-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-022-00924-9