Abstract
Background and Aims
The use of organic amendments improves soil functioning and thus crop productivity. Our previous studies have shown that the banding of organic amendments increases the transpiration efficiency (TE) of wheat plants, but the underlying mechanism remained unclear. This study aims to determine whether and how the organic amendments can increase the TE of corn plants (Zea mays L.).
Methods
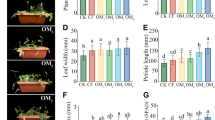
The effects of nutrient-enriched poultry litter, compost and brown coal on TE were compared with inorganic fertilizer. Corn plants were grown in Chromosol topsoil in pots for 50 days.
Results
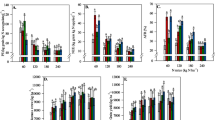
The poultry litter and compost but not brown coal, increased the TE of corn plants by 25% and 14%, respectively (P < 0.05), compared to inorganic fertilizer. At the leaf level, poultry litter and compost also increased the instantaneous TE due to either decreased transpiration or increased instantaneous CO2 assimilation rates. The increased TE at the plant level was closely associated with increased abundances of soil fungi, bacteria and bacteria in genus Bacillus. Meanwhile, there were increases in the concentrations of leaf hormones abscisic acid (ABA) (> 50%), methyl jasmonate (JA) (> 80%) and indole acetic acid (IAA).
Conclusion
Organic amendments enhanced the population of plant beneficial soil microorganisms such as those in the Bacillus genus, which likely led to the increased biosynthesis of leaf hormones ABA and JA, resulting in stomatal close, reduced total transpiration and increased transpiration efficiency of the corn canopy.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoah-Antwi C, Kwiatkowska-Malina J, Thornton SF, Fenton O, Malina G, Szara E (2020) Restoration of soil quality using biochar and brown coal waste: A review. Sci Total Environ 722:137852
Anli M, Baslam M, Tahiri A, Raklami A, Symanczik S, Boutasknit A, Ait-El-Mokhtar M, Ben-Laouane R, Toubali S, Ait Rahou Y (2020) Biofertilizers as strategies to improve photosynthetic apparatus, growth, and drought stress tolerance in the date palm. Front Plant Sci 11:516818
Barnawal D, Bharti N, Pandey SS, Pandey A, Chanotiya CS, Kalra A (2017) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria enhance wheat salt and drought stress tolerance by altering endogenous phytohormone levels and TaCTR1/TaDREB2 expression. Physiol Plant 161:502–514
Blum A (2009) Effective use of water (EUW) and not water-use efficiency (WUE) is the target of crop yield improvement under drought stress. Field Crops Res 112:119–123
Borneman J, Hartin RJ (2000) PCR primers that amplify fungal rRNA genes from environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4356–4360
Brenzinger K, Costa OY, Ho A, Koorneef G, Robroek B, Molenaar D, Korthals G, Bodelier PL (2021) Steering microbiomes by organic amendments towards climate-smart agricultural soils. Biol Fertil Soils 57:1053–1074
Cabrera-Bosquet L, Molero G, Bort J, Nogués S, Araus JL (2007) The combined effect of constant water deficit and nitrogen supply on WUE, NUE and Δ13C in durum wheat potted plants. Ann Appl Biol 151:277–289
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Huntley J, Fierer N, Owens SM, Betley J, Fraser L, Bauer M (2012) Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J 6:1621–1624
Chater CC, Oliver J, Casson S, Gray JE (2014) Putting the brakes on: abscisic acid as a central environmental regulator of stomatal development. New Phytol 202:376–391
Chen W, Meng P, Feng H, Wang C (2020) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and physiological performance of Catalpa bungei CA Mey. under drought stress. Forests 11:1117
Chu H, Lin X, Fujii T, Morimoto S, Yagi K, Hu J, Zhang J (2007) Soil microbial biomass, dehydrogenase activity, bacterial community structure in response to long-term fertilizer management. Soil Biol Biochem 39:2971–2976
Cohen AC, Bottini R, Pontin M, Berli FJ, Moreno D, Boccanlandro H, Travaglia CN, Piccoli PN (2015) Azospirillum brasilense ameliorates the response of Arabidopsis thaliana to drought mainly via enhancement of ABA levels. Physiol Plant 153:79–90
Condon AG, Richards R, Rebetzke G, Farquhar G (2002) Improving intrinsic water-use efficiency and crop yield. Crop Sci 42:122–131
de Lima BC, Moro AL, Santos ACP, Bonifacio A, Araujo ASF, de Araujo FF (2019) Bacillus subtilis ameliorates water stress tolerance in maize and common bean. J Plant Interact 14:432–439
Denman SE, McSweeney CS (2006) Development of a real-time PCR assay for monitoring anaerobic fungal and cellulolytic bacterial populations within the rumen. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 58:572–582
Elhindi KM, El-Din AS, Elgorban AM (2017) The impact of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in mitigating salt-induced adverse effects in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Saudi J Biol Sci 24:170–179
Escalona J, Tomàs M, Martorell S, Medrano H, Ribas-Carbo M, Flexas J (2012) Carbon balance in grapevines under different soil water supply: importance of whole plant respiration. Aust J Grape Wine Res 18:308–318
Espinosa D, Sale PW, Tang C (2011) Changes in pasture root growth and transpiration efficiency following the incorporation of organic manures into a clay subsoil. Plant Soil 348:329–343
Fang Y, Xu B, Turner NC, Li F (2010) Does root pruning increase yield and water-use efficiency of winter wheat? Crop past Sci 61:899–910
Fonseca MdCd, Bossolani JW, de Oliveira SL, Moretti LG, Portugal JR, Scudeletti D, de Oliveira EF, Crusciol CAC (2022) Bacillus subtilis inoculation improves nutrient uptake and physiological activity in sugarcane under drought stress. Microorganisms 10:809
Francioli D, Schulz E, Lentendu G, Wubet T, Buscot F, Reitz T (2016) Mineral vs. organic amendments: microbial community structure, activity and abundance of agriculturally relevant microbes are driven by long-term fertilization strategies. Front Microbiol 7:1446
Green SJ, Prakash O, Jasrotia P, Overholt WA, Cardenas E, Hubbard D, Tiedje JM, Watson DB, Schadt CW, Brooks SC (2012) Denitrifying bacteria from the genus Rhodanobacter dominate bacterial communities in the highly contaminated subsurface of a nuclear legacy waste site. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1039–1047
Hatfield Dold (2019) Water-use efficiency: advances and challenges in a changing climate. Front Plant Sci 10:103
Hobbie JE, Hobbie EA (2013) Microbes in nature are limited by carbon and energy: the starving-survival lifestyle in soil and consequences for estimating microbial rates. Front Microbiol 4:324
Isbell R (2016) The Australian soil classification. CSIRO publishing
Jackson P, Basnayake J, Inman-Bamber G, Lakshmanan P, Natarajan S, Stokes C (2016) Genetic variation in transpiration efficiency and relationships between whole plant and leaf gas exchange measurements in Saccharum spp. and related germplasm. J Exp Bot 67:861–871
Kumar AS, Lakshmanan V, Caplan JL, Powell D, Czymmek KJ, Levia DF, Bais HP (2012) Rhizobacteria Bacillus subtilis restricts foliar pathogen entry through stomata. Plant J 72:694–706
Lastochkina O, Pusenkova L, Yuldashev R, Babaev M, Garipova S, Dy B, Khairullin R, Aliniaeifard S (2017) Effects of Bacillus subtilis on some physiological and biochemical parameters of Triticum aestivum L. (wheat) under salinity. Plant Physiol Biochem 121:80–88
Li Y, Xu S, Gao J, Pan S, Wang G (2016) Bacillus subtilis-regulation of stomatal movement and instantaneous water use efficiency in Vicia faba. Plant Growth Regul 78:43–55
Li Q, Li H, Zhang L, Zhang S, Chen Y (2018) Mulching improves yield and water-use efficiency of potato crop** in China: a meta-analysis. Field Crops Res 221:50–60
Lou J, Yang L, Wang H, Wu L, Xu J (2018) Assessing soil bacterial community and dynamics by integrated high-throughput absolute abundance quantification. PeerJ 6:e4514
Martel JL, Brissette FP, Lucas-Picher P, Troin M, Arsenault R (2021) Climate change and rainfall intersity-during-frequency curves: overview of science and guidelines for adaptation. J Hydrol Eng 26:03121001
Mir AR, Siddiqui H, Alam P, Hayat S (2020) Foliar spray of Auxin/IAA modulates photosynthesis, elemental composition, ROS localization and antioxidant machinery to promote growth of Brassica juncea. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26:2503–2520
Müller M, Munné-Bosch S (2021) Hormonal impact on photosynthesis and photoprotection in plants. Plant Physiol 185:1500–1522
Munemasa S, Mori IC, Murata Y (2011) Methyl jasmonate signaling and signal crosstalk between methyl jasmonate and abscisic acid in guard cells. Plant Signal Behav 6:939–941
Nehela Y, Hijaz F, Elzaawely AA, El-Zahaby HM, Killiny N (2016) Phytohormone profiling of the sweet orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) leaves and roots using GC–MS-based method. J Plant Physiol 199:12–17
Osnas JL, Lichstein JW, Reich PB, Pacala SW (2013) Global leaf trait relationships: mass, area, and the leaf economics spectrum. Science 340:741–744
Otto E, Ishi R, Kumara A (1989) Interaction of nitrogen supply and soil water stress on photosynthesis and transpiration rate. Japanese J Crop Sci 58:424–429
Pastor A, Palazzo A, Havlik P, Biemans H, Wada Y, Obersteiner M, Kabat P, Ludwig F (2019) The global nexus of food-trade-water sustaining environmental flows by 2050. Nat Sustain 2:499–507
Pons S, Fournier S, Chervin C, Bécard G, Rochange S, Frei Dit Frey N, Puech Pagès V (2020) Phytohormone production by the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis. PLoS ONE 15:e0240886
Puga-Freitas R, Blouin M (2015) A review of the effects of soil organisms on plant hormone signalling pathways. Environ Exp Bot 114:104–116
Reddy P, Plozza T, Ezernieks V, Stefanelli D, Scalisi A, Goodwin I, Rochfort S (2022) Metabolic pathways for observed impacts of crop load on floral induction in apple. Int J Mol Sci 23:6019
Salomon MV, Bottini R, de Souza Filho GA, Cohen AC, Moreno D, Gil M, Piccoli P (2014) Bacteria isolated from roots and rhizosphere of Vitis vinifera retard water losses, induce abscisic acid accumulation and synthesis of defense-related terpenes in in vitro cultured grapevine. Physiol Plant 151:359–374
Samaniego-Gámez BY, Garruña R, Tun-Suárez JM, Kantun-Can J, Reyes-Ramírez A, Cervantes-Díaz L (2016) Bacillus spp. inoculation improves photosystem II efficiency and enhances photosynthesis in pepper plants. Chil J Agric Res 76:409–416
Sanchez G (2013) PLS path modeling with R. In Berkeley: Trowchez Editions 383:551
Schmid CA, Schröder P, Armbruster M, Schloter M (2018) Organic amendments in a long-term field trial-consequences for the bulk soil bacterial community as revealed by network analysis. Microb Ecol 76:226–239
Shu X, He J, Zhou Z, **a L, Hu Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Luo Y, Chu H, Liu W (2022) Organic amendments enhance soil microbial diversity, microbial functionality and crop yields: A meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 829:154627
Sinclair TR (2012) Is transpiration efficiency a viable plant trait in breeding for crop improvement? Funct Plant Biol 39:359–365
Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J (2011) Auxin and plant-microbe interactions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:a001438
Tan L, Gu S, Li S, Ren Z, Deng Y, Liu Z, Gong Z, **ao W, Hu Q (2019) Responses of microbial communities and interaction networks to different management practices in tea plantation soils. Sustainability 11:4428
Tomás M, Medrano H, Pou A, Escalona J, Martorell S, Ribas-Carbó M, Flexas J (2012) Water-use efficiency in grapevine cultivars grown under controlled conditions: effects of water stress at the leaf and whole-plant level. Aust J Grape Wine Res 18:164–172
Tomás M, Medrano H, Escalona JM, Martorell S, Pou A, Ribas-Carbó M, Flexas J (2014) Variability of water use efficiency in grapevines. Environ Exp Bot 103:148–157
Tsotetsi T, Nephali L, Malebe M, Tugizimana F (2022) Bacillus for plant growth promotion and stress resilience: What have we learned? Plants 11:2482
Tran CKT, Rose MT, Cavagnaro TR, Patti AF (2015) Lignite amendment has limited impacts on soil microbial communities and mineral nitrogen availability. Appl Soil Ecol 95:140–150
Vadez V, Kholova J, Medina S, Kakkera A, Anderberg H (2014) Transpiration efficiency: new insights into an old story. J Exp Bot 65:6141–6153
Wang X, Tang C (2018) The role of rhizosphere pH in regulating the rhizosphere priming effect and implications for the availability of soil-derived nitrogen to plants. Ann Bot 121:143–151
Wang Y, Naumann U, Wright ST, Warton DI (2012) mvabund–an R package for model-based analysis of multivariate abundance data. Methods Ecol Evol 3:471–474
Wang L, Wang S, Chen W, Li H, Deng X (2017) Physiological mechanisms contributing to increased water-use efficiency in winter wheat under organic fertilization. PLoS ONE 12:e0180205
Wang X, Sale P, Franks A, ** J, Krohn C, Armstrong R, Tang C (2021) An insight into the effect of organic amendments on the transpiration efficiency of wheat plant in a sodic duplex soil. Front Plant Sci 12:722000
Wild B, Alaei S, Bengtson P, Bodé S, Boeckx P, Schnecker J, Mayerhofer W, Rütting T (2017) Short-term carbon input increases microbial nitrogen demand, but not microbial nitrogen mining, in a set of boreal forest soils. Biogeochemistry 136:261–278
Xu H-L, Wang X, Fujita M (2001) Effects of organic farming practices on photosynthesis, transpiration and water relations, and their contributions to fruit yield and the incidence of leaf-scorch in pear trees. J Crop Prod 3:127–138
Zhang H, **e X, Kim MS, Kornyeyev DA, Holaday S, Paré PW (2008) Soil bacteria augment Arabidopsis photosynthesis by decreasing glucose sensing and abscisic acid levels in planta. Plant J 56:264–273
Zhang Y, Li Y, Hassan MJ, Li Z, Peng Y (2020) Indole-3-acetic acid improves drought tolerance of white clover via activating auxin, abscisic acid and jasmonic acid related genes and inhibiting senescence genes. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–12
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by AgBioEn and an ABC Scheme Award at La Trobe University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW, PS, JW and CT designed the study. XW performed the experiment and data analysis. XW, PS, J W, PR, AF, GC, JJ, SR, JH and CT wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ian Dodd.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X.(., Sale, P., Wood, J.L. et al. Organic amendments enhance transpiration efficiency of corn plants via changes in soil microbial abundance and leaf hormones. Plant Soil 497, 549–565 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06413-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06413-9