Abstract
Background and aims
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) has a key role in soil biogeochemistry and is vulnerable to global climate change such as drought stress. Intercrop** provides greater bioavailable resources and soil carbon inputs, compared to monoculture. However, little data exist on the DOM quantity and quality of intercrop** soil responses to drought.
Methods
We conducted a two-year manipulated rainfall-reduction field experiment including water (the control and drought), and crop** system (millet/peanut intercrop** and corresponding monoculture). After crop harvesting, DOM contents and compositions were determined and characterized using ultraviolet–visible absorbance and fluorescence spectroscopy.
Results
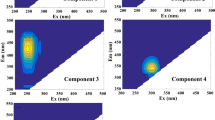
In 0–20 cm, DOC contents were reduced by 44.3% in intercrop** and 23.8% under drought. However, the specific ultraviolet absorbance at 254 nm (SUVA254) and 260 nm (SUVA260) of DOM were increased in intercrop**, indicating greater aromatic and hydrophobic DOM in intercrop** soil, and the enhanced effect was observed under drought. Four identified DOM components were UVC humic-like (C1), microbial-derived humic-like (C2), unidentified humic-like (C3), and tyrosine-like (C4). In detail, C1, C2, C3, and C4 were all higher in intercrop**, especially under drought treatment (P < 0.05). Humification index (HIX), fluorescence index (FI), and biological index (BIX) indicated mixed DOM sources (terrestrially-derived and microbial-derived), FI and BIX were higher under drought.
Conclusion
Although drought decreased DOC content, the DOM components in intercrop** could be more stable due to their higher aromaticity and hydrophobicity. These findings provide a new theoretical basis to evaluate soil fertility in various agroecosystems and understand how soil DOM responding to drought.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Andersson S, Nilsson SI, Saetre P (2000) Leaching of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in mor humus as affected by temperature and pH. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00103-0
Battin TJ, Luyssaert S, Kaplan LA, Aufdenkampe AK, Richter A, Tranvik LJ (2009) The boundless carbon cycle. Nat Geosci 2:598–600. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo618
Blazewicz SJ, Schwartz E, Firestone MK (2014) Growth and death of bacteria and fungi underlie rainfall-induced carbon dioxide pulses from seasonally dried soil. Ecology 95:1162–1172. https://doi.org/10.1890/13-1031.1
Bonnett SA, Ostle N, Freeman C (2006) Seasonal variations in decomposition processes in a valley-bottom riparian peatland. Sci Total Environ 370:561–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.08.032
Catalán N, Casas-Ruiz JP, Arce MI, Abril M, Bravo AG, del Campo R, Estévez E, Freixa A, Giménez-Grau P, González-Ferreras AM, Gómez-Gener L, Lupon A, Martínez A, Palacin-Lizarbe C, Poblador S, Rasines-Ladero R, Reyes M, Rodríguez-Castillo T, Rodríguez-Lozano P, Sanpera-Calbet I, Tornero I, Pastor A (2018) Behind the scenes: mechanisms regulating climatic patterns of dissolved organic carbon uptake in headwater streams. Global Biogeochem Cycles 32:1528–1541. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GB005919
Chen BF, Huang W, Ma SZ, Feng MH, Liu C, Gu XZ, Chen KN (2018) Characterization of Chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the littoral zones of eutrophic lakes Taihu and Hongze during the algal bloom season. Water 10:861. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070861
Clark JM, Heinemeyer A, Martin P, Bottrell SH (2012) Processes controlling DOC in pore water during simulated drought cycles in six different UK peats. Biogeochemistry 109:253–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-011-9624-9
Cong WF, Hoffland E, Li L, Janssen BH, van der Werf W (2015) Intercrop** affects the rate of decomposition of soil organic matter and root litter. Plant Soil 391:399–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2433-5
Cookson WR, Abaye DA, Marschner P, Murphy DV, Stockdale EA, Goulding KWT (2005) The contribution of soil organic matter fractions to carbon and nitrogen mineralization and microbial community size and structure. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1726–1737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.02.007
Corvasce M, Zsolnay A, D’Orazio V, Lopez R, Miano TM (2006) Characterization of water extractable organic matter in a deep soil profile. Chemosphere 62:1583–1590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.07.065
Cory RM, McKnight DM (2005) Fluorescence spectroscopy reveals ubiquitous presence of oxidized and reduced quinones in dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 39:8142–8149. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0506962
Cotrufo MF, Soong JL, Horton AJ, Campbell EE, Haddix ML, Wall DH, Parton AJ (2015) Formation of soil organic matter via biochemical and physical pathways of litter mass loss. Nat Geosci 8:776–779. https://doi.org/10.1038/Ngeo2520
Dai A, Trenberth KE, Qian TT (2004) A global dataset of palmer drought severity index for 1870–2002: relationship with soil moisture and effects of surface warming. J Hydrometeorol 5:1117–1130. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jhm-386.1
Dainard PG, Guéguen C, McDonald N, Williams WJ (2015) Photobleaching of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in Beaufort Sea and North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre. Mar Chem 177:630–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2015.10.004
Dilling J, Kaiser K (2002) Estimation of the hydrophobic fraction of dissolved organic matter in water samples using UV photometry. Water Res 36:5037–5044. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00365-2
Evans SE, Wallenstein MD (2014) Climate change alters ecological strategies of soil bacteria. Ecol Lett 17:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12206
Fellman JB, Hood E, Spencer RGM (2010) Fluorescence spectroscopy opens new windows into dissolved organic matter dynamics in freshwater ecosystems: A review. Limnol Oceanogr 55:2452–2462. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2010.55.6.2452
Fenner N, Freeman C (2011) Drought-induced carbon loss in peatlands. Nat Geosci 4:895–900. https://doi.org/10.1038/Ngeo1323
Franco JG, King SR, Volder A (2018) Component crop physiology and water use efficiency in response to intercrop**. Eur J Agron 93:27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2017.11.005
Fujii K, Uemura M, Hayakawa C, Funakawa S, Sukartiningsih KT, Ohta S (2009) Fluxes of dissolved organic carbon in two tropical forest ecosystems of East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Geoderma 152:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.05.028
Gong XW, Liu CJ, Li J, Luo Y, Yang QH, Zhang WL, Yang P, Feng BL (2019) Responses of rhizosphere soil properties, enzyme activities and microbial diversity to intercrop** patterns on the Loess Plateau of China. Soil Till Res 195:104355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104355
Guan S, An N, Zong N, He YT, Shi P, Zhang JJ, He NP (2018) Climate warming impacts on soil organic carbon fractions and aggregate stability in a Tibetan alpine meadow. Soil Biol Biochem 116:224–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.10.011
Hassouna M, Massiani C, Dudal Y, Pech N, Theraulaz F (2010) Changes in water extractable organic matter (WEOM) in a calcareous soil under field conditions with time and soil depth. Geoderma 155:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.11.026
He W, Jung H, Lee JH, Hur J (2016) Differences in spectroscopic characteristics between dissolved and particulate organic matters in sediments: Insight into distribution behavior of sediment organic matter. Sci Total Environ 547:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.146
Huguet A, Vacher L, Relexans S, Saubusse S, Froidefond JM, Parlanti E (2009) Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org Geochem 40:706–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.03.002
Hur J, Park MH, Schlautman MA (2009) Microbial transformation of dissolved leaf litter organic matter and its effects on selected organic matter operational descriptors. Environ Sci Technol 43:2315–2321. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802773b
Jensen KD, Beier C, Michelsen A, Emmett BA (2003) Effects of experimental drought on microbial processes in two temperate heathlands at contrasting water conditions. Appl Soil Ecol 24:165–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0929-1393(03)00091-X
Jiang T, Kaal J, Liang J, Zhang Y, Wei S, Wang D, Green NW (2017) Composition of dissolved organic matter (DOM) from periodically submerged soils in the Three Gorges Reservoir areas as determined by elemental and optical analysis, infrared spectroscopy, pyrolysis-GC–MS and thermally assisted hydrolysis and methylation. Sci Total Environ 603–604:461–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.114
Jones V, Meador TB, Gogou A, Migon C, Penkman KEH, Collins MJ, Repeta DJ (2013) Characterisation and dynamics of dissolved organic matter in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Prog Oceanogr 119:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2013.06.007
Kaisermann A, de Vries FT, Griffiths RI, Bardgett RD (2017) Legacy effects of drought on plant-soil feedbacks and plant-plant interactions. New Phytol 215:1413–1424. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14661
Kalbitz K, Schmerwitz J, Schwesig D, Matzner E (2003) Biodegradation of soil-derived dissolved organic matter as related to its properties. Geoderma 113:273–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00365-8
Kalbitz K, Solinger S, Park JH, Michalzik B, Matzner E (2000) Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: A review. Soil Sci 165:277–304. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-200004000-00001
Kiikkila O, Kanerva S, Kitunen V, Smolander A (2014) Soil microbial activity in relation to dissolved organic matter properties under different tree species. Plant Soil 377:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1988-2
King AD, Pitman AJ, Henley BJ, Ukkola AM, Brown JR (2020) The role of climate variability in Australian drought. Nat Clim Change 10:177–179. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-020-0718-z
Kothawala DN, von Wachenfeldt E, Koehler B, Tranvik LJ (2012) Selective loss and preservation of lake water dissolved organic matter fluorescence during long-term dark incubations. Sci Total Environ 433:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.029
Li TT, Zhang JZ, Zhang HY, Chrisite P, Zhang JL (2022) Fractionation of soil organic carbon in a calcareous soil after long-term tillage and straw residue management. J Integr Agric 21:3611–3625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jia.2022.08.072
Li W, Jia X, Li M, Wu H (2019) Insight into the vertical characteristics of dissolved organic matter in 5-m soil profiles under different land-use types on the Loess Plateau. Sci Total Environ 692:613–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.339
Liu C, Li Z, Berhe AA, **ao H, Liu L, Wang D, Peng H, Zeng G (2019) Characterizing dissolved organic matter in eroded sediments from a loess hilly catchment using fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC and UV–Visible absorption: Insights from source identification and carbon cycling. Geoderma 334:37–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.07.029
Liu WX, Zhang Z, Wan SQ (2009) Predominant role of water in regulating soil and microbial respiration and their responses to climate change in a semiarid grassland. Global Change Biol 15:184–195. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01728.x
Lou YS, Li ZP, Zhang TL, Liang YC (2004) CO2 emissions from subtropical arable soils of China. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1835–1842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.05.006
McDowell WH (2003) Dissolved organic matter in soils - future directions and unanswered questions. Geoderma 113:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00360-9
McKnight DM, Boyer EW, Westerhoff PK, Doran PT, Kulbe T, Andersen DT (2001) Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol Oceanogr 46:38–48. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2001.46.1.0038
Murphy KR, Stedmon CA, Wenig P, Bro R (2014) OpenFluor-an online spectral library of auto-fluorescence by organic compounds in the environment. Anal Methods 6:658–661. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ay41935e
Musadji NY, Lemée L, Caner L, Porel G, Poinot P, Geffroy-Rodier C (2020) Spectral characteristics of soil dissolved organic matter: Long-term effects of exogenous organic matter on soil organic matter and spatial-temporal changes. Chemosphere 240:124808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124808
Neff JC, Asner GP (2001) Dissolved organic carbon in terrestrial ecosystems: Synthesis and a model. Ecosystems 4:29–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100210000058
Ohno T (2002) Fluorescence inner-filtering correction for determining the humification index of dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 36:742–746. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0155276
Parlanti E, Worz K, Geoffroy L, Lamotte M (2000) Dissolved organic matter fluorescence spectroscopy as a tool to estimate biological activity in a coastal zone submitted to anthropogenic inputs. Org Geochem 31:1765–1781. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00124-8
Peng YM, Xu HS, Wang Z, Li L, Shang JY, Li BG, Wang X (2023) Effects of intercrop** and drought on soil aggregation and associated organic carbon and nitrogen. Soil Use Manag 39:316–328. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12866
Pivato B, Semblat A, Guégan T, Jacquiod S, Martin J, Deau F, Moutier N, Lecomte C, Burstin J, Lemanceau P (2021) Rhizosphere bacterial networks, but not diversity, are impacted by pea-wheat intercrop**. Front Microbiol 12:674556. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.674556
Ren JH, Zhang LZ, Duan Y, Zhang J, Evers JB, Zhang Y, Su ZC, van der Werf W (2019) Intercrop** potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) with hairy vetch (Vicia villosa) increases water use efficiency in dry conditions. Field Crops Res 240:168–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.12.002
Reyes T, Quiroz R, Luukkanen O, de Mendiburu F (2009) Spice crops agroforestry systems in the East Usambara Mountains, Tanzania: growth analysis. Agroforest Syst 76:513–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-009-9210-5
Scott EE, Rothstein DE (2014) The dynamic exchange of dissolved organic matter percolating through six diverse soils. Soil Biol Biochem 69:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.10.052
Singh S, Mayes MA, Shekoofa A, Kivlin SN, Bansal S, Jagadamma S (2021) Soil organic carbon cycling in response to simulated soil moisture variation under field conditions. Sci Rep 11:10841. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-90359-4
Søndergaard M, Stedmon CA, Borch NH (2003) Fate of terrigenous dissolved organic matter (DOM) in estuaries: Aggregation and bioavailability. Ophelia 57:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1080/00785236.2003.10409512
Stedmon CA, Bro R (2008) Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: a tutorial. Limnol Oceanogr-Meth 6:572–579. https://doi.org/10.4319/lom.2008.6.572
Stedmon CA, Markager S (2005) Tracing the production and degradation of autochthonous fractions of dissolved organic matter by fluorescence analysis. Limnol Oceanogr 50:1415–1426. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2005.50.5.1415
Tian JH, Tang MT, Xu X, Luo SS, Condron LM, Lambers H, Cai KZ, Wang JW (2020) Soybean (Glycine max(L.) Merrill) intercrop** with reduced nitrogen input influences rhizosphere phosphorus dynamics and phosphorus acquisition of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum). Biol Fertility Soils 56:1063–1075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01484-7
Tian XL, Wang CB, Bao XG, Wang P, Li XF, Yang SC, Ding GC, Christie P, Li L (2019) Crop diversity facilitates soil aggregation in relation to soil microbial community composition driven by intercrop**. Plant Soil 436:173–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-03924-8
Tiemann LK, Billings SA (2011) Changes in variability of soil moisture alter microbial community C and N resource use. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1837–1847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.04.020
Wang C, Linderholm HW, Song Y, Wang F, Liu Y, Tian J, Xu J, Song Y, Ren G (2020) Impacts of drought on maize and soybean production in Northeast China during the past five decades. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072459
Wang D, Yi WB, Zhou YL, He SR, Tang L, Yin XH, Zhao P, Long GQ (2021a) Intercrop** and N application enhance soil dissolved organic carbon concentration with complicated chemical composition. Soil Tillage Res 210:104979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.104979
Wang JL, Shi XX, Li ZZ, Zhang Y, Liu YQ, Peng YX (2021b) Responses of runoff and soil erosion to planting pattern, row direction, and straw mulching on sloped farmland in the corn belt of northeast China. Agric Water Manage 253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106935
Wang L, Zhu Y, Yin W, Zheng D, Chai Q, University GA (2016) Competitiveness and yield response to belowground interaction and density in barley-pea intercrop** system. Chinese J Ecoagric 24:265–273. https://doi.org/10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.151006
Wang Y, Wang H, He JS, Feng X (2017) Iron-mediated soil carbon response to water-table decline in an alpine wetland. Nat Commun 8:15972. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15972
Wang ZG, Bao XG, Li XF, ** X, Zhao JH, Sun JH, Christie P, Li L (2015) Intercrop** maintains soil fertility in terms of chemical properties and enzyme activities on a timescale of one decade. Plant Soil 391:265–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2428-2
Weishaar JL, Aiken GR, Bergamaschi BA, Fram MS, Fujii R, Mopper K (2003) Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ Sci Technol 37:4702–4708. https://doi.org/10.1021/es030360x
Wieder WR, Cleveland CC, Townsend AR (2009) Controls over leaf litter decomposition in wet tropical forests. Ecology 90:3333–3341. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-2294.1
Wieder WR, Cleveland CC, Townsend AR (2011) Throughfall exclusion and leaf litter addition drive higher rates of soil nitrous oxide emissions from a lowland wet tropical forest. Global Change Biol 17:3195–3207. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02426.x
Wilson HF, Xenopoulos MA (2009) Effects of agricultural land use on the composition of fluvial dissolved organic matter. Nat Geosci 2:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/Ngeo391
Worrall F, Burt TP (2008) The effect of severe drought on the dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentration and flux from British rivers. J Hydrol 361:262–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.07.051
Worrall F, Burt TP, Adamson JK (2006) Trends in drought frequency-The fate of DOC export from British peatlands. Clim Change 76:339–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9069-7
**ang SR, Doyle A, Holden PA, Schimel JP (2008) Drying and rewetting effects on C and N mineralization and microbial activity in surface and subsurface California grassland soils. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2281–2289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.05.004
Xu X, Lu K, Wang Z, Wang M, Wang S (2021) Effects of drainage on dissolved organic carbon (DOC) characteristics of surface water from a mountain peatland. Sci Total Environ 789:147848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147848
Yamashita Y, Jaffé R, Maie N, Tanoue E (2008) Assessing the dynamics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in coastal environments by excitation emission matrix fluorescence and parallel factor analysis (EEM-PARAFAC). Limnol Oceanogr 53:1900–1908. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2008.53.5.1900
Yang L, Hur J (2014) Critical evaluation of spectroscopic indices for organic matter source tracing via end member mixing analysis based on two contrasting sources. Water Res 59:80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.04.018
Yang Z, Yang W, Li S, Hao J, Su Z, Sun M, Gao Z, Zhang C (2016) Variation of bacterial community diversity in rhizosphere soil of sole-cropped versus intercropped wheat field after harvest. PLoS One 11:e0150618. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150618
Yao SH, Zhang B, Hu F (2011) Soil biophysical controls over rice straw decomposition and sequestration in soil: The effects of drying intensity and frequency of drying and wetting cycles. Soil Biol Biochem 43:590–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.11.027
Zhang R, Huang Q, Yan T, Yang J, Zheng Y, Li H, Li M (2019) Effects of intercrop** mulch on the content and composition of soil dissolved organic matter in apple orchard on the loess plateau. J Environ Manage 250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109531
Zhao BZ, Chen J, Zhang JB, Qin SW (2010) Soil microbial biomass and activity response to repeated drying-rewetting cycles along a soil fertility gradient modified by long-term fertilization management practices. Geoderma 160:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.09.024
Zhou SX, Huang CD, **ang YB, Tie LH, Han BH, Scheu S (2018) Effects of reduced precipitation on litter decomposition in an evergreen broad-leaved forest in western China. For Ecol Manage 430:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2018.08.022
Zsolnay A, Gorlitz H (1994) Water extractable organic matter in arable soils: effects of drought and long-term fertilization. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1257–1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(94)90151-1
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Ruipeng Yu, Hao Yang, and Ran An for their help in the statistical analysis.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42077063, 31700366) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2020TC118).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huasen Xu and **ang Wang contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Yumei Peng, Zi Wang, Jia Shi and Junfei Lv. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Yumei Peng and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans Lambers.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Y., Xu, H., Wang, Z. et al. Responses of the content and spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter in intercrop** soil to drought in northeast China. Plant Soil (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-05931-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-05931-w