Abstract
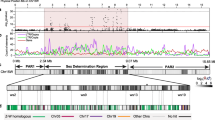
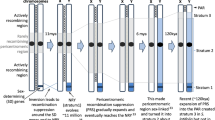
Sex chromosomes have evolved from a pair of homologous autosomes which differentiated into sex determination systems, such as XY or ZW system, as a consequence of successive recombination suppression between the gametologous chromosomes. Identifying the regions of recombination suppression, namely, the “evolutionary strata”, is central to understanding the history and dynamics of sex chromosome evolution. Evolution of sex chromosomes as a consequence of serial recombination suppressions is well-studied for mammals and birds, but not for plants, although 48 dioecious plants have already been reported. Only two plants Silene latifolia and papaya have been studied until now for the presence of evolutionary strata on their X chromosomes, made possible by the sequencing of sex-linked genes on both the X and Y chromosomes, which is a requirement of all current methods that determine stratum structure based on the comparison of gametologous sex chromosomes. To circumvent this limitation and detect strata even if only the sequence of sex chromosome in the homogametic sex (i.e. X or Z chromosome) is available, we have developed an integrated segmentation and clustering method. In application to gene sequences on the papaya X chromosome and protein-coding sequences on the S. latifolia X chromosome, our method could decipher all known evolutionary strata, as reported by previous studies. Our method, after validating on known strata on the papaya and S. latifolia X chromosome, was applied to the chromosome 19 of Populus trichocarpa, an incipient sex chromosome, deciphering two, yet unknown, evolutionary strata. In addition, we applied this approach to the recently sequenced sex chromosome V of the brown alga Ectocarpus sp. that has a haploid sex determination system (UV system) recovering the sex determining and pseudoautosomal regions, and then to the mating-type chromosomes of an anther-smut fungus Microbotryum lychnidis-dioicae predicting five strata in the non-recombining region of both the chromosomes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Cock JM, Pessia E, Luthringer R, Cormier A, Robuchon M, Sterck L, Peter AF, Dittami SM, Corre E et al (2014) A haploid system of sex determination in the brown alga Ectocarpus sp. Curr Biol 24(17):1945–1957
Arvey AJ, Azad RK, Raval A, Lawrence JG (2009) Detection of genomic islands via segmental genome heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res 37:5255–5266
Azad RK, Li J (2013) Interpreting genomic data via entropic dissection. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e23
Azad RK, Bernaola-Galvan P, Ramaswamy R, Rao JS (2002) Segmentation of genomic DNA through entropic divergence: power laws and scaling. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 65: Epub 051909
Bachtrog D (2008) The temporal dynamics of processes underlying Y chromosome degeneration. Genetics 179:1513–1525
Bachtrog D (2013) Y-chromosome evolution: emerging insights into processes of Y-chromosome degeneration. Nat Rev Genet 14:113–124
Badouin H, Hood ME, Gouzy J, Aguileta G, Siguenza S, Perlin MH, Cuomo CA, Fairhead C, Branca A, Giraud T (2015) Chaos of rearrangements in the mating-type chromosomes of the anther-smut fungus Microbotryum Lychnidis-dioicae. Genetics 200(4):1275–1284
Bergero R, Charlesworth D (2011) Preservation of the Y transcriptome in a 10 MY old plant sex chromosome system. Curr Biol 21:1470–1474
Bergero R, Forrest A, Kamau E, Charlesworth D (2007) Evolutionary strata on the X chromosomes of the dioecious plant Silene latifolia: evidence from new sex-linked genes. Genetics 175:1945–1954
Bergero R, Qiu S, Forrest A, Borthwick H, Charlesworth D (2013) Expansion of the pseudo-autosomal region and ongoing recombination suppression in the Silene latifolia sex chromosomes. Genetics 194:673–686
Bernaola-Galvan P, Roman-Roldan R, Oliver JL (1996) Compositional segmentation and long-range fractal correlations in DNA sequences. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics 53:5181–5189
Brookfield JFY (1991) Models of repression of transposition in P-M hybrid dysgenesis by P cytotype and by zygotically encoded repressor proteins. Genetics 128:471–486
Charlesworth B (1978) Model for evolution of Y chromosomes and dosage compensation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:5618–5622
Charlesworth B, Charlesworth D (2000) The degeneration of Y chromosomes. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 355:1563–1572
Charlesworth D, Charlesworth B, Marais G (2005) Steps in the evolution of heteromorphic sex chromosomes. Heredity 95(2):118–128
Dolgin ES, Charlesworth B (2008) The effects of recombination rate on the distribution and abundance of transposable elements. Genetics 178(4):2169–2177
Filatov DA (2005) Evolutionary history of Silene latifolia sex chromosomes revealed by genetic map** of four genes. Genetics 170:975–979
Finnegan DJ (1992) Transposable elements. The Genome of Drosophila melanogaster, pp 1096–1107
Fontanillas E, Hood M, Badouin H, Petit E, Barbe V, Gouzy J, deVienne DM, Aguileta G, Poulain J, Wincker P, Chen Z et al (2015) Degeneration of the non-recombining regions in the mating type chromosomes of the anther smut fungi. Mol Biol Evol 32:928–943
Gaudet M, Jorge V, Paolucci I, Beritognolo I, Mugnozza G, Sabatti M (2008) Genetic linkage maps of Populus nigra L. including AFLPs, SSRs, SNPs, and sex trait. Tree Genet Genomes 4:25–36
Geraldes A, Hefer CA, Capron A, Kolosova N, MartinezNuñez F, Soolanayakanahally RY, Stanton B, Guy RD, Mansfield S, Douglas CJ, Cronk QCB (2015) Recent Y chromosome divergence despite ancient origin of dioecy in poplars (Populus). Mol Ecol 24(13):3243–3256
Grosse I, Bernaola-Galvan P, Carpena P, Roman-Roldan R, Oliver J, Stanley HE (2002) Analysis of symbolic sequences using the Jensen-Shannon divergence. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 65:041905
Hobza R, Kejnovsky E, Vyskot B, Widmer A (2007) The role of chromosomal rearrangements in the evolution of Silene latifolia sex chromosomes. Mol Genet Genomics 278:633–638
Hood ME, Antonovics J, Koskella B (2004) Shared forces of sex chromosome evolution in haploids-mating and diploids-mating organisms: Microbotryum violaceum and other model organisms. Genetics 168:141–146
Hood ME, Petit E, Giraud T (2013) Extensive divergence between mating-type chromosomes of the anther-smut fungus. Genetics 193:309–315
Hou J, Ning Y, Defang Z, Yingnan C, Lecheng F, **aogang D, Tongming Y (2015) Different autosomes evolved into sex chromosomes in the sister genera of Salix and Populus. Sci Rep 5:9076
Jordan C, Charlesworth D (2012) The potential for sexually antagonistic polymorphism in different genome regions. Evolution 66:505–516
Kirkpatrick M, Barton N (2006) Chromosome inversions, local adaptation and speciation. Genetics 173:419–434
Lahn BT, Page DC (1999) Four evolutionary strata on the human X chromosome. Science 286:964–967
Lemaitre C, Braga MD, Gautier C, Sagot MF, Tannier E, Marais GA (2009a) Footprints of inversions at present and past pseudoautosomal boundaries in human sex chromosomes. Genome Biol Evol 1:56–66
Lemaitre JF, Ramm SA, Barton RA, Stockley P (2009b) Sperm competition and brain size evolution in mammals. J Evol Biol 22:2215–2221
Li Wentian (2001) New stop** criteria for segmenting DNA sequences. Phys Rev Lett 86:5815–5818
Lin J (1991) Divergence measures based on the Shannon entropy. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 37:145–151
Liu Z, Moore PH, Ma H, Ackerman CM, Ragiba M, Yu Q, Pearl HM, Kim MS, Charlton JW, Ming R et al (2004) A primitive Y chromosome in papaya marks incipient sex chromosome evolution. Nature 427:348–352
Ming R, Moore PH (2007) Genomics of sex chromosomes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:123–130
Ming R, Bendahmane A, Renner SS (2011) Sex chromosome in land plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:485–514
Montgomery EA, Charlesworth B, Langley CH (1987) A test for the role of natural selection in the stabilization of transposable element copy number in a population of Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res 49:31–41
Muller HJ (1964) The relation of recombination to mutational advance. Mutat Res 1:2–9
Nam K, Ellegren H (2008) The chicken (Gallus gallus) Z chromosome contains at least three nonlinear evolutionary strata. Genetics 180:1131–1136
Nei M (1970) Accumulation of nonfunctional genes on sheltered chromosomes. Am Nat 104:311–322
Pandey RS, Wilson MA, Azad RK (2013) Detecting evolutionary strata on the human X chromosome in the absence of gametologous Y-linked sequences. Genome Biol Evol 5:1863–1871
Rice WR (1984) Sex chromosomes and the evolution of sexual dimorphism. Evolution 38:735–742
Rice WR (1987) The accumulation of sexually antagonistic genes as a selective agent promoting the evolution of reduced recombination between primitive sex-chromosomes. Evolution 41:911–914
Rice WR (1996) Evolution of the Y sex chromosome in animals. Biosciences 46:331–343
Ross MT, Grafham DV, Coffey AJ, Scherer S, Mclay K, Muzny D, Platzer M, Howell GR, Burrows C, Bird CP et al (2005) The DNA sequence of the human X chromosome. Nature 434:325–337
Sandstedt SA, Tucker PK (2004) Evolutionary strata on the mouse X chromosome correspond to strata on the human X chromosome. Genome Res 14:267–272
Skaletsky H, Kuroda-Kawaguchi T, Minx PJ, Cordum HS, Hillier L, Brown LG, Rep** S, Pyntikova T, Ali J, Bieri T et al (2003) The male-specific region of the human Y chromosome is a mosaic of discrete sequence classes. Nature 423:825–837
Smit AFA, Hubley R, Green P (2013–2015) RepeatMakser Open-4.0. http://www.repeatmasker.org
Sterck L, Billiau K, Abeel T, Rouze P, Van de Peer Y (2012) ORCAE: online resource for community annotation of eukaryotes. Nat Methods 9:1041
Thakur V, Azad RK, Ramaswamy R (2007) Markov models of genome segmentation. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 75:011915
Tuskan GA, DiFazio S, Faivre-Rampant P, Gaudet M, Harfouche A, Jorge V, Labbe JL, Ranjan P, Sabatti M, Salavov G et al (2012) The obscure events contributing to the evolution of an incipient sex chromosome in Populus: a retrospective working hypothesis. True Genet Genomics 8:559–571
Veyrunes F, Waters PD, Miethke P, Rens W, McMillan D, Alsop AE, Grutzner F, Deakin JE, Whittington CM, Schatzkamer K et al (2008) Bird-like sex chromosomes of platypus imply recent origin of mammal sex chromosomes. Genome Res 18:965–973
Votintseva AA, Filatov DA (2009) Evolutionary strata in a small mating-type-specific region of the smut fungus Microbotryum violaceum. Genetics 182:1391–1396
Wang J, Na JK, Yu Q, Gschwend AR, Han J, Zeng F, Aryal R, VanBuren R, Murray JE, Zhang W et al (2012) Sequencing papaya X and Yh chromosomes reveals molecular basis of incipient sex chromosome evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:13710–13715
Whittle CA, Votintseva A, Ridout K, Filatov DA (2015) Recent and massive expansion of the mating-type specific region in the smut fungus Microbotryum. Genetics 199:809–816
Wilson MA, Makova KD (2009) Evolution and survival on eutherian sex chromosomes. PLoS Genet 5:e1000568
Wilson MA, Makova KD (2013) Gene survival and death on the human Y chromosome. Mol Biol Evol 30:781–787
Yin T, Difazio SP, Gunter LE, Zhang X, Sewell MM, Woolbright SA, Allan GJ, Kelleher CT, Douglas CJ, Wang M et al (2008) Genome structure and emerging evidence of an incipient sex chromosome in Populus. Genome Res 18:422–430
Yu Q, Navajas-Pérez R, Tong E, Robertson J, Moore PH, Paterson AH, Ray Ming R (2008) Recent origin of dioecious and gynodioecious Y chromosomes in papaya. Trop Plant Biol 1:49–57
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a faculty start-up fund and JFSRF award from the University of North Texas to RKA and a Beth Baird graduate student scholarship to RSP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, R.S., Azad, R.K. Deciphering evolutionary strata on plant sex chromosomes and fungal mating-type chromosomes through compositional segmentation. Plant Mol Biol 90, 359–373 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0422-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0422-y