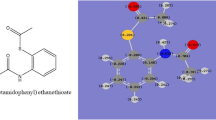
Sulfonamides are commonly used worldwide. In this study, several sulfonamide compounds such as N-(4-acetylphenyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide (PSASF), N-(3-acetylphenyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide (PSASF-1), 1-tosyl-1H-imidazole (PSASF-x), 4-methyl-N-(pyridin-4-yl) benzenesulfonamide (PSASF-2), and 1-ethyl-4-tosylpiperazine (PSASF-3) have been synthesized, with antibacterial activities against Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853, and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 have been evaluated. Antibacterial properties of drugs were studied in depth using molecular docking research. In addition, the synthesized compounds were characterized using spectral analysis. Antibacterial activities of synthesized derivates were determined against E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) by using the broth microdilution method. All prepared compounds exhibited significant antibacterial activity against S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa. The MIC value for E. coli and P. aeruginosa was determined as 256 μg/mL. MIC against S. aureus was observed to be 256 and 512 μg/mL for the PSASF compound and the other compounds respectively. Results of the current study revealed that four of the five compounds had weaker antibacterial activity against S. aureus at a concentration of 512 μg/mL. However, the MIC values from our experiments are significantly higher in comparison with the reference drugs such as amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, meropenem, and vancomycin in E. coli and S. aureus. On the other hand, in a comparison of the synthesized compounds with reference drugs in P. aeruginosa, no statistical difference was demonstrated. Antibacterial activity of the produced derivates was likewise an agreement with regard to the molecular docking and the laboratory results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. A. N. El-Dien, G. G. Mohamed, E. Khaled, and E. Y. Z. Frag, J. Adv. Res., 1(3), 215 – 220 (2010).
I. R. Ezabadi, C. Camoutsis, P. Zoumpoulakis, et al., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 16(3), 1150 – 1161 (2008).
M. A. Gonzalez, D. B. Gorman, C. T. Hamilton, and G. A. Roth, Org. Process. Res. Dev., 12(2), 301 – 303 (2008).
J. DeRuiter, Structural features of organic medicinal agents. Principle of Drug Action, 1, 10 – 13 (2005).
L. Kaur, A. Chopra, L. Singh, and M. P. Singh, Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res., 8(10), 4461 – 4472 (2017).
M. Remko and C-W. Von Der Lieth, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 12(20), 5395 – 5403 (2004).
P. Zajdel, K. Marciniec, A. Maoelankiewicz, et al., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 20, 1545 – 1556 (2012).
A. Kolaczek, I. Fusiarz, J. Lawecka and D. Branowska, Chemik, 68(7), 620 – 628 (2014).
S. S. Stokes, R. Albert, E. T. Buurman, B., et al., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 22(23), 7019 – 7023 (2012).
M. Showan and M. Suniti, Tetrahedron, 76(48), 131662 (2020).
W. Hu, Z. Guo, F. Chu, et al., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 11(7), 1153 – 1160 (2003).
M. Médebielle, O. Onomura, R. Keirouz, et al., Synthesis, 17, 2601 – 2608 (2002).
S. K. R. Parumala and R. K. Peddinti, Tetrahedron Lett., 57(11), 1232 – 1235 (2016).
E. A. Wydysh, S. M. Medghalchi, A. Vadlamudi, and C. A. Townsend, J. Med. Chem., 52(10), 3317 – 3327 (2009).
N. N. Al-Mohammed, Y. Alias, Z. Abdullah, et al., Molecules, 18, 11978 – 11995 (2013).
S. Kaya, S. Erkan and D. Karakaº, Spectrochim. Acta. Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spect., 244, 118829 (2021).
S. Erkan, J. Mol. Struct., 1189, 257 – 264 (2019).
M. Abdul Qadir, M. Ahmed, H. Aslam, et al., J. Chemistry, 8 pages (2015).
R. A. Azzam, R. E. Elsayed and G. H. Elgemeie, ACS Omega, 5(18), 10401– 10414 (2020).
Y. Hui and Y. Zhang, Chin. J. Chem., 34(4), 359 – 362 (2016).
T. Meºeli, ª. D. Doðan, M. G. Gündüz, et al., New J. Chem., 45, 8166 – 8177 (2021).
H. Tian, A. Cao, L. Qiao, et al., Tetrahedron, 70(47), 9107 – 9112 (2014).
G. Reyes-Rangel, J. Vargas-Caporali and E. Juaristi, Tetrahedron, 72(3), 379 – 391 (2016).
M. A. Solekhova and Yu. V. Kurbatov, Russ. J. Org. Chem., 38(8), 1192 – 1194 (2005).
S. Riganas, I. Papanastasiou, G. B. Foscolos, et al., J. Med. Chem., 55(22), 10241–10261 (2012).
P. R. Griffiths and J. A. de Haseth, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry, 2nd ed.; JohnWiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA (2007).
European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters; EUCAST, Version 11.1. 2021.
II R. D. Dennington, T. A. Keith, J. M. Millam, GaussView 5.0, Wallingford, CT (2009)
Z. Bikadi and E. Hazai, J. Cheminformatics, 1(1), 1 – 16 (2009).
H. H. Khalid, S. Erkan and N. Bulut, Optik, 166324 (2021).
R. Huey, G. M. Morris, A. J. Olson and D. S. Goodsell, J. Comput. Chem., 28(6), 1145 – 1152 (2007).
H. C. Neu and T. D. Gootz, In: Medical Microbiology, S. Baron (ed.), The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Galveston (1996).
K. C. Van Meter and R. J. Hubert, Microbiology for the Healthcare Professional, Elsevier, China (2016), pp. 214 – 232.
V. M. Varagiæ and M. P. Miloševiæ, Farmakologija, Elitmedica, Beograd (2009), pp. 622 – 627.
A. Taèiæ, V. Nikoliæ, L. Nikoliæ and I. Saviæ, Adv. Technol., 6(1), 58 – 71 (2017).
M. A. Miller-Hjelle, V. Somaraju, and J. T. Hjelle, In: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications, C. R. Craig and R. E. Stitzel (eds.), Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, London, Buenos Aires, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo (2004), pp. 515 – 525.
K. Zessel, S. Mohring, G. Hamscher, et al., Chemosphere, 100, 167 – 174 (2014).
L. Garoff, D. L. Huseby, L. Praski Alzrigat, D. Hughes, J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 73(12), 3285 – 3292 (2018).
M. A. Foxley, S. N. Wright, A. K. Lam, ACS Med. Chem. Lett., 8(10), 1083 – 1088 (2017).
X. Qi, X. Li, J. Zhao, et al., J. Antibiot. (Tokyo), 72(4), 237 – 240 (2019).
M. T. Suller, D. Lloyd, J. Appl. Microbiol., 92(5), 866 – 872 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ozbey, G., Tanriverdi, E.S., Senkal, B.F. et al. Investigation of Antimicrobial Activities and Molecular Docking Studies of Synthesized Sulfonamide Compounds. Pharm Chem J 57, 1394–1400 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-03002-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-03002-z