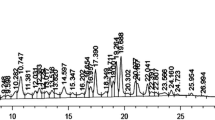
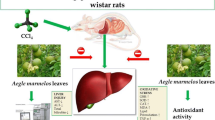
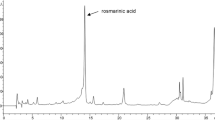
This work was aimed at investigating the hepatoprotective effect of Hep-X, a polyherbal formulation containing Silybum marianum L. (Milk thistle), Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Rosemary), Curcuma longa L. (Turmeric) and Fumaria officinalis L. (Fumitory) as standardized botanical dietary supplement, on mice with CCl4-induced acute liver injury. The total phenolic and flavonoid contents of Hep-X were determined as 0.125 and 0.528 mg/mL, respectively. The quercetin content was determined as 50 µg/mL using HPLC analysis. The total antioxidant capacity showed correlation between the Hep-X concentration and percentage inhibition of free radicals. Hep-X was administered orally at 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg b.w./day against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. The hepatic damage was measured using blood biochemical parameters. Animals upon Hep-X treatment exhibited better drug effIcacy in certain blood parameters than silymarin-treated mice. Also, Hep-X administration significantly ameliorated the liver damage by suppressing iNOS expression and apoptosis as well as by recovery of the histological structure. The obtained results suggest that Hep-X is able to significantly alleviate the hepatotoxicity induced by CCl4 in mice, which can be due to antioxidant properties of the polyherbal formulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Kaplowitz, Sem. Liver Dis., 22, 137 (2002).
N. Singh, V. Kamath, K. Narasimhamurthy, and P. S. Ra**i, Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 26(2), 241 – 246 (2008).
A. Aslan, Ö. Gok, O. Erman, and T. Kuloglu, Biomed. Pharmacother., 105, 662 – 669 (2018).
J. A. Brent and B. H. Rumack, Clin. Toxicol., 3, 139 – 71 (1993).
L. Bergendi, L. Benes, Z. Duracková, and M. Ferencik, Life Sci., 65, 1865 – 74 (1999).
T. Jawaid, R. Patel, and P. Gautam, Int. J. Med. Pharm. Sci., No. 2, 1 – 9 (2011).
T. Martinelli, F. Fulvio, M. Pietrella, et al., Fitoterapia, 148, 104797 (2021).
A. Kurkin, Pharm. Chem. J., 37, 189 – 202 (2003).
N. E. Thomas-Eapen, Explore, 5(2), 114 – 115 (2009).
M. R. Al-Sereitia, K. M. Abu-Amer, and P. K. M. Sen, Indian J. Exp. Biol., 37, 124 – 131 (1999).
A. A. N. Aziz, R. Hasham R. M. Sarmidi, et al., Saudi Pharm. J., 29, 143 – 165 (2021).
A. Meda, E. C. Lamien, M. Romito, et al., Chemistry, 91, 571 – 577 (2005).
C. C. Chang, H. M. Yang, H. M. Wen, and J. C. Chern, J. Food Drug Anal., 10, 178 – 82 (2002).
Z. Spacil, L. Novakova, and P. Solich, Talanta, 76, 189 – 199 (2008).
M. S. Blois, Nature, 181, 1199 – 200 (1958).
T. Miyazawa, T. Suzuki, K. Fujimoto, T. Kaneda, J. Biochem., 107, 689 – 693 (1990).
Y. Shibayama, J. Pathol. 159(4), 335 – 339 (1989).
N. U. Karabay Yavaþoðlu, Ç. Köksal, M. Daðdeviren, et al., Environ. Toxicol., 29(3), 345 – 353 (2014).
J. Quan, T. Li, W. Zhao, H. Xu, et al., J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr., 52(3), 244 – 252 (2013).
D .L. Diesen and P. C. Kuo, J. Surg. Res. 162(1), 95–109 (2010).
S .L. Jothy, A. Aziz, Y. Chen, and S. Sasidharan, Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med., 1 – 10 (2012).
A. Dechakhamphu and N. Wongchum, Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed., 5(12), 1042 – 1045 (2015).
N. S. V. Bhujun, N. Munogee, and V. Coolen, J. Herb. Med., 4, 1 – 9 (2014).
L. **-Wei, S. Ding, and X. Ding, Process Biochem., 40, 3607 – 13 (2005).
M. Kifayatullah, S. M. Mustafa, P. Senguptha, et al., J. Acute Dis., 14, 1 – 7 (2015).
D. R. Dufour, J. A. Lott, F. S. Nolte, et al., Clin. Chem., 46, 2027 – 49 (2000)
S. K. Ramaiah, Food Chem. Toxicol. 45(9), 1551 – 1557 (2007).
A. Singh, T. K. Bhat, and P. O. Sharma, J. Clin. Toxicol., No. 4, 1 – 19 (2011).
B. R. Thapa and A. Walia, Indian J. Pediatr., 74, 663 – 671 (2007).
S. F. Friedman, P. Martin, and J. S. Munoz, Laboratory evaluation of the patient with liver disease, in: Hepatology, a Textbook of Liver Disease, Philedelphia (2003), Vol. 1, pp. 661 – 709.
L. Trapani, M. Segatto, and V. Pallottini, World J. Hepatol., 4, 184 – 190 (2012).
Y. J. Surh, K. S. Chun, H. H. Cha, et al., Mutat. Res. Fund. Mol. Mech. Mutagen., 480, 243 – 268 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karayildirim, C.K., Guner, A., Yigitturk, G. et al. Tetrachloromethane Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice: Biochemical and Histopathological Study of the Hepatoprotective Effect of Hep-X Standardized Botanical Dietary Supplement. Pharm Chem J 56, 1639–1649 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02839-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02839-8