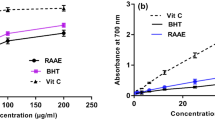
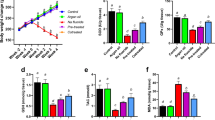
The present work was undertaken to study the effect of sodium fluoride (NaF) exposure on renal oxidative stress status in rats and to evaluate the protective effects of both Punica granatum L. (PGJ) juice and gallic acid (GA). Thirty-six maleWistar rats were divided into six groups: C (n = 6) served as a control; NaF (n = 6) were treated with NaF at 100 ppm; NaF+GA(n = 6) were administered NaF at 100 ppm plus 20 mg/kg of GA; NaF+PGJ (n = 6) were treated by both NaF (100 ppm) and PGJ (1 mL); NaF+GA+PGJ (n = 6) were treated with NaF at 100 ppm plus both GA(20 mg/kg) and PGJ (1 ml); and PGJ (n = 6): received 1 mL of PGJ. After three weeks, data showed that NaF administration caused a rise in urea, creatinine, uric acid, and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and a decrease in glutathione peroxidase (GPx), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD) activities as well as reduced glutathione level. Furthermore, histological examination revealed a moderate inflammatory infiltration. However, supplementation of GA and/or PGJ improved both the renal histological structure and all other studied parameters. The obtained results clearly showed the ability of P. granatum juice and gallic acid to protect renal tissues from oxidative damage caused by sodium fluoride.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zhang and R. D. Ji, Chin. J. Hygiene Res., No. 4, 217 – 221 (1996).
A. A. Ibrahim, N. Raafat, and N. A. Ibrahim, Brit. J. Sci., 9(1), 29 – 39 (2013).
R. Ullah, M. Souhail Zafar, N. Shahani, Iran J. Basic. Med. Sci., No. 20, 841 – 848 (2017).
G. Liu, C. Chai, and L. Cui, Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., No. 13, 199 – 204 (2003).
M. Sireli and A. Bulbul, Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci., No. 28, 591 – 595 (2004).
E. A. Garcia-Montalvo, H. Reyes-Perez, and L. M. Del Razo, Toxicology, No. 263, 75 – 83 (2009).
H. A. Hassan and M. I. Yousef, Food Chem. Toxicol., No. 47, 2332 – 2337 (2009).
S. F. Nabavi, S. M. Nabavi, S. Habtemariam, et al., Ind. Crop. Prod., No. 44, 50 – 55 (2013).
X. C. Ling and K. L. Kuo, R. R. T., 4(53), 1 – 9 (2018).
T. K. Lim, Springer Fruits, No. 5, 136 – 194 (2013).
A. Doostkam, S. Bassiri-Jahromi, K. Iravani, Intel J. Fruit Sci., (2019), https://doi.org/10.1080/155538362.2019.
S. Kawaii and E. P. Lansky, J. Food Spring, 7(1): 13 – 18 (2004).
E. P. Lansky, G. Harison, P. Froom, et al., Invest. New Drugs. 23(2), 121 – 122 (2005).
N. P. Seeram, L. S. Adams, S. M. Henning, et al., J. Nutr. Biochem., No. 16, 360 – 367 (2005).
M. A. E. Ahmed, E. M. ElMorsy, A. A. E. Ahmed, Life Sci., No. 110, 61 – 69 (2014).
A. Mansourian, N. Boojarpour, S. Ashnagar, et al., J. Mycol. Méd., No. 24, 163 – 168 (2014).
M. Aviram, M. Rosenblat, and D. Gaitini, Clin. Nutr., 23(3), 423 – 433 (2004).
Y. Farbood, A. Sarkaki, S. Hashemi, et al., Avicenna J. Phytomed., 3(4), 329 – 340 (2013).
G. Turk, M. Sonmez, M. Aydin, et al., Clin. Nutr., No. 27, 289 – 296 (2008).
T. F. X. Collins, R. L. Sprando, T. N. Black, et al., Food Chem. Toxicol., No. 39, 601 – 613 (2001).
L. Prasad, T. H. Khan, T. Jahangir, et al., Hum. Exp. Toxicol., 25(09): 523 – 529 (2006).
J. A. Buege and S. D. Aust, Methods Enzymol., No. 105, 302 – 310 (1984).
D. J. Jollow, J. R. Mitchel, Z. Zamppaglione, et al., Pharmacology, No. 11, 51 – 57 (1974).
L. Flohe and W. A. Gunzler, Methods Enzymol., No. 105, 114 – 121 (1984).
H. Aebi, Methods. Enzymol., No. 105, 673 – 884 (1974).
K. Asada, M. Takahashi, and M. Nagat, Agric. Biol. Chem., No. 38, 471 – 47 (1974).
M. Bradford, Anal. Biochem., No. 72, 248 – 254 (1976).
R. Hould,. ‘Techniques d’histopathologie et de cytopathologie’, Edition Maloine. Paris. (1984), pp. 19 – 21, 225 – 7.
R Core Team: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computig, Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/.(2019).
R. Ihaka and Gentleman, J. C. G. S., No. 5, 299 – 314 (1996).
H. Wickham, Springer-Verlag, New York (2016).
A. Kassambara, R Package Version 0.1.3, https://CRAN.Rproject.org/package=ggcorrplot. (2019).
A. Dinno, R package version 1.3.5. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dunn.test. (2017).
H. Bouaziz, F., Croute, T. Boudawara, et al., Exp. Toxicol. Pathol., No. 58, 339 – 349 (2007).
Y. M. Shivarajashankara, A. R. Shivashankara, and S. H. Rao, Fluoride, No. 34, 103 – 7 (2001).
N. R. Rathod, D. Biswas, H. R. Chitme, et al., J. Ethnopharmacol., No. 140, 234 – 238 (2012).
P. V. Vijaya, P. Sowmya, T. Arun Felix, et al., Food Chem. Toxicol., No. 49, 991 – 998 (2011).
J. B. Schulz, J. Lindenau, J. Seyfried, et al., Eur. J. Biochem., 267(16) : 4904 – 4911 (2000).
M. Guney, B. Oral, G. Take, et al., Toxicology, No. 231, 215 – 223 (2007).
M. Mittal and S. J. S. Flora, Chem-Biol. Interact., No. 162, 128 – 139 (2006).
A. Bouasla, I. Bouasla, A. Boumendjel, et al., Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., No. 94, 709 – 718 (2016).
K. Jacyszyn and A. Marut, Fluoride, No. 19, 26 – 32 (1986).
L. Panneerselvam, K. Subbiah, A. Arumugam, et al., Biol. Trace Elem. Res., No. 151, 85 – 91 (2013).
Y. Ri-An, X. Tao, W. Ai-Guo, et al., Biomed. Environ, Sci., No. 19, 439 – 444 (2006).
K. Pratap Reddy, G. Sailaja, and K. Chirumari, J. Environ. Biol., No. 30, 859 – 864 (2009).
L. Altintas, D. Essiz, G. Eraslan, et al., Food Chem. Toxicol., No. 48, 2838 – 2841 (2010).
H. A. Hassan and A. F. Abdel-Aziz, Food Chem. Toxicol., No. 48, 1999 – 2004 (2010).
P. Basha Mahaboob, P. Rai, S. Begum, Biol. Trace Elem. Res., No. 142, 623 – 626 (2011).
R. J. Verma and D. M. Guna Sherlin, Food Chem. Toxicol., No. 40, 1781 – 1788 (2002).
Y. Lu, Q. Luo, H. Cui, et al., Aging, 9(6): 1623 – 1639 (2017).
J. Ni, Y. Li, W. Zhang, et al., Chem. Biol. Interact. (2018), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.08.021.
C. M. Matthaiou, N. Goutzourelas, D. Stagos, et al., Food Chem. Toxicol., No. 73, 1 – 6 (2014).
M. I. Gil, F. A. Tomas-Barberan, B. Hess-Pierce, et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., No. 48, 4581 – 4589 (2000).
B. Cerda, J. J. Ceron, and F. A. Tomas-Barberan, J. Agric. Food Chem., No. 51, 3493 – 3501 (2003).
W. El-Falleh, N. Tlili, N. Nasri, et al., J. Food Sci., 76(5), 707 – 713 (2011).
N. Li, J. Shi, and K. Wang, J. Agric. Food Chem., 62(3), 574 – 581 (2014).
M. S. Korani, Y. Farbood, A. Sarkaki, et al., Eur. J. Pharmacol., No. 733, 62 – 67 (2014).
V. P. Punithavathi, P. Stanely Mainzen Prince, R. Kumar, et al., Eur. J. Pharmacol. No. 650, 465 – 471 (2011).
A. Bouasla, I. Bouasla, A. Boumendjel, et al., Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 29(2), 14 – 18 (2014.
L. Kolodziejczyk, A. Put, and P. Szczecin Grzela, Fluoride, 33(1), 6 – 16 (2000).
E. Dabrowaska, R. Letko, and M. Balunowska, Adv. Med. Sci., No. 51, 91 – 95 (2006).
J. Ghosh, J. Das, P. Manna, et al., Toxicol. In Vitro, No. 22, 1918 – 1926 (2006).
H. S. Parmar and A. Kar, Nutr. Res., No. 27, 710 – 18 (2007).
A. E. Abdel Moneim and M. F. El-Khadragy, J. Physiol. Biochem., No. 69, 359 – 370 (2013).
N. S. Rathod, K. S. Halagali, R. B. Nidavani, et al., J. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol., 6(3): 1 – 6 (2016).
S. N. Mestry, N. B Gawali, and S. A. Pai, J-AIM., No. 30, 1 – 9 (2017).
E. M. Al-Olayan, M. F. El-Khadragy, D. M. Metwally, et al., BMC. Complement. Altern. Med., No. 14, 164 – 173 (2014).
R. N. Jadeja, M. C. Thounaojam, D. K. Patel, et al., Cardiovasc. Toxicol., No. 10, 174 – 180 (2010).
S. O. Abarikwu, O. F. Akiri, M. A. Durojaiye, et al., J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., No. 143, 49 – 60 (2014).
Acknowledgments
The present research was supported by the Algerian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Directorate General for Scientific Research and Technological Development through the Research Laboratory of Biochemical and Environmental Toxicology, Faculty of Sciences, University of Badji Mokhtar, Annaba, Algeria.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouasla, A., Barour, C., Bouasla, I. et al. Beneficial Effects of Punica granatum L. Juice and Gallic Acid Against Kidney Oxidative Damage Caused by Sodium Fluoride. Pharm Chem J 55, 920–928 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-021-02516-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-021-02516-8