Abstract
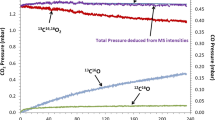
In parallel to the formation of a duplex oxide scale, 9Cr–1Mo steel carburizes strongly under CO2 at 550 °C and this carburization accelerates with time. It is observed that an increase of the total CO2 pressure in the environment from 1 to 250 bars induces a higher carbon deposition in the inner Fe–Cr rich spinel oxide layer. In order to explain this phenomenon, modelling of the carburization process was carried out. A mechanism involving gas diffusion of CO2 and CO through the oxide layer, the Boudouard reaction and carbon diffusion through the metallic substrate is proposed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Rouillard, G. Moine, L. Martinelli, and J. C. Ruiz, Oxidation of Metals (2011). doi:10.1007/s11085-011-9271-5.
G. B. Gibbs, R. E. Pendlebury, and M. R. Wooton, Corrosion of Steels in CO 2 (Reading University, Reading, 1974).
J. E. Antill, K. A. Peakall, and J. Warburton, Corrosion Science 8, 689 (1968).
P. L. Surman and A. M. Brown, Corrosion of Steels in CO 2 , (Reading University, Reading, 1974).
P. L. Harrison, R. B. Dooley, S. K. Lister, D. B. Meadowcroft, P. J. Nolan, R. E. Pendlebury, P. L. Surman, and M. R. Wooton, Proceedings of BNES International Conference on Corrosion of Steels in CO 2 (Reading University, Reading, 1974).
C. T. Fujii and R. A. Meussner, Journal of the Electrochemical Society 114, 435 (1967).
K. Shimizu, H. Habazaki, P. Skeldon, and G. E. Thompson, Surface and Interface Analysis 35, 564 (2003).
L. Martinelli, F. Balbaud-Célérier, A. Terlain, S. Bosonnet, G. Picard, and G. Santarini, Corrosion Science 50, 2537 (2008).
HSC Chemistry 5.11, Outokumpu Research Oy, Pori, Finland (2002).
D. R. Holmes, R. B. Hill, and L. M. Wyatt, Proceedings of BNES International Conference on Corrosion of Steels in CO 2 (Reading University, Reading, 1974).
A. M. Pritchard and A. E. Truswell, Proceedings of BNES International Conference on Corrosion of Steels in CO 2 (Reading University, Reading, 1974).
Acknowledgments
The authors are very thankful to the society SERMA for having performed observations and analyses of specimens by TEM and to Mr S. Gossé (CEA/DEN/DANS/DPC/SCP/LM2T) for providing ThermoCalc® software and database.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rouillard, F., Moine, G., Tabarant, M. et al. Corrosion of 9Cr Steel in CO2 at Intermediate Temperature II: Mechanism of Carburization. Oxid Met 77, 57–70 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-011-9272-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-011-9272-4