Abstract
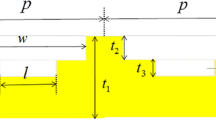
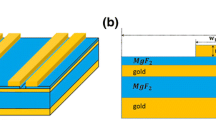
We use in this work a gold grating structure, as a plasmonic refractive index sensor, for sensing chemical or biological entities in aqueous solutions. This device was operated in an infrared band by using the rigorous coupled-wave analysis. The performance parameters of the proposed sensor in terms of absorbance at resonance are refractive index sensitivity, figure of merit (FoM), and quality factor (QF), were examined by applying the optical interrogation technique. Based on some numerical results, we optimize the geometric structure and the direction of the incident light to improve the performance of our device as a perfect absorber sensor. The analysis of the results obtained shows us the effect of several geometric and also optical parameters on the function of the instrument proposed as an optical detector of the variation of the refractive index. Our detector shows excellent results compared to others published in the literature. With azimuthally incident direction and optimal geometric and optical parameters, we obtain an optimal absorbance peak ranging between 99.92 and 99.99%, a high refractive index sensitivity of 1400 nm/RIU, a FoM of 211.54 RIU−1, and a QF of 285.28. In addition, the performance of our sensor is demonstrated by high sensitivity values of 1555.55 nm/RIU and 1522.84 nm/RIU for polydimethylsiloxane and ethanol solutions.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abadla, M.M., Elsayed, H.A.: Detection and sensing of hemoglobin using one-dimensional binary photonic crystals comprising a defect layer. Appl. Opt. 59, 418–424 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.379041
Abderrahmane, A., Senouci, K., Hachemi, B., Ko, P.J.: 2D gallium sulfide-based 1D photonic crystal biosensor for glucose concentration detection. Materials 16(13), 4621 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134621
Almawgani, A.H., Taya, S.A., Abutailkh, M.A., Abohassan, K.M., Hindi, A.T., Colak, I., Pal, A., Patel, S.K.: Development of a biosensor based on a surface plasmon resonance structure comprising strontium titanate, graphene and affinity layers for malaria diagnosis. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 37(36), 2350190 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984923501907
Aly, A.H., Mohamed, B.A., Awasthi, S.K., Abdallah, S.A.O., Amin, A.F.: MATLAB simulation based study on poliovirus sensing through one-dimensional photonic crystal with defect. Sci. Rep. 13(1), 9422 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35595-6
Anker, J.N., et al.: Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat. Mater. 7(6), 442–453 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2162
Ansari, N., Mohebbi, E., Nazari, E.: The role of the defect in photonic crystals based on WS2 or WSe2 monolayers: a vision on how to achieve high quality factor and wavelength adjustability in defect modes. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55, 319 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04282-7
Ashrafi, T., Mohanty, G.: Highly sensitive GaN-WS2-based surface plasmon resonance sensor: a theoretical approach. Plasmonics 17, 1673–1680 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-022-01653-4
Azab, M.Y., Hameed, M.F.O., Mahdiraji, G.A., Adikan, F.R.M., Obayya, S.S.A.: Experimental and numerical characterization of a D-shaped PCF refractive index sensor. Opt. Quant. Electron. 54(12), 846 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04232-3
Baranzadeh, F., Nozhat, N.: Tunable metasurface refractive index plasmonic nano-sensor utilizing an ITO thin layer in the near-infrared region. Appl. Opt. 58(10), 2616–2623 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.58.002616
Butt, M.A.: Plasmonic sensor realized on metal-insulator-metal waveguide configuration for refractive index detection. Photonics Lett Pol 14(1), 1–3 (2022). https://doi.org/10.4302/plp.v14i1.1122
Butt, M.A., Khonina, S.N., Kazanskiy, N.L.: A compact design of a modified Bragg grating filter based on a metal-insulator-metal waveguide for filtering and temperature sensing applications. Optik 251, 168466 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.168466
Butt, M.A., Shahbaz, M., Piramidowicz, R.: Racetrack ring resonator integrated with multimode interferometer structure based on low-cost silica-titania platform for refractive index sensing application. Photonics 10(9), 978 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10090978
Carvalho, I., Xavier, R., Fim, F., Moreira, C., Santa Cruz, R.: A field-enhancement optical fiber SPR sensor using graphene, molybdenum disulfide, and zinc oxide. Plasmonics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01880-3
Chau, Y.F.C., Chao, C.T.C., Huang, H.J., Anwar, U., Lim, C.M., Voo, N.Y., Mahadi, A.H., Kumara, N.T.R.N., Chiang, H.P.: Plasmonic perfect absorber based on metal nanorod arrays connected with veins. Results Phys 15, 102567 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102567
Chen, X., Gao, Z., Li, Z., Wang, J., Wang, H., Chen, S., Shen, J., Li, S.: A High-sensitivity sensor based on insulator-metal-insulator structure. Photonics 10(5), 502 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10050502
Chou Chao, C.T., Chou Chau, Y.F., Chen, S.H., Huang, H.J., Lim, C.M., Kooh, M.R.R., Thotagamuge, R., Chiang, H.P.: Ultrahigh sensitivity of a plasmonic pressure sensor with a compact size. Nanomaterials 11(11), 3147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11113147
Currie, L.A.: Nomenclature in evaluation of analytical methods including detection and quantification capabilities (IUPAC Recommendations 1995). Pure Appl. Chem. 67(10), 1699–1723 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199567101699
Daher, M.G., Taya, S.A., Colak, I., Ramahi, O.M.: Design of a novel optical sensor for the detection of waterborne bacteria based on a photonic crystal with an ultra-high sensitivity. Opt. Quant. Electron. 54(2), 108 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03486-7
Daher, M.G., Alsalman, O., Ahmed, N.M., Sassi, I., Sorathiya, V., Tsui, H.C.L., Patel, S.K.: Modeling of a novel chikungunya virus detector based on silicon and titanium nitride multilayer thin films. Optik (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2023.171136
Danaie, M., Hajshahvaladi, L., Ghaderpanah, E.: A single-mode tunable plasmonic sensor based on an 8-shaped resonator for cancer cell detection. Sci. Rep. 13, 13976 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-41193-3
Dogan, Y., Erdogan, I.: Highly sensitive MoS2/graphene based D-shaped optical fiber SPR refractive index sensor with Ag/Au grated structure. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55, 1066 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05315-5
Hamouleh-Alipour, A., Forouzeshfard, M., Baghbani, R., Vafapour, Z.: Blood hemoglobin concentration sensing by optical nano biosensor-based plasmonic metasurface: a feasibility study. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 21, 620–628 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2022.3213560
Han, L., He, X., Ge, L., Huang, T., Ding, H., Wu, C.: Comprehensive study of SPR biosensor performance based on metal-ITO-graphene/TMDC hybrid multilayer. Plasmonics 14, 2021–2030 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-01004-w
Haque, M.A., Rahad, R., Rakib, A.K.M., Sharar, S.S., Sagor, R.H.: Plasmonic sensor for rapid detection of water adulteration in honey and quantitative measurement of lactose concentration in solution. Results Phys. 51, 106733 (2023)
Haque, M.A., Rahad, R., Faruque, M.O., Mobassir, M.S., Sagor, R.H.: Numerical analysis of a metal-insulator-metal waveguide-integrated magnetic field sensor operating at sub-wavelength scales. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 43, 100618 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2023.100618
He, S., Liu, Y., Chen, H., Qiu, K., Fu, S.: Design of multilayer grating in VUV spectrum by rigorous coupled-wave method. In: 5th International Symposium on Advanced Optical Manufacturing and Testing Technologies: Advanced Optical Manufacturing Technologies. 7655. SPIE, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.866135
Hma Salah, N.: Sensitivity enhancement of the surface plasmon resonance-based gas sensing by few layers of black phosphorus. Plasmonics 18, 2225–2233 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01951-5
Homola, J.: Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem. Rev. 108(2), 462–493 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr068107d
Jafari, B., Gholizadeh, E., Jafari, B., Zhoulideh, M., Adibnia, E., Ghafariasl, M., Noori, M., Golmohammadi, S.: Highly sensitive label-free biosensor: graphene/CaF2 multilayer for gas, cancer, virus, and diabetes detection with enhanced quality factor and figure of merit. Sci. Rep. 13, 16184 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-43480-5
Kassa-Baghdouche, L., Cassan, E.: Mid-infrared gas sensor based on high-Q/V point-defect photonic crystal nanocavities. Opt. Quant. Electron. 52(5), 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-020-02366-w
Kazanskiy, N.L., Butt, M.A., Khonina, S.N.: Silicon-tapered waveguide for mode conversion in metal–insulator–metal waveguide-based plasmonic sensor for refractive index sensing. Appl. Opt. 62(32), 8678–8685 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.507402
Khemiri, M., Sassi, I.: Regions of validity of geometric optics and Kirchhoff approximations for reflection from Gaussian random rough dielectric surfaces. Waves Random Complex Media 25(4), 656–668 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2015.1070974
Kumar, V., Pal, S.: Tantalum disulfide (TaS2)–based symmetrical long-range surface plasmon resonance biosensor with ultrahigh imaging sensitivity and figure of merit. Plasmonics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01993-9
Kumar, S., Yadav, A., Malomed, B.A.: High performance surface plasmon resonance based sensor using black phosphorus and magnesium oxide adhesion layer. Front. Mater. 10, 1131412 (2023a). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2023.1131412
Kumar, V., Raghuwanshi, S.K., Kumar, S.: Nanomaterial-based surface plasmon resonance sensing chip for detection of skin and breast cancer. Plasmonics (2023b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02022-5
Kundal, S., Kumar, R., Khandelwal, A., Hiremath, K.R.: Mathematical modelling of a ring resonator based refractive index sensor for cancer detection. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55, 1020 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05278-7
Lee, K.L., Tsai, P.C., You, M.L., Pan, M.Y., Shi, X., Ueno, K., Misawa, H., Wei, P.K.: Enhancing surface sensitivity of nanostructure-based aluminum sensors using capped dielectric layers. ACS Omega 2(10), 7461–7470 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b01349
Li, Y., Huang, J., Chen, F.: Quintuple plasmonic fano resonances for the sensing application of glucose concentration and water-soluble vitamins. Plasmonics 18, 1825–1835 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01893-y
Liedberg, B., Nylander, C., Lunström, I.: Surface plasmon resonance for gas detection and biosensing. Sens. Actuators 4, 299–304 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1016/0250-6874(83)85036-7
Lifeng, L.: Fourier modal method for crossed anisotropic gratings with arbitrary permittivity and permeability tensors. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 5(4), 345 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1088/1464-4258/5/4/307
Liu, P., Yan, S., Ren, Y., Zhang, X., Li, T., Wu, X., Shen, L., Hua, E.: A MIM waveguide structure of a high-performance refractive index and temperature sensor based on Fano resonance. Appl. Sci. 11(22), 10629 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210629
Lu, X., Zhang, T., Wan, R., Xu, Y., Zhao, C., Guo, S.: Numerical investigation of narrowband infrared absorber and sensor based on dielectric-metal metasurface. Opt. Express 26(8), 10179–10187 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.26.010179
Ma, Z., Tang, P., Xue, J., Zhou, J.: Enhancing photoresponse of GaAs-based photodetector by plasmon grating structures. Plasmonics 18, 1571–1579 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01849-2
Mayer, K.M., Hafner, J.H.: Localized surface plasmon resonance sensors. Chem. Rev. 111(6), 3828–3857 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr100313v
Mohamed, Z.E.A., Elshahat, S., Abd-Elnaiem, A.M., Almokhtar, M.: Sensing performance of Fano resonance induced by the coupling of two 1D topological photonic crystals. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55(11), 943 (2023a). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05092-1
Mohamed, Z.E.A., Taya, S.A., Almawgani, A.H., Hindi, A.T.: Fano resonance based on coupling between nanoring resonator and MIM Waveguide for refractive index sensor. Plasmonics (2023b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02009-2
Nga, D.T., Phan, A.D., Lam, V.D., Badloe, T., Rho, J.: Optimizing the design of broadband solar metamaterial absorbers based on titanium nitride nanorings. Opt. Mater. Express 13(10), 2787–2797 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1364/OME.499630
Parimala Devi, M., Awasthi, S.K., Alipour-Banaei, H., Nambi, R.: Refractive index EV sensor based on conventional and mirror image 1D defective photonic crystal designs: theoretical study. J. Comput. Electron. 21, 1404–1415 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-022-01945-2
Paswan, M.K., Basu, R.: Hybrid structure-based SPR sensor for chemical sensing with enhanced sensitivity. Plasmonics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02020-7
Patel, S.K., Surve, J., Parmar, J., Armghan, A., Aliqab, K., Altahan, B.R., Ahmed, K., Bui, F.M., Al-Zahrani, F.A.: Graphene-based H-shaped biosensor with high sensitivity and optimization using ML-based algorithm. Alex. Eng. J. 68, 15–28 (2023a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2023.01.002
Patel, S.K., Wekalao, J., Alsalman, O., Surve, J., Parmar, J., Taya, S.A.: Development of surface plasmon resonance sensor with enhanced sensitivity for low refractive index detection. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55(11), 1001 (2023b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05265-y
Popescu, V.A., Sharma, A.K.: High-performance plasmonic sensor based on silver, gold and graphene layers for cancer cell detection at 632.8 nm wavelength with photonic spin hall effect. Plasmonics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01977-9
Rafiee, E., Negahdari, R.: Split ring shaped plasmonic-graphene/black phosphorous nano structure for cancer cell detection. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55, 1035 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05346-y
Rahad, R., Rakib, A.K.M., Haque, M.A., Sharar, S.S., Sagor, R.H.: Plasmonic refractive index sensing in the early diagnosis of diabetes, anemia, and cancer: an exploration of biological biomarkers. Results Phys. 49, 106478 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2023.106478
Rahmatiyar, M., Afsahi, M., Danaie, M.: Design of a refractive index plasmonic sensor based on a ring resonator coupled to a MIM waveguide containing tapered defects. Plasmonics 15, 2169–2176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01238-z
Rakhshani, M.R.: Refractive index sensor based on dual side-coupled rectangular resonators and nanorods array for medical applications. Opt. Quant. Electron. 53, 232 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-02857-4
Rashid, K.S., Tathfif, I., Yaseer, A.A., Hassan, M.F., Sagor, R.H.: Cog-shaped refractive index sensor embedded with gold nanorods for temperature sensing of multiple analytes. Opt. Express 29(23), 37541–37554 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.442954
Rich, R.L., Myszka, D.G.: Advances in surface plasmon resonance biosensor analysis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 11(1), 54–61 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-1669(99)00054-3
Rider, A.E., Ostrikov, K., Furman, S.A.: Plasmas meet plasmonics. Eur. Phys. J. D 66, 226 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2012-30273-3
Sahu, S., Ali, J., Yupapin, P.P., Singh, G.: Optical biosensor based on a cladding modulated grating waveguide. Optik 166, 103–109 (2018a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.04.034
Sahu, S., Ali, J., Yupapin, P.P., Singh, G.: Porous silicon based Bragg-grating resonator for refractive index biosensor. Photonic Sens. 8, 248–254 (2018b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13320-018-0459-z
Sassi, I., Ben El Hadj Rhouma, M.: Sensitivity enhancement of SPR sensor assisted by Ag, TiO2 and BP for glucose and hemoglobin detection: numerical analysis. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55, 959 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05217-6
Sassi, I., Mghaieth, R.: Infrared thermal source or perfect absorber sensor based on silver 2D grating. Appl. Phys. A 126(675), 1–14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03854-2
Sassi, I., Sifaoui, M.S.: Comparison of geometric optics approximation and integral method for reflection and transmission from microgeometrical dielectric surfaces. JOSA A 24(2), 451–462 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.24.000451
Sassi, I., Ghmari, F., Sifaoui, M.S.: Effect of the material of rough surfaces and the incident light polarization on the validity of the surface impedance boundary condition and the geometric optics approximation for reflection and emission. JOSA A 26(3), 480–488 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.26.000480
Sassi, I., Khemiri, M., Oumezzine, M.: Light reflection from finite conductors with a Gaussian random roughness using Kirchhoff and geometric optics approximations. Opt. Rev. 23, 926–935 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-016-0274-y
Sassi, I., Dhibi, A., Oumezzine, M.: Resonances in reflection, transmission and absorption of 1-D triangular-relief metallic gratings. Indian J. Phys. 91, 149–155 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-016-0910-1
Sassi, I.A., Ben El Hadj Rhouma, M., Daher, M.G.: Highly sensitive refractive index gas sensor using two-dimensional silicon carbide grating based on surface plasmon resonance. Opt. Quant. Electron. 55(402), 1–17 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-04682-3
Sbeah, Z.A., Adhikari, R., Sorathiya, V., Chauhan, D., Ponomarev, R.S., Dwivedi, R.P.: High-sensitive plasmonic multilayer SiO2/VO2 metamaterial sensor. Appl. Phys. A 129(8), 596 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06846-0
Shaban, N., Prajapati, Y.K., Mohammadkhani, R.: Performance enhancement of waveguide-coupled and metamaterial surface plasmon resonance sensors based on silver-bismuth ferrite and graphene. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 309 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09721-5
Sharma, S., Singh, M., Tewari, R.K., Kumar, A.: A biosensor for the detection of anemia using metal Ag and defect multilayer photonic crystal. Plasmonics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-02088-1
Singh, S., Singh, S., Singh, P.K., Yadav, R.K., Lohia, P., Dwivedi, D.K.: Theoretical study of malaria detection in blood samples using bimetal layer and zinc telluride nanomaterial-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Plasmonics (2023a). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01913-x
Singh, L., Almawgani, A.H.M., Vasimalla, Y., Kumar, R., Alsuzian, T.: SPR-based label-free sensor for RI-based detection of urea concentration. Plasmonics (2023b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01956-0
Skoog, D.A., West, D.M., Holler, F.J., Crouch, S.R.: Fundamentals of analytical chemistry. Cengage Learning (2013)
Snyder, L.R., Kirkland, J.J., Dolan, J.W.: Basic concepts and the control of separation. Introd. Mod. Liq. Chromatogr. 2, 15–82 (2010)
Sovizi, M., Aliannezhadi, M.: Highly sensitive asymmetric and symmetric cancer sensors with ultra-high-quality factor and resolution power. Sci. Rep. 13, 12251 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-39422-w
Tathfif, I., Hassan, M.F., Rashid, K.S., Yaseer, A.A., Sagor, R.H.: A highly sensitive plasmonic refractive index sensor based on concentric triple ring resonator for cancer biomarker and chemical concentration detection. Opt. Commun. 519, 128429 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2022.128429
Taya, S.A., Al-Ashi, N.E., Ramahi, O.M., Colak, I., Amiri, I.S.: Surface plasmon resonance-based optical sensor using a thin layer of plasma. JOSA B 38(8), 2362–2367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.420129
Taya, S.A., Daher, M.G., Almawgani, A.H., Hindi, A.T.: Detection of virus SARS-CoV-2 using a surface plasmon resonance device based on BiFeO3-graphene layers. Plasmonics 18, 1441–1448 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01867-0
Tian, J., Li, J.: Investigation on plasmon induced transparency and its application in an MIM type compound plasmonic waveguide. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 98, 199–212 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2528/PIERC19102001
Uniyal, A., Srivastava, G., Sarkar, P., Kumar, M., Singh, S., Taya, S.A., Muduli, A., Pal, A.: Fluorinated graphene and CNT-based surface plasmon resonance sensor for detecting the viral particles of SARS-CoV-2. Physica B 669, 415282 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2023.415282
Varasteanu, P.: Transition metal dichalcogenides/gold-based surface plasmon resonance sensors: exploring the geometrical and material parameters. Plasmonics 15(1), 243–253 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-01033-5
Vashist, S.K., Schneider, E.M., Venkatesh, A.G., Luong, J.H.: Emerging human fetuin a assays for biomedical diagnostics. Trends Biotechnol. 35(5), 407–421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.12.006
Vasimalla, Y., Pradhan, H.S.: Modeling of a novel SCHOTT B270 prism based SPR sensor using Ag-Si-BP/MXene structure for detection of specific biological samples. Opt. Quant. Electron. 54, 612 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-022-04022-x
Vikas, R.K., Verma, R.K.: High figure of merit fiber optic surface plasmon resonance sensor with topological insulator (BSTS). Opt. Quant. Electron. 54(1), 55 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-021-03435-4
Wang, H., Zhang, H., Dong, J., Hu, S., Zhu, W., Qiu, W., Luo, Y.: Sensitivity-enhanced surface plasmon resonance sensor utilizing a tungsten disulfide (WS2) nanosheets overlayer. Photonics Res. 6(6), 485–491 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/PRJ.6.000485
Wang, H., Tong, C., Guo, X., Li, Z., Shen, J., Li, C.: A high-sensitivity bimetallic grating-coupled surface plasmon resonance sensor based on two-dimensional materials. Photonics 10(8), 899 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10080899
Wei, W., Nong, J., Tang, L., Wang, N., Chuang, C.J., Huang, Y.: Graphene-MoS2 hybrid structure enhanced fiber optic surface plasmon resonance sensor. Plasmonics 12, 1205–1212 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0377-0
**ao, L.P., Wang, F.Q., Liang, R.S., Zou, S.W., Hu, M.: A high-sensitivity refractive-index sensor based on plasmonic waveguides asymmetrically coupled with a nanodisk resonator. Chin. Phys. Lett. 32, 070701 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/32/7/070701
Yang, Y., **ang, Y., Qi, X.: Design of photonic crystal biosensors for cancer cell detection. Micromachines 14(7), 1478 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14071478
Yu, J., Zhu, J., Ye, S., Wang, X.: Ultra-wide sensing range plasmonic refractive index sensor based on a two-dimensional circular-hole grating engraved on a gold film. Results Phys. 26, 104396 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104396
Zaky, Z.A., Sharma, A., Alamri, S., Saleh, N., Aly, A.H.: Detection of fat concentration in milk using ternary photonic crystal. SILICON (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01379-8
Zeng, S., Baillargeat, D., Ho, H.P., Yong, K.T.: Nanomaterials enhanced surface plasmon resonance for biological and chemical sensing applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43(10), 3426–3452 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60479a
Zhang, R., Pu, S., Li, X.: Gold-film-thickness dependent SPR refractive index and temperature sensing with hetero-core optical fiber structure. Sensors 19(19), 4345 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194345
Zhao, B., Wang, L., Shuai, Y., Zhang, Z.M.: Thermophotovoltaic emitters based on a two-dimensional grating/thin-film nanostructure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 67, 637–645 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.08.047
Zhu, J., Lin, S., Ren, Y.: Numerical analysis of a novel higher power refractive index sensor based on MIM waveguide structure. Results Opt. 12, 100447 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rio.2023.100447
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection, investigation, and analysis were performed by IMED SASSI. The first draft of the manuscript was written by IMED SASSI and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable. The work presented in this manuscript is mathematical modeling only for the proposed biosensor. No experiment was performed on the human body and living organism/animal. So, ethical approval from an ethical committee is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sassi, I., Ben El Hadj Rhouma, M., Taya, S.A. et al. The effects of the geometric and optical parameters on the performance of a grating perfect absorber sensor in near-infrared band. Opt Quant Electron 56, 992 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-024-06713-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-024-06713-z