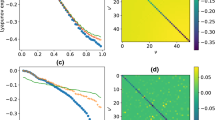
Abstract
Heat conduction in real physical networks such as nanotube/nanowire networks has been attracting more and more attention, but its theoretical understanding is far behind. To open a way to this problem, we present a multi-body vibration model to study heat conduction in complex networks, where nodes’ degrees satisfy a random distribution, and links consist of 1D atom chains with nonlinear springs. Based on this model, we find two interesting phenomenons: (1) The main heat fluxes of a network always localize in a skeleton subnetwork, which may have potential applications in thermal management and thermal concentrators, and (2) there exists an abnormal size effect of heat conduction in complex networks, i.e., the total heat flux of a network will enlarge with the increase of atoms on links, which is in contrast to the previous result on a 1D chain. Furthermore, we introduce a transmission diagram to characterize the skeleton of localized heat fluxes and then discover a jum** transition of total heat flux in the process of removing links, implying that the control of heat flux can be effective only when the change in a network topology focuses on the links within the skeleton. A brief theory is introduced to explain the abnormal size effect.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statements
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Albert, R., Barabasi, A.: Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 47 (2002)
Boccaletti, S., Latora, V., Moreno, Y., Chavez, M., Hwang, D.-U.: Complex networks: Structure and dynamics. Phys. Rep. 424, 175 (2006)
Dorogovtsev, S.N., Goltsev, A.V., Mendes, J.F.F.: Critical phenomena in complex networks. Rev. Mod. Pyhs. 80, 1275 (2008)
Albert, R., Jeong, H., Barabsi, A.L.: Error and attack tolerance of complex networks. Nature 406, 378–382 (2000)
Stam, C.J.: Characterization of anatomical and functional connectivity in the brain: a complex networks perspective. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 77, 186–194 (2010)
Pastor-Satorras, R., Castellano, C., Van Mieghem, P., Vespignani, A.: Epidemic processes in complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 925 (2015)
Tian, C., Cao, L., Bi, H., Xu, K., Liu, Z.: Chimera states in neuronal networks with time delay and electromagnetic induction. Nonlinear Dynam. 93, 1695–1704 (2018)
Wu, J., Zheng, M., Xu, K., Gu, C.: Effects of two channels on explosive information spreading. Nonlinear Dyn. 99, 2387–2397 (2020)
Liu, Z.H., Wu, X., Yang, H.J., Gupte, N., Li, B.W.: Heat flux distribution and rectification of complex networks. New J. Phys. 12, 023016 (2010)
Volkov, A.N., Zhigilei, L.V.: Scaling laws and mesoscopic modeling of thermal conductivity in carbon nanotube materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 215902 (2010)
**ong, K., Zhou, J., Tang, M., Zeng, C., Liu, Z.: Control of thermal conduction and rectification in a model of complex networks with two asymmetric parts. Phys. Rev. E 98, 062144 (2018)
**ong, K., Zeng, C., Liu, Z.: Effect of degree correlation on the thermal transport in complex networks. Nonlinear Dyn. 94, 3067 (2018)
**ong, K., Zeng, C., Liu, Z., Li, B.: Influence of the degree of a complex network on heat conduction. Phys. Rev. E 98, 022115 (2018)
**ong, K., Liu, Z., Zeng, C., Li, B.: Thermal-siphon phenomenon and thermal/electric conduction in complex networks. Natl. Sci. Rev. 7, 270–277 (2020)
**ong, K., Yan, Z., **e, Y., Liu, Z.: Regulating heat conduction of complex networks by distributed nodes masses. Sci. Rep. 11, 5501 (2021)
Lee, B.Y., Sung, M.G., Lee, H., Namgung, S., Park, S.Y., Choi, D.S., Hong, S.: Integrated devices based on networks of nanotubes and nanowires. NPG Asia. Mater. 2, 103–111 (2010)
Ceylan, H., et al.: Size-controlled conformal nanofabrication of biotemplated three-dimensional tio 2 and zno nanonetworks. Sci. Rep. 3, 2306 (2013)
Yang, Y., Yang, X., Liang, L., Gao, Y., Cheng, H., Li, X., Duan, X.: Large-area graphene-nanomesh/carbon-nanotube hybrid membranes for ionic and molecular nanofiltration. Science 364, 1057–1062 (2019)
Pomerantseva, E., Bonaccorso, F., Feng, X., Cui, Y., Gogotsi, Y.: Energy storage: The future enabled by nanomaterials. Science 366, 6468 (2019)
Son, D., Kang, J., Vardoulis, O., Kim, Y., Matsuhisa, N., Oh, J.Y., Bao, Z.: An integrated self-healable electronic skin system fabricated via dynamic reconstruction of a nanostructured conducting network. Nat. Nanotechnol. 13, 1057–1065 (2018)
Kang, T.H., Chang, H., Choi, D., Kim, S., Moon, J., Lim, J.A., Yi, H.: Hydrogel-templated transfer-printing of conductive nanonetworks for wearable sensors on topographic flexible substrates. Nano Lett. 19, 3684–3691 (2019)
Hochstetter, J., Zhu, R., Loeffler, A., Diaz-Alvarez, A., Nakayama, T., Kuncic, Z.: Avalanches and edge-of-chaos learning in neuromorphic nanowire networks. Nat. Commun. 12, 1–13 (2021)
Shen, D., Zhan, Z., Liu, Z., Cao, Y., Zhou, L., Liu, Y., Yu, J.: Enhanced thermal conductivity of epoxy composites filled with silicon carbide nanowires. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–11 (2017)
Vignolini, S., Yufa, N. A., Cunha, P. S., Guldin, S., Rushkin, I., Stefik, M., et al.: A 3d optical metamaterial made by self-assembly. Adv. Mater. 24, OP23–OP27 (2012)
Rauber, M., Alber, I., Muller, S., Neumann, R., Picht, O., Roth, C., Ensinger, W.: Highly-ordered supportless three-dimensional nanowire networks with tunable complexity and interwire connectivity for device integration. Nano Lett. 11, 2304–2310 (2011)
Lepri, S., Livi, R., Politi, A.: Thermal conduction in classical low-dimensional lattices. Phys. Rep. 377, 1 (2003)
Dhar, A.: Heat transport in low-dimensional systems. Adv. Phys. 57, 457 (2008)
Li, N., Ren, J., Wang, L., Zhang, G., Hanggi, P., Li, B.: Colloquium: phononics: manipulating heat flow with electronic analogs and beyond. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 1045 (2012)
Liu, Z., Li, B.: Heat conduction in simple networks: the effect of interchain coupling. Phys. Rev. E 76, 051118 (2007)
Lepri, S., Livi, R., Politi, A.: Heat conduction in chains of nonlinear oscillators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1896 (1997)
Chen, J., Zhang, G., Li, B.: Molecular dynamics simulations of heat conduction in nanostructures: effect of heat bath. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 79, 074604 (2010)
Hu, B., Li, B., Zhao, H.: Heat conduction in one-dimensional chains. Phys. Rev. E 57, 2992 (1998)
Hu, B., Li, B., Zhao, H.: Heat conduction in one-dimensional nonintegrable systems. Phys. Rev. E 61, 3828 (2000)
Li, B., Wang, L., Casati, G.: Thermal diode: rectification of heat flux. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 184301 (2004)
Kryven, I.: Bond percolation in coloured and multiplex networks. Nat. Commun. 10, 404 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Blattner, M., Yu, Y.: Heat conduction process on community networks as a recommendation model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 154301 (2007)
Shen, X., Li, Y., Jiang, C., Ni, Y., Huang, J.: A thermal theory for unifying and designing transparency, concentrating and cloaking. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 031907 (2016)
Wang, R., Xu, L., Ji, Q., Huang, J.: Thermal cloak-concentrator. Appl. Phys. 123, 115117 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 12005166, 11675056 and 11835003, and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education under Grant No. 20JK0764.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
**ong, K., Yan, Z., **e, Y. et al. Heat flux localization and abnormal size effect induced by multi-body vibration in complex networks. Nonlinear Dyn 110, 2771–2779 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07684-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07684-0