Abstract
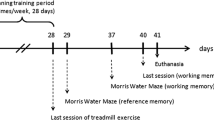
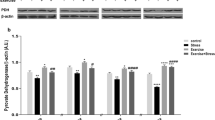
Sleep deprivation (SD) has deleterious effects on cognitive functions including learning and memory. However, some studies have shown that SD can improve cognitive functions. Interestingly, treadmill exercise has both impairment and improvement effects on memory function. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of SD for 4 (short-term) and 24 (long-term) hours, and two protocols of treadmill exercise (mild short-term and moderate long-term) on spatial memory performance, and oxidative and antioxidant markers in the serum of rats. Morris Water Maze apparatus was used to assess spatial memory performance. Also, SD was done using gentle handling method. In addition, the serum level of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) was measured. The results showed that 24 h SD (but not 4 h) had negative effect on spatial memory performance, decreased SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px level, and increased MDA level. Long-term moderate (but not short-term mild) treadmill exercise had also negative effect on spatial memory performance, decreased SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px level, and increased MDA level. Interestingly, both protocols of treadmill exercise reversed spatial memory impairment and oxidative stress induced by 24 h SD. In conclusion, it seems that SD and treadmill exercise interact with each other, and moderate long-term exercise can reverse the negative effects of long-term SD on memory and oxidative status; although, it disrupted memory function and increased oxidative stress by itself.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Will be made available upon a reasonable request.
References
Torabi Z, Rezaie M, Aramvash A, Nasiri-Khalili MA, Nasehi M, Abedi B, Vaseghi S (2022) Interaction of lithium and sleep deprivation on memory performance and anxiety-like behavior in male Wistar rats. Behav Brain Res 113890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2022.113890
Rezaie M, Nasehi M, Vaseghi S, Alimohammadzadeh K, Islami Vaghar M, Mohammadi-Mahdiabadi-Hasani MH, Zarrindast MR (2021) The interaction effect of sleep deprivation and cannabinoid type 1 receptor in the CA1 hippocampal region on passive avoidance memory, depressive-like behavior and locomotor activity in rats. Behav Brain Res 396:112901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112901
Looti Bashiyan M, Nasehi M, Vaseghi S, Khalifeh S (2021) Investigating the effect of crocin on memory deficits induced by total sleep deprivation (TSD) with respect to the BDNF, TrkB and ERK levels in the hippocampus of male Wistar rats. J Psychopharmacol 2698811211000762. https://doi.org/10.1177/02698811211000762
Edem EE, Nebo KE, Rimamchatin P, Bello A, Akinluyi E, Fafure A, Adeoluwa O, Adekeye A, Oremosu A (2022) Sleep disruption exacerbates cognitive dysfunction by promoting Lipid-Immune Dysregulation in the Corticohippocampal System of Pentylenetetrazol-Kindled rats. FASEB J 36(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.2022.36.S1.R2906
Ke P, Zheng C, Liu F, Wu L, Tang Y, Wu Y, Lv D, Chen H, Qian L, Wu X, Zeng K (2022) Relationship between circadian genes and memory impairment caused by sleep deprivation. PeerJ 10:e13165. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.13165
Hennecke E, Lange D, Steenbergen F, Fronczek-Poncelet J, Elmenhorst D, Bauer A, Aeschbach D, Elmenhorst EM (2021) Adverse interaction effects of chronic and acute sleep deficits on spatial working memory but not on verbal working memory or declarative memory. J Sleep Res 30(4):e13225. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.13225
Kurinec CA, Whitney P, Hinson JM, Hansen DA, Van Dongen HPA (2021) Sleep deprivation impairs binding of information with its context. Sleep 44(8). https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsab113
Santisteban JA, Brown TG, Ouimet MC, Gruber R (2019) Cumulative mild partial sleep deprivation negatively impacts working memory capacity but not sustained attention, response inhibition, or decision making: a randomized controlled trial. Sleep Health 5(1):101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2018.09.007
Guo B, Chen C, Yang L, Zhu R (2021) Effects of dexmedetomidine on postoperative cognitive function of sleep deprivation rats based on changes in inflammatory response. Bioengineered 12(1):7920–7928. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1981757
Chen P, Wu H, Yao H, Zhang J, Fan W, Chen Z, Su W, Wang Y, Li P (2022) Multi-Omics Analysis reveals the systematic relationship between oral homeostasis and chronic sleep deprivation in rats. Front Immunol 13:847132. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.847132
Lasisi TJ, Shittu ST, Abeje JI, Ogunremi KJ, Shittu SA (2021) Paradoxical sleep deprivation induces oxidative stress in the submandibular glands of Wistar rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2020-0178
Massadeh AM, Alzoubi KH, Milhem AM, Rababa’h AM, Khabour OF (2021) Evaluating the effect of selenium on spatial memory Impairment Induced by Sleep Deprivation. Physiol Behav 113669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2021.113669
Khodaverdiloo A, Farhadi M, Jameie M, Jameie SB, Pirhajati V (2021) Neurogenesis in the rat neonate’s hippocampus with maternal short-term REM sleep deprivation restores by royal jelly treatment. Brain Behav 11(12):e2423. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.2423
Lu Y, **ao Y, Tu Y, Dai W, **e Y (2022) Propofol-induced sleep ameliorates cognition impairment in sleep-deprived rats. Sleep Breath. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-022-02591-5
Marzabadi EA, Meftahi GH, Refahi S (2022) Pretreatment with combined low-level laser therapy and methylene blue improves learning and memory in sleep-deprived mice. Lasers Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-021-03497-6
Arjmandi-Rad S, Ebrahimnejad M, Zarrindast MR, Vaseghi S (2022) Do sleep disturbances have a dual effect on Alzheimer’s Disease? Cell Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01228-1
Vecsey CG, Huang T, Abel T (2018) Sleep deprivation impairs synaptic tagging in mouse hippocampal slices. Neurobiol Learn Mem 154:136–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2018.03.016
Vaseghi S, Arjmandi-Rad S, Kholghi G, Nasehi M (2021) Inconsistent effects of sleep deprivation on memory function. EXCLI J 20:1011–1027. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2021-3764
Wu J, Dou Y, Ladiges WC (2020) Adverse neurological Effects of Short-Term Sleep Deprivation in Aging mice are prevented by SS31 peptide. Clocks Sleep 2(3):325–333. https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep2030024
Vaccaro A, Kaplan Dor Y, Nambara K, Pollina EA, Lin C, Greenberg ME, Rogulja D (2020) Sleep loss can cause death through Accumulation of reactive oxygen species in the gut. Cell 181(6):1307–1328e1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.049
Zhou HR, Wu JR, Bei L, Wang BX, Xu H, Wang JT, Ma SX (2020) Hydroalcoholic extract from Abelmoschus manihot (Linn.) Medicus flower reverses sleep deprivation-evoked learning and memory deficit. Food Funct 11(10):8978–8986. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo02158j
Cheng O, Li R, Zhao L, Yu L, Yang B, Wang J, Chen B, Yang J (2015) Short-term sleep deprivation stimulates hippocampal neurogenesis in rats following global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0125877. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125877
Mahboubi S, Nasehi M, Imani A, Sadat-Shirazi MS, Zarrindast MR, Vousooghi N, Noroozian M (2019) Benefit effect of REM-sleep deprivation on memory impairment induced by intensive exercise in male wistar rats: with respect to hippocampal BDNF and TrkB. Nat Sci Sleep 11:179–188. https://doi.org/10.2147/NSS.S207339
Mueller AD, Meerlo P, McGinty D, Mistlberger RE (2015) Sleep and adult neurogenesis: implications for cognition and mood. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 25:151–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/7854_2013_251
El-Domiaty HF, El-Roghy ES, Salem HR (2022) Combination of magnesium supplementation with treadmill exercise improves memory deficit in aged rats by enhancing hippocampal neurogenesis and plasticity: a functional and histological study. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 47(3):296–308. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2021-0133
Yang L, Wu C, Li Y, Dong Y, Wu CY, Lee RH, Brann DW, Lin HW, Zhang Q (2022) Long-term exercise pre-training attenuates Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology in a transgenic rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Geroscience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-022-00534-2
Navazani P, Vaseghi S, Hashemi M, Shafaati MR, Nasehi M (2021) Effects of Treadmill Exercise on the expression level of BAX, BAD, BCL-2, BCL-XL, TFAM, and PGC-1alpha in the Hippocampus of Thimerosal-Treated rats. Neurotox Res 39(4):1274–1284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00370-w
Park SS, Kim TW, Sung YH, Park YJ, Kim MK, Shin MS (2021) Treadmill Exercise ameliorates short-term memory impairment by suppressing hippocampal neuroinflammation in Poloxamer-407-Induced hyperlipidemia rats. Int Neurourol J 25(Suppl 2):S81–89. https://doi.org/10.5213/inj.2142342.171
Kim SH, Ko IG, ** JJ, Hwang L, Baek SS (2021) Treadmill exercise ameliorates impairment of spatial learning memory in pups born to old and obese mother rats. J Exerc Rehabil 17(4):234–240. https://doi.org/10.12965/jer.2142466.233
Ko YJ, Ko IG (2020) Voluntary Wheel running improves spatial learning memory by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis via inactivation of nuclear factor Kappa B in Brain inflammation rats. Int Neurourol J 24(Suppl 2):96–103. https://doi.org/10.5213/inj.2040432.216
Mokhtari-Zaer A, Hosseini M, Roshan NM, Boskabady MH (2020) Treadmill exercise ameliorates memory deficits and hippocampal inflammation in ovalbumin-sensitized juvenile rats. Brain Res Bull 165:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.09.016
Ebrahimnejad M, Azizi P, Alipour V, Zarrindast MR, Vaseghi S (2022) Complicated role of Exercise in modulating memory: a discussion of the Mechanisms involved. Neurochem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03552-w
He F, Li J, Liu Z, Chuang CC, Yang W, Zuo L (2016) Redox mechanism of reactive oxygen species in Exercise. Front Physiol 7:486. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2016.00486
Jahangiri Z, Gholamnezhad Z, Hosseini M, Beheshti F, Kasraie N (2019) The effects of moderate exercise and overtraining on learning and memory, hippocampal inflammatory cytokine levels, and brain oxidative stress markers in rats. J Physiol Sci 69(6):993–1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-019-00719-z
Silva RH, Abilio VC, Takatsu AL, Kameda SR, Grassl C, Chehin AB, Medrano WA, Calzavara MB, Registro S, Andersen ML, Machado RB, Carvalho RC, Ribeiro Rde A, Tufik S, Frussa-Filho R (2004) Role of hippocampal oxidative stress in memory deficits induced by sleep deprivation in mice. Neuropharmacology 46(6):895–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2003.11.032
De Lima MNM, Polydoro M, Laranja DC, Bonatto F, Bromberg E, Moreira JCF, Dal-Pizzol F, Schröder N (2005) Recognition memory impairment and brain oxidative stress induced by postnatal iron administration. Eur J Neurosci 21(9):2521–2528
Assaran AH, Akbarian M, Amirahmadi S, Salmani H, Shirzad S, Hosseini M, Beheshti F, Rajabian A (2022) Ellagic acid prevents oxidative stress and memory deficits in a rat model of scopolamine-induced Alzheimer’s Disease. Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry (formerly current Medicinal Chemistry-Central Nervous. Syst Agents) 22(3):214–227
Olayinka J, Eduviere A, Adeoluwa O, Fafure A, Adebanjo A, Ozolua R (2022) Quercetin mitigates memory deficits in scopolamine mice model via protection against neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Life Sci 292:120326
Souza LC, Andrade MK, Azevedo EM, Ramos DC, Bail EL, Vital MA (2022) Andrographolide attenuates short-term spatial and recognition memory impairment and neuroinflammation induced by a streptozotocin rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotox Res 40(5):1440–1454
Arjmandi-Rad S, Zarrindast MR, Shadfar S, Nasehi M (2022) The role of sleep deprivation in streptozotocin-induced Alzheimer’s disease-like sporadic dementia in rats with respect to the serum level of oxidative and inflammatory markers. Exp Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-022-06471-y
Massadeh AM, Alzoubi KH, Milhem AM, Rababa’h AM, Khabour OF (2022) Evaluating the effect of selenium on spatial memory impairment induced by sleep deprivation. Physiol Behav 244:113669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2021.113669
Konakanchi S, Raavi V, Ml HK, Shankar Ms V (2022) Effect of chronic sleep deprivation and sleep recovery on hippocampal CA3 neurons, spatial memory and anxiety-like behavior in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 187:107559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2021.107559
Kordestani-Moghadam P, Nasehi M, Vaseghi S, Khodagholi F, Zarrindast MR (2020) The role of sleep disturbances in depressive-like behavior with emphasis on alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity in rats. Physiol Behav 224:113023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2020.113023
In: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health, 8th edn., Washington (DC). https://doi.org/10.17226/12910
Shi HS, Luo YX, Xue YX, Wu P, Zhu WL, Ding ZB, Lu L (2011) Effects of sleep deprivation on retrieval and reconsolidation of morphine reward memory in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 98(2):299–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2011.01.006
Vaseghi S, Babapour V, Nasehi M, Zarrindast MR (2018) The role of CA1 CB1 receptors on lithium-induced spatial memory impairment in rats. EXCLI J 17:916–934. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2018-1511
Vaseghi S, Babapour V, Nasehi M, Zarrindast MR (2020) Synergistic but not additive effect between ACPA and lithium in the dorsal hippocampal region on spatial learning and memory in rats: isobolographic analyses. Chem Biol Interact 315:108895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108895
Molaei P, Vaseghi S, Entezari M, Hashemi M, Nasehi M (2021) The Effect of NeuroAid (MLC901) on Cholestasis-Induced spatial memory impairment with respect to the expression of BAX, BCL-2, BAD, PGC-1alpha and TFAM genes in the Hippocampus of male Wistar rats. Neurochem Res 46(8):2154–2166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03353-7
Al-Dhuhli F, Al-Siyabi S, Al-Maamari H, Al-Farsi S, Albarwani S (2022) Moderate-intensity exercise training reduces vasorelaxation of mesenteric arteries: role of BKCa channels and nitric oxide. Physiol Res 71(1):67–77. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.934671
Gessner N, Shinbashi M, Chuluun B, Heller C, Pittaras E (2022) Handling, task complexity, time-of-day, and sleep deprivation as dynamic modulators of recognition memory in mice. Physiol Behav 251:113803
Li ZH, Cheng L, Wen C, Ding L, You QY, Zhang SB (2022) Activation of CNR1/PI3K/AKT pathway by Tanshinone IIA protects hippocampal neurons and ameliorates Sleep Deprivation-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction in rats. Front Pharmacol 13:823732. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.823732
Ghaheri S, Panahpour H, Abdollahzadeh M, Saadati H (2022) Adolescent enriched environment exposure alleviates cognitive impairments in sleep-deprived male rats: role of hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Int J Dev Neurosci 82(2):133–145. https://doi.org/10.1002/jdn.10165
Han Y, Wang J, Zhao Q, **e X, Song R, **ao Y, Kang X, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Peng C, You Z (2020) Pioglitazone alleviates maternal sleep deprivation-induced cognitive deficits in male rat offspring by enhancing microglia-mediated neurogenesis. Brain Behav Immun 87:568–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2020.02.002
Li Y, Zhang W, Liu M, Zhang Q, Lin Z, Jia M, Liu D, Lin L (2021) Imbalance of Autophagy and Apoptosis Induced by Oxidative Stress May Be Involved in Thyroid Damage Caused by Sleep Deprivation in Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:5645090. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5645090
Forouzanfar F, Gholami J, Foroughnia M, Payvar B, Nemati S, Khodadadegan MA, Saheb M, Hajali V (2021) The beneficial effects of green tea on sleep deprivation-induced cognitive deficits in rats: the involvement of hippocampal antioxidant defense. Heliyon 7(11):e08336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08336
Kang X, Jiang L, Lan F, Tang YY, Zhang P, Zou W, Chen YJ, Tang XQ (2021) Hydrogen sulfide antagonizes sleep deprivation-induced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors by inhibiting neuroinflammation in a hippocampal Sirt1-dependent manner. Brain Res Bull 177:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.10.002
Yao ZY, Li XH, Zuo L, **ong Q, He WT, Li DX, Dong ZF (2022) Maternal sleep deprivation induces gut microbial dysbiosis and neuroinflammation in offspring rats. Zool Res 43(3):380–390. https://doi.org/10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2022.023
Tang H, Li K, Dou X, Zhao Y, Huang C, Shu F (2020) The neuroprotective effect of osthole against chronic sleep deprivation (CSD)-induced memory impairment in rats. Life Sci 263:118524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118524
Havekes R, Bruinenberg VM, Tudor JC, Ferri SL, Baumann A, Meerlo P, Abel T (2014) Transiently increasing cAMP levels selectively in hippocampal excitatory neurons during sleep deprivation prevents memory deficits caused by sleep loss. J Neurosci 34(47):15715–15721. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2403-14.2014
Rajizadeh MA, Esmaeilpour K, Haghparast E, Ebrahimi MN, Sheibani V (2020) Voluntary exercise modulates learning & memory and synaptic plasticity impairments in sleep deprived female rats. Brain Res 1729:146598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146598
Peng Y, Wang W, Tan T, He W, Dong Z, Wang YT, Han H (2016) Maternal sleep deprivation at different stages of pregnancy impairs the emotional and cognitive functions, and suppresses hippocampal long-term potentiation in the offspring rats. Mol Brain 9:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-016-0197-3
Junek A, Rusak B, Semba K (2010) Short-term sleep deprivation may alter the dynamics of hippocampal cell proliferation in adult rats. Neuroscience 170(4):1140–1152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.08.018
Grassi Zucconi G, Cipriani S, Balgkouranidou I, Scattoni R (2006) ‘one night’ sleep deprivation stimulates hippocampal neurogenesis. Brain Res Bull 69(4):375–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2006.01.009
Moldovan M, Constantinescu AO, Balseanu A, Oprescu N, Zagrean L, Popa-Wagner A (2010) Sleep deprivation attenuates experimental stroke severity in rats. Exp Neurol 222(1):135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.12.023
Fujihara H, Sei H, Morita Y, Ueta Y, Morita K (2003) Short-term sleep disturbance enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression in rat hippocampus by acting as internal stressor. J Mol Neurosci 21(3):223–232. https://doi.org/10.1385/jmn:21:3:223
Hairston IS, Peyron C, Denning DP, Ruby NF, Flores J, Sapolsky RM, Heller HC, O’Hara BF (2004) Sleep deprivation effects on growth factor expression in neonatal rats: a potential role for BDNF in the mediation of delta power. J Neurophysiol 91(4):1586–1595. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00894.2003
Sahin L, Cevik OS, Cevik K, Guven C, Taskin E, Kocahan S (2021) Mild regular treadmill exercise ameliorated the detrimental effects of acute sleep deprivation on spatial memory. Brain Res 1759:147367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147367
Gopalakrishnan A, Ji LL, Cirelli C (2004) Sleep deprivation and cellular responses to oxidative stress. Sleep 27(1):27–35. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/27.1.27
Melgarejo-Gutierrez M, Acosta-Pena E, Venebra-Munoz A, Escobar C, Santiago-Garcia J, Garcia-Garcia F (2013) Sleep deprivation reduces neuroglobin immunoreactivity in the rat brain. NeuroReport 24(3):120–125. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0b013e32835d4b74
Ramanathan L, Hu S, Frautschy SA, Siegel JM (2010) Short-term total sleep deprivation in the rat increases antioxidant responses in multiple brain regions without impairing spontaneous alternation behavior. Behav Brain Res 207(2):305–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.10.014
Hafedh M, Parnow A (2022) Exercise training improves memory and produces changes in the adrenal gland morphology in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Endocr Regul 56(1):31–37. https://doi.org/10.2478/enr-2022-0004
Sun GC, Lee YJ, Lee YC, Yu HF, Wang DC (2021) Exercise prevents the impairment of learning and memory in prenatally phthalate-exposed male rats by improving the expression of plasticity-related proteins. Behav Brain Res 413:113444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113444
Xu L, Zhu L, Zhu L, Chen D, Cai K, Liu Z, Chen A (2021) Moderate Exercise combined with enriched Environment enhances Learning and Memory through BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway in rats. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(16). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18168283
Jeong JH, Koo JH, Yook JS, Cho JY, Kang EB (2021) Neuroprotective benefits of Exercise and MitoQ on memory function, mitochondrial Dynamics, oxidative stress, and Neuroinflammation in D-Galactose-Induced aging rats. Brain Sci 11(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020164
Lan Y, Huang Z, Jiang Y, Zhou X, Zhang J, Zhang D, Wang B, Hou G (2018) Strength exercise weakens aerobic exercise-induced cognitive improvements in rats. PLoS ONE 13(10):e0205562. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0205562
Vilela TC, Muller AP, Damiani AP, Macan TP, da Silva S, Canteiro PB, de Sena Casagrande A, Pedroso GDS, Nesi RT, de Andrade VM, de Pinho RA (2017) Strength and aerobic exercises improve spatial memory in aging rats through stimulating distinct neuroplasticity mechanisms. Mol Neurobiol 54(10):7928–7937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0272-x
Nokia MS, Lensu S, Ahtiainen JP, Johansson PP, Koch LG, Britton SL, Kainulainen H (2016) Physical exercise increases adult hippocampal neurogenesis in male rats provided it is aerobic and sustained. J Physiol 594(7):1855–1873. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP271552
Duman RS, Aghajanian GK, Sanacora G, Krystal JH (2016) Synaptic plasticity and depression: new insights from stress and rapid-acting antidepressants. Nat Med 22(3):238–249. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4050
Gray JD, Milner TA, McEwen BS (2013) Dynamic plasticity: the role of glucocorticoids, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and other trophic factors. Neuroscience 239:214–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.08.034
Rajizadeh MA, Sheibani V, Bejeshk MA, Mohtashami Borzadaran F, Saghari H, Esmaeilpour K (2019) The effects of high intensity exercise on learning and memory impairments followed by combination of sleep deprivation and demyelination induced by etidium bromide. Int J Neurosci 129(12):1166–1178. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2019.1640695
Mohammadipoor-Ghasemabad L, Sangtarash MH, Esmaeili-Mahani S, Sheibani V, Sasan HA (2019) Abnormal hippocampal miR-1b expression is ameliorated by regular treadmill exercise in the sleep-deprived female rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 22(5):485–490. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2019.31988.7734
Rajizadeh MA, Esmaeilpour K, Masoumi-Ardakani Y, Bejeshk MA, Shabani M, Nakhaee N, Ranjbar MP, Borzadaran FM, Sheibani V (2018) Voluntary exercise impact on cognitive impairments in sleep-deprived intact female rats. Physiol Behav 188:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.12.030
Salari M, Sheibani V, Saadati H, Pourrahimi A, khaksarihadad M, Esmaeelpour K, Khodamoradi M (2015) The compensatory effect of regular exercise on long-term memory impairment in sleep deprived female rats. Behav Processes 119:50–57. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2015.06.014
Chen G-H, Wei R-M, Zhang Y-M, Li Y, Wu Q-T, Wang Y-T, Li X-Y, Li X-W (2022) Altered cognition and anxiety in adolescent offspring whose mothers underwent different-pattern maternal sleep deprivation, and cognition link to hippocampal expressions of Bdnf and Syt-1. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience:483
Zagaar M, Dao A, Alhaider I, Alkadhi K (2013) Regular treadmill exercise prevents sleep deprivation-induced disruption of synaptic plasticity and associated signaling cascade in the dentate gyrus. Mol Cell Neurosci 56:375–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2013.07.011
Fernandes J, Baliego LGZ, Peixinho-Pena LF, de Almeida AA, Venancio DP, Scorza FA, de Mello MT, Arida RM (2013) Aerobic exercise attenuates inhibitory avoidance memory deficit induced by paradoxical sleep deprivation in rats. Brain Res 1529:66–73
Landers MR, Kinney JW, Allen DN, van Breukelen F (2013) A comparison of voluntary and forced exercise in protecting against behavioral asymmetry in a juvenile hemiparkinsonian rat model. Behav Brain Res 248:121–128
Van Dongen P, Baynard MD, Maislin G, Dinges DF (2004) Systematic interindividual differences in neurobehavioral impairment from sleep loss: evidence of trait-like differential vulnerability. Sleep 27(3):423–433
Deurveilher S, Bush JE, Rusak B, Eskes GA, Semba K (2015) Psychomotor vigilance task performance during and following chronic sleep restriction in rats. Sleep 38(4):515–528
Yang Y, Lagisz M, Foo YZ, Noble DW, Anwer H, Nakagawa S (2021) Beneficial intergenerational effects of exercise on brain and cognition: a multilevel meta-analysis of mean and variance. Biol Rev 96(4):1504–1527
Kronman CA, Kern KL, Nauer RK, Dunne MF, Storer TW, Schon K (2020) Cardiorespiratory fitness predicts effective connectivity between the hippocampus and default mode network nodes in young adults. Hippocampus 30(5):526–541
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
There is no providing financial support to this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G. KH., V. A., and M. R. collected data. MR. Z. analyzed data, reviewing, and validations. S. V. designing the study, collecting data, writing the original draft, and review and editing. All authors approved the final version. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
N/A.
Consent for publication
N/A.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kholghi, G., Alipour, V., Rezaie, M. et al. The Interaction Effect of Sleep Deprivation and Treadmill Exercise in Various Durations on Spatial Memory with Respect to the Oxidative Status of Rats. Neurochem Res 48, 2077–2092 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-03890-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-03890-3