Abstract
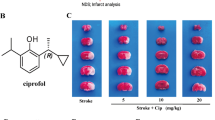
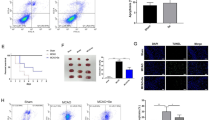
Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion involves multiple pathological processes and ferroptosis played a crucial role in the disease progression. Nevertheless, whether Vitexin could ameliorate ischemia/reperfusion injury via meditate the ferroptosis still remains unknown. In this study, we established the oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R) neuron cell and middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) rat model. The cell viability, cell apoptosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were tested by CCK-8 assay and Flow cytometry, respectively. Hematoxylin-eosin staining, TTC, TEM, immunofluorescence analysis and western blot were used to investigate the effects of Vitexin. The results demonstrated that Vitexin could enhanced the cell viability and decreased the cell apoptosis in OGD/R cell model. Meanwhile, incubation with Vitexin maintained the neuroprotective effects in OGD/R induced generation of lipid ROS and neuronal cell ferroptosis via regulated the expressions of Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 relative protein levels. Moreover, treatment with Vitexin reversed brain infracted volume, the normal histopathology and mitochondrial function in MCAO/R rat model. Vitexin significantly decreased the Nrf2 transfer ration from nuclear to cytosol and regulated the expression of Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling both in vitro and in vivo. Nevertheless, the protective effects of Vitexin were blocked with the Nrf2 inhibitor ML385. Vitexin could protect the neuron cell and brain related with the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Vitexin was a useful candidate for stroke therapy and our research may provide an attractive therapeutic target for the treatment of stroke.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Toman NG, Grande AW, Low WC (2019) Neural repair in stroke. Cell Transpl 28(9–10):1123–1126. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689719863784
Przykaza L (2021) Understanding the connection between common stroke comorbidities, their Associated inflammation, and the course of the cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Cascade. Front Immunol 12:782569. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.782569
Amani H, Mostafavi E, Alebouyeh MR, Arzaghi H, Akbarzadeh A, Pazoki-Toroudi H, Webster TJ (2019) Would Colloidal Gold Nanocarriers Present an effective diagnosis or treatment for ischemic stroke? Int J Nanomedicine 14:8013–8031. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S210035
Dong R, Huang R, Shi X, Xu Z, Mang J (2021) Exploration of the mechanism of luteolin against ischemic stroke based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental verification. Bioengineered 12(2):12274–12293. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.2006966
Wu R, Li X, Xu P, Huang L, Cheng J, Huang X, Jiang J, Wu LJ, Tang Y (2017) TREM2 protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Brain 10(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-017-0296-9
Qin Y, Zhang Q, Liu Y (2020) Analysis of knowledge bases and research focuses of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion from the perspective of map** knowledge domain. Brain Res Bull 156:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.12.004
Weiss HR, Chi OZ, Kiss GK, Liu X, Damito S, Jacinto E (2018) Akt activation improves microregional oxygen supply/consumption balance after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Brain Res 1683:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.01.019
Zhang K, Liu Q, Luo L, Feng X, Hu Q, Fan X, Mao S (2021) Neuroprotective effect of alpha-asarone on the rats model of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion stroke via ameliorating glial activation and autophagy. Neuroscience 473:130–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.08.006
Guan X, Li Z, Zhu S, Cheng M, Ju Y, Ren L, Yang G, Min D (2021) Galangin attenuated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibition of ferroptosis through activating the SLC7A11/GPX4 axis in gerbils. Life Sci 264:118660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118660
Stockwell BR et al (2017) Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death Nexus linking metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 171(2):273–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.021
Li C et al (2021) Nuclear receptor coactivator 4-mediated ferritinophagy contributes to cerebral ischemia-induced ferroptosis in ischemic stroke. Pharmacol Res 174:105933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105933
Clemente LP, Rabenau M, Tang S, Stanka J, Cors E, Stroh J, Culmsee C, von Karstedt S (2020) Dynasore Blocks ferroptosis through combined modulation of Iron Uptake and Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration. Cells 9(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102259
Chen G, Li C, Zhang L, Yang J, Meng H, Wan H, He Y (2022) Hydroxysafflor yellow A and anhydrosafflor yellow B alleviate ferroptosis and parthanatos in PC12 cells injured by OGD/R. Free Radic Biol Med 179:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.12.262
Hu ZY, Yang ZB, Zhang R, Luo XJ, Peng J (2022) The Protective Effect of Vitexin compound B-1 on Rat Cerebral I/R Injury through a mechanism involving modulation of miR-92b/NOX4 pathway. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527321666220324115848. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets
Wang Y, Zhen Y, Wu X, Jiang Q, Li X, Chen Z, Zhang G, Dong L (2015) Vitexin protects brain against ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulating mitogen-activated protein kinase and apoptosis signaling in mice. Phytomedicine 22(3):379–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2015.01.009
Cui YH, Zhang XQ, Wang ND, Zheng MD, Yan J (2019) Vitexin protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain endothelial permeability. Eur J Pharmacol 853:210–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.015
Min JW et al (2015) Vitexin reduces hypoxia-ischemia neonatal brain injury by the inhibition of HIF-1alpha in a rat pup model. Neuropharmacology 99:38–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.07.007
Luo WD, Min JW, Huang WX, Wang X, Peng YY, Han S, Yin J, Liu WH, He XH, Peng BW (2018) Vitexin reduces epilepsy after hypoxic ischemia in the neonatal brain via inhibition of NKCC1. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):186. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1221-6
Ganesan K, Ramkumar KM, Xu B (2020) Vitexin restores pancreatic beta-cell function and insulin signaling through Nrf2 and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol 888:173606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173606
Zhang S, ** S, Zhang S, Li YY, Wang H, Chen Y, Lu H (2022) Vitexin protects against high glucose-induced endothelial cell apoptosis and oxidative stress via Wnt/beta-catenin and Nrf2 signalling pathway. Arch Physiol Biochem 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2022.2028845
Lim S, Kim TJ, Kim YJ, Kim C, Ko SB, Kim BS (2021) Senolytic therapy for cerebral ischemia-reperfusion Injury. Int J Mol Sci 22(21). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111967
Huang L, Zhao B, Li Q, Wu J, Jiang H, Li Q (2021) Ephedrine alleviates middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced neurological deficits and hippocampal neuronal damage in rats by activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Bioengineered 12(1):4136–4149. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1953218
Hou Y, Wang K, Wan W, Cheng Y, Pu X, Ye X (2018) Resveratrol provides neuroprotection by regulating the JAK2/STAT3/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway after stroke in rats. Genes Dis 5(3):245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2018.06.001
Bhatt PC, Pathak S, Kumar V, Panda BP (2018) Attenuation of neurobehavioral and neurochemical abnormalities in animal model of cognitive deficits of Alzheimer’s disease by fermented soybean nanonutraceutical. Inflammopharmacology 26(1):105–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0381-9
Du J, Yin G, Hu Y, Shi S, Jiang J, Song X, Zhang Z, Wei Z, Tang C, Lyu H (2020) Coicis semen protects against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and promoting angiogenesis via the TGFbeta/ALK1/Smad1/5 signaling pathway. Aging 13(1):877–893. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202194
Tanaka K, Matsumoto S, Yamada T, Yamasaki R, Suzuki M, Kido MA, Kira JI (2020) Reduced post-ischemic Brain Injury in transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 knockout mice. Front Neurosci 14:453. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00453
Ye Y, ** T, Zhang X, Zeng Z, Ye B, Wang J, Zhong Y, **ong X, Gu L (2019) Meisoindigo protects against Focal Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and regulating Microglia/Macrophage polarization via TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Front Cell Neurosci 13:553. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00553
Fu K, Chen M, Zheng H, Li C, Yang F, Niu Q (2021) Pelargonidin ameliorates MCAO-induced cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by the action on the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Transl Neurosci 12(1):20–31. https://doi.org/10.1515/tnsci-2021-0006
Abdulai IL, Kwofie SK, Gbewonyo WS, Boison D, Puplampu JB, Adinortey MB (2021) Multitargeted Effects of Vitexin and Isovitexin on Diabetes Mellitus and its complications. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6641128. ScientificWorldJournal 2021:6641128
Zhang C, Li S, Sun C, Liu L, Fang Y, Yang X, Pan X, Zhang B (2021) Vitexin ameliorates glycochenodeoxycholate-induced hepatocyte injury through SIRT6 and JAK2/STAT3 pathways. Iran J Basic Med Sci 24(12):1717–1725. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJBMS.2021.59424.13196
Zhou P, Zheng ZH, Wan T, Wu J, Liao CW, Sun XJ (2021) Vitexin inhibits gastric Cancer Growth and Metastasis through HMGB1-mediated inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/HIF-1alpha signaling pathway. J Gastric Cancer 21(4):439–456. https://doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2021.21.e40
Zhao S, Guan X, Hou R, Zhang X, Guo F, Zhang Z, Hua C (2020) Vitexin attenuates epithelial ovarian cancer cell viability and motility in vitro and carcinogenesis in vivo via p38 and ERK1/2 pathways related VEGFA. Ann Transl Med 8(18):1139. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-5586
Mehta K, Bhagwat DP, Devraj P, Sehgal G, Mittal, Suchal K (2022) Vitex negundo protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse via attenuating behavioral deficits and oxidative damage. Psychopharmacology 239(2):573–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-06050-z
Tuo QZ et al (2022) Thrombin induces ACSL4-dependent ferroptosis during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7(1):59. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-00917-z
Yuan H, Pratte J, Giardina C (2021) Ferroptosis and its potential as a therapeutic target. Biochem Pharmacol 186:114486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114486
** Y, Chen L, Li L, Huang G, Huang H, Tang C (2022) SNAI2 promotes the development of ovarian cancer through regulating ferroptosis. Bioengineered 13(3):6451–6463. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.2024319
Qian X, Tang J, Li L, Chen Z, Chen L, Chu Y (2021) A new ferroptosis-related gene model for prognostic prediction of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Bioengineered 12(1):2341–2351. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1935400
Sun Y et al (2020) The emerging role of ferroptosis in inflammation. Biomed Pharmacother 127:110108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110108
Stockwell BR, Jiang X, Gu W (2020) Emerging mechanisms and Disease Relevance of Ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol 30(6):478–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2020.02.009
Song X, Long D (2020) Nrf2 and ferroptosis: a New Research Direction for neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Neurosci 14:267. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00267
Wang Q, Bin C, Xue Q, Gao Q, Huang A, Wang K, Tang N (2021) GSTZ1 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib-induced ferroptosis via inhibition of NRF2/GPX4 axis. Cell Death Dis 12(5):426. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03718-4
Farina M, Vieira LE, Buttari B, Profumo E, Saso L (2021) The Nrf2 pathway in ischemic stroke: a review. Molecules 26(16). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165001
Zhu L, Wei M, Yang N, Li X (2021) Glycyrrhizic acid alleviates the meconium-induced acute lung injury in neonatal rats by inhibiting oxidative stress through mediating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signal pathway. Bioengineered 12(1):2616–2626. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1937445
Huang J, Chen G, Wang J, Liu S, Su J (2022) Platycodin D regulates high glucose-induced ferroptosis of HK-2 cells through glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4). Bioengineered 13(3):6627–6637. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2045834
Yuan Y, Zhai Y, Chen J, Xu X, Wang H (2021) Kaempferol ameliorates oxygen-glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced neuronal ferroptosis by activating Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 Axis. Biomolecules 11(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11070923
Wang H, Wei W, Lan X, Liu N, Li Y, Ma H, Sun T, Peng X, Zhuang C, Yu J (2019) Neuroprotective effect of Swertiamain on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by inducing the Nrf2 protective pathway. ACS Chem Neurosci 10(5):2276–2286. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00605
Pan X, Fan J, Peng F, **ao L, Yang Z (2022) SET domain containing 7 promotes oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced PC12 cell inflammation and oxidative stress by regulating Keap1/Nrf2/ARE and NF-kappaB pathways. Bioengineered 13(3):7253–7261. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2045830
Shi M, Wang J, Bi F, Bai Z (2022) Diosmetin alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through Keap1-mediated Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway activation and NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. Environ Toxicol 37(6):1529–1542. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.23504
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there were no conflicts of interest in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, L., Shi, L. Vitexin Improves Cerebral ischemia‑reperfusion Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Injury and Ferroptosis via Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1signaling. Neurochem Res 48, 980–995 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03829-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03829-0