Abstract
Purpose
To report the outcomes of a large series of intracranial meningiomas (IMs) submitted to proton therapy (PT) with curative intent.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective analysis on all consecutive IM patients treated between 2014 and 2021. The median PT prescription dose was 55.8 Gy relative biological effectiveness (RBE) and 66 GyRBE for benign/radiologically diagnosed and atypical/anaplastic IMs, respectively. Local recurrence-free survival (LRFS), distant recurrence-free survival (DRFS), overall survival (OS), and radionecrosis-free survival (RNFS) were evaluated with the Kaplan-Meier method. Univariable analysis was performed to identify potential prognostic factors for clinical outcomes. Toxicity was reported according to the latest Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0.
Results
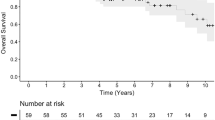
Overall, 167 patients were included. With a median follow-up of 41 months (range, 6–99), twelve patients (7%) developed tumor local recurrence after a median time of 39 months. The 5-year LRFS was 88% for the entire cohort, with a significant difference between benign/radiologically diagnosed and atypical/anaplastic IMs (98% vs. 47%, p < 0.001); this significant difference was maintained also for the 5-year OS and the 5-year DRFS rates. Patients aged ≤ 56 years reported significantly better outcomes, whereas lower prescription doses and skull base location were associated with better RNFS rates. Two patients experienced G3 acute toxicities (1.2%), and three patients G3 late toxicities (1.8%). There were no G4-G5 adverse events.
Conclusion
PT proved to be effective with an acceptable toxicity profile. To the best of our knowledge this is one of the largest series including IM patients submitted to PT.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset generated and analysed during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Wiemels J, Wrensch M, Claus EB (2010) Epidemiology and etiology of meningioma. J Neurooncol 99:307–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0386-3
Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P et al (2021) The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Neurooncology 23:1231–1251. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noab106
Islim AI, Kolamunnage-Dona R, Mohan M et al (2020) A prognostic model to personalize monitoring regimes for patients with incidental asymptomatic meningiomas. Neurooncology 22:278–289. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noz160
Buerki RA, Horbinski CM, Kruser T et al (2018) An overview of meningiomas. Future Oncol 14:2161–2177. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2018-0006
Jenkinson MD, Weber DC, Haylock BJ et al (2015) Atypical meningoma: current management dilemmas and prospective clinical trials. J Neurooncol 121:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1620-1
Pechlivanis I, Wawrzyniak S, Engelhardt M, Schmieder K (2011) Evidence level in the treatment of meningioma with focus on the comparison between surgery versus radiotherapy. A review. J Neurosurg Sci 55:319–328
Goldbrunner R, Stavrinou P, Jenkinson MD et al (2021) EANO guideline on the diagnosis and management of meningiomas. Neurooncology 23:1821–1834. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noab150
Mohan R (2022) A review of proton therapy– current status and future directions. Precision Radiation Oncol 6:164–176. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro6.1149
Dutz A, Agolli L, Bütof R et al (2020) Neurocognitive function and quality of life after proton beam therapy for brain tumour patients. Radiother Oncol 143:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2019.12.024
Florijn MA, Sharfo AWM, Wiggenraad RGJ et al (2020) Lower doses to hippocampi and other brain structures for skull-base meningiomas with intensity modulated proton therapy compared to photon therapy. Radiother Oncol 142:147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2019.08.019
Mizumoto M, Oshiro Y, Tsuboi K (2013) Proton Beam therapy for intracranial and skull base tumors. Translational Cancer Res 2
Vernimmen F (2016) Intracranial Stereotactic Radiation Therapy with Charged particle beams: an opportunity to regain the Momentum. Int J Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 95:52–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.10.016
Ahmed SK, Brown PD, Foote RL (2018) Protons vs Photons for Brain and Skull Base tumors. Semin Radiat Oncol 28:97–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semradonc.2017.11.001
Hug EB, Devries A, Thornton AF et al (2000) Management of atypical and malignant meningiomas: role of high-dose, 3D-conformal radiation therapy. J Neurooncol 48:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1006434124794
Walcott BP, Nahed BV, Brastianos PK, Loeffler JS (2013) Radiation Treatment for WHO Grade II and III meningiomas. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2013.00227. Front Oncol 3:
Mayo C, Yorke E, Merchant TE (2010) Radiation Associated Brainstem Injury. Int J Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 76:S36–S41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.08.078
Mayo C, Martel MK, Marks LB et al (2010) Radiation dose–volume effects of Optic nerves and Chiasm. Int J Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 76:S28–S35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1753
(2017) Common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE)
Vlachogiannis P, Gudjonsson O, Montelius A et al (2017) Hypofractionated high-energy proton-beam irradiation is an alternative treatment for WHO grade I meningiomas. Acta Neurochir 159:2391–2400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3352-4
El Shafie RA, Czech M, Kessel KA et al (2018) Clinical outcome after particle therapy for meningiomas of the skull base: toxicity and local control in patients treated with active rasterscanning. Radiat Oncol 13:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-018-1002-5
Holtzman AL, Glassman GE, Dagan R et al (2023) Long-term outcomes of fractionated proton beam therapy for benign or radiographic intracranial meningioma. J Neurooncol 161:481–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04207-0
Krcek R, Leiser D, García-Marqueta M et al (2023) Long Term Outcome and Quality of Life of Intracranial Meningioma Patients Treated with Pencil Beam scanning Proton Therapy. Cancers 15:3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123099
Weber DC, Bizzocchi N, Bolsi A, Jenkinson MD (2020) Proton Therapy for Intracranial Meningioma for the treatment of Primary/Recurrent Disease Including Re-irradiation. Front Oncol 10:558845. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.558845
Gondi V, Deshmukh S, Brown PD et al (2018) Preservation of neurocognitive function (NCF) with conformal avoidance of the Hippocampus during whole-brain radiotherapy (HA-WBRT) for brain metastases: preliminary results of Phase III Trial NRG oncology CC001. Int J Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 102:1607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.08.056
Gondi V, Hermann BP, Mehta MP, Tomé WA (2012) Hippocampal Dosimetry predicts neurocognitive function impairment after fractionated stereotactic Radiotherapy for Benign or Low-Grade Adult Brain tumors. Int J Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 83:e487–e493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.10.021
Murray FR, Snider JW, Bolsi A et al (2017) Long-term clinical outcomes of Pencil Beam scanning Proton Therapy for Benign and Non-benign Intracranial meningiomas. Int J Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 99:1190–1198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.08.005
O’Connor KP, Algan O, Vesely SK et al (2019) Factors Associated with Treatment failure and radiosurgery-related Edema in WHO Grade 1 and 2 Meningioma patients receiving Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. World Neurosurg 130:e558–e565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.06.152
Kaprealian T, Raleigh DR, Sneed PK et al (2016) Parameters influencing local control of meningiomas treated with radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 128:357–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2121-1
Przybylowski CJ, Raper DMS, Starke RM et al (2015) Stereotactic radiosurgery of meningiomas following resection: predictors of progression. J Clin Neurosci 22:161–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2014.07.028
Aboukais R, Zairi F, Lejeune J-P et al (2015) Grade 2 meningioma and radiosurgery. JNS 122:1157–1162. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.9.JNS14233
McDonald MW, Plankenhorn DA, McMullen KP et al (2015) Proton therapy for atypical meningiomas. J Neurooncol 123:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1770-9
Wenkel E, Thornton AF, Finkelstein D et al (2000) Benign meningioma: partially resected, biopsied, and recurrent intracranial tumors treated with combined proton and photon radiotherapy. Int J Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 48:1363–1370. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3016(00)01411-5
Labuschagne JJ, Chetty D (2019) Glioblastoma Multiforme as a secondary malignancy following stereotactic radiosurgery of a meningioma: case report. NeuroSurg Focus 46:E11. https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.3.FOCUS1948
Gosztonyi G, Slowik F, Pásztor E (2004) Intracranial meningiomas develo** at Long intervals following low-dose X-Ray irradiation of the Head. J Neurooncol 70:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEON.0000040812.19235.d1
Coggins WS, Pham NK, Nguyen AV et al (2019) A systematic review of Ion Radiotherapy in maintaining local control regarding atypical and anaplastic meningiomas. World Neurosurg 132:282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.08.149
Wu A, ** MC, Meola A et al (2019) Efficacy and toxicity of particle radiotherapy in WHO grade II and grade III meningiomas: a systematic review. NeuroSurg Focus 46:E12. https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.3.FOCUS1967
Qiu X, Gao J, Hu J et al (2023) Particle beam radiotherapy in the treatment of WHO grade 2 and 3 meningiomas: an early experience from Shanghai Proton and Heavy Ion Center. J Neurooncol 165:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-023-04401-8
Weber DC, Ares C, Villa S et al (2018) Adjuvant postoperative high-dose radiotherapy for atypical and malignant meningioma: a phase-II parallel non-randomized and observation study (EORTC 22042–26042). Radiother Oncol 128:260–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2018.06.018
Rogers CL, Won M, Vogelbaum MA et al (2020) High-risk Meningioma: initial outcomes from NRG Oncology/RTOG 0539. Int J Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 106:790–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.11.028
Kaur G, Sayegh ET, Larson A et al (2014) Adjuvant radiotherapy for atypical and malignant meningiomas: a systematic review. Neurooncology 16:628–636. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nou025
Porra L, Seppälä T, Wendland L et al (2022) Accelerator-based boron neutron capture therapy facility at the Helsinki University Hospital. Acta Oncol 61:269–273. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2021.1979646
Suzuki M (2020) Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT): a unique role in radiotherapy with a view to entering the accelerator-based BNCT era. Int J Clin Oncol 25:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01480-4
Monti Hughes A (2022) Importance of radiobiological studies for the advancement of boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Expert Rev Mol Med 24:e14. https://doi.org/10.1017/erm.2022.7
Nikitaki Z, Velalopoulou A, Zanni V et al (2022) Key biological mechanisms involved in high-LET radiation therapies with a focus on DNA damage and repair. Expert Rev Mol Med 24:e15. https://doi.org/10.1017/erm.2022.6
Nakahara Y, Ito H, Masuoka J, Abe T (2020) Boron Neutron capture Therapy and Photodynamic Therapy for High-Grade meningiomas. Cancers 12:1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051334
Cheng X, Li F, Liang L (2022) Boron Neutron capture Therapy: clinical application and Research Progress. Curr Oncol 29:7868–7886. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100622
Lan T-L, Lin C-F, Lee Y-Y et al (2023) Advances in Boron Neutron capture Therapy (BNCT) for recurrent intracranial meningioma. IJMS 24:4978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054978
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Data collection was performed by AI, GR, LC, SM, LT, MC. Statistical analysis was conducted by GF. Results were interpreted by AI, GR, SL, LC, GF, EO. The first draft of the manuscript was written by AI, GR, LC, GF, EO, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Pavia (Date November 15, 2022 / No CNAO OSS 54 2022).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Iannalfi, A., Riva, G., Lillo, S. et al. Proton therapy for intracranial meningioma: a single-institution retrospective analysis of efficacy, survival and toxicity outcomes. J Neurooncol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-024-04751-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-024-04751-x