Abstract
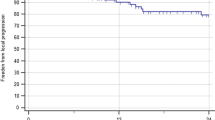
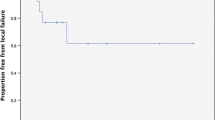
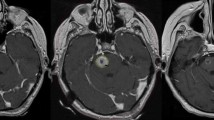
To review the safety and efficacy of linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for brainstem metastases. We reviewed all patients with brain metastases treated with SRS at DF/BWCC from 2001 to 2009 to identify patients who had SRS to a single brainstem metastasis. Overall survival and freedom-from-local failure rates were calculated from the date of SRS using the Kaplan–Meier method. Prognostic factors were evaluated using the log-rank test and Cox proportional hazards model. A total of 24 consecutive patients with brainstem metastases had SRS. At the time of SRS, 21/24 had metastatic lesions elsewhere within the brain. 23/24 had undergone prior WBRT. Primary diagnoses included eight NSCLC, eight breast cancer, three melanoma, three renal cell carcinoma and two others. Median dose was 13 Gy (range, 8–16). One patient had fractionated SRS 5 Gy ×5. Median target volume was 0.2 cc (range, 0.02–2.39). The median age was 57 years (range, 42–92). Follow-up information was available in 22/24 cases. At the time of analysis, 18/22 patients (82%) had died. The median overall survival time was 5.3 months (range, 0.8–21.1 months). The only prognostic factor that trended toward statistical significance for overall survival was the absence of synchronous brain metastasis at the time of SRS; 1-year overall survival was 31% with versus 67% without synchronous brain metastasis (log rank P = 0.11). Non-significant factors included primary tumor histology and status of extracranial disease (progressing vs. stable/absent). Local failure occurred in 4/22 cases (18%). Actuarial freedom from local failure for all cases was 78.6% at 1 year. RTOG grade 3 toxicities were recorded in two patients (ataxia, confusion). Linac-based SRS for small volume brainstem metastases using a median dose of 13 Gy is associated with acceptable local control and low morbidity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chason JL, Walker FB, Landers JW (1963) Metastatic carcinoma in the central nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. A prospective autopsy study. Cancer 16:781–787
Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT et al (1988) Distribution of brain metastases. Arch Neurol 45:741–744
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L et al (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG 90–05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW et al (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Koyfman SA, Tendulkar RD, Chao ST et al (2010) Stereotactic radiosurgery for single brainstem metastases: the cleveland clinic experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(2):409–414
Lorenzoni JG, Devriendt D, Massager N et al (2009) Brainstem metastases treated with radiosurgery: prognostic factors of survival and life expectancy estimation. Surg Neurol 71:188–195
Kased N, Huang K, Nakamura JL et al (2008) Gamma knife radiosurgery for brainstem metastases: the UCSF experience. J Neuro-oncol 86:195–205
Hussain A, Brown PD, Stafford SL et al (2007) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brainstem metastases: survival, tumor control, and patient outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67:521–524
Fuentes S, Delsanti C, Metellus P et al (2006) Brain stem metastases: management using gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 58:37–42
Yen CP, Sheehan J, Patterson G et al (2006) Gamma knife surgery from metastatic brain stem tumors. J Neurosurgery 105:213–219
Shuto T, Fu**o H, Asada H et al (2003) Gamma knife radiosurgery for metastatic tumours in the brain stem. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145:755–760
Huang CF, Kondziolka D, Flickenger JC et al (1999) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain stem metastases. J Neurosurg 91:563–568
Valery CA, Boskos C, Boisserie G et al (2010) Minimized doses for linear accelerator radiosurgery of brainstem metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.02.028
Ramakrishna N, Rosca F, Friesen S et al (2010) A clinical comparison of patient setup and intra-fraction motion using frame-based radiosurgery versus a frameless image-guided radiosurgery system for intracranial lesions. Radiother Oncol 95:109–115
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). European J Cancer Vol 45:228–247
Sheline GE, Wara WM, Smith V (1980) Therapeutic irradiation and brain injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 6:1215–1228
Emami B, Lyman J, Brown A, Coia L, Goitein M, Munzenrider JE et al (1991) Tolerance of normal tissue to therapeutic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 21:109–122
Boden G (1950) Radiation myelitis of the brain stem. J Fac Radiol 2:79–94
Torcuator R, Zuniga R, Mohan YS, Rock J, Doyle T, Anderson J, Gutierrez J, Ryu S, Jain R, Rosenblum M, Mikkelsen T (2009) Initial experience with bevacizumab treatment for biopsy confirmed cerebral radiation necrosis. J Neurooncol 94(1):63–68
Liu AK, Macy ME, Foreman NK (2009) Bevacizumab as therapy for radiation necrosis in four children with pontine gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75(4):1148–1154
Mayo C, Yorke E, Merchant TE (2010) Radiation associated brainstem injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(3 Suppl):S36–S41. Review
Maruyama K, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2004) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brainstem arteriovenous malformations: factors affecting outcome. J Neurosurg 100(3):407–413
Sharma MS, Kondziolka D, Khan A, Kano H, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2008) Radiation tolerance limits of the brainstem. Neurosurgery 63(4):728–732 Discussion 732–733
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortman RD, Carrie C, Hassel MB, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge D, Collette S, Collette L, Mueller RP (2010) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1655
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelly, P.J., Lin, Y.B., Yu, A.Y.C. et al. Linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery for brainstem metastases: the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center experience. J Neurooncol 104, 553–557 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0514-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0514-0