Abstract
Introduction
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is an effective treatment for small and medium-sized meningiomas. Although uncommon, peritumoral edema can develop as a delayed complication after SRS. The purpose of the study was to evaluate the clinical and molecular risk factors for peritumoral edema after SRS for intracranial meningiomas.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the results from 18 patients with intracranial meningiomas who underwent SRS. Tissue was obtained from 14 of these patients who also underwent surgery (13 before SRS). Peritumoral edema, before and after SRS, was estimated using the edema index. Quantitative differences in molecular markers of angiogenesis (VEGF, VRGFr) and hypoxia (HIF-1, GLUT-1, and CA-IX) as well as proliferative indices between patients with and without an elevated edema index after SRS were evaluated.
Results
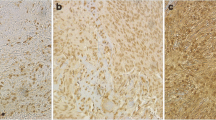
Of the 18 patients studied, symptomatic peritumoral edema developed in three after SRS. They were treated with steroids and one required surgical intervention. The mean time to edema onset was 5.5 months, with an average duration of 16 months. Sagittal sinus occlusion and high-grade histology appear to be more common in the edema group. VEGF and HIF-1 were found in tumors with higher edema index and the elevation of these proteins was correlated with peritumoral edema after SRS. Proliferative index was not predictive for peritumoral edema.
Conclusion
Clinical characteristics and molecular markers may identify patients with meningiomas at risk of peritumoral edema after SRS. Judicious use of steroids or perhaps the use of stereotactic fractionated radiation should be considered in these high-risk patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stafford SL, Pollock BE, Foote RL et al (2001) Meningioma radiosurgery: tumor control, outcomes, and complications among 190 consecutive patients. Neurosurgery 49:1029–1037, discussion 1037–1038
Pollock BE (2003) Stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial meningiomas: indications and results. Neurosurg Focus 14(5):e4
Singh VP, Kansai S, Vaishya S, et al (2000) Early complications following gamma knife radiosurgery for intracranial meningiomas. J Neurosurg 93(Suppl 3):57–61
El Shehaby A, Ganz JC, Reda WA, et al (2005) Temporary symptomatic swelling of meningiomas following gamma knife surgery. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):293–296
El Shehaby A, Ganz JC, Reda WA, et al (2005) Mechanisms of edema after gamma knife surgery for meningiomas–report of two cases. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):1–3
Zagzag D, Zhong H, Scalzitti JM, et al (2000) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in brain tumors: association with angiogenesis, invasion, and progression. Cancer 88:2606–2618
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, et al (1991) Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis–correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 324:1–8
Chang JH, Chang JW, Choi JY et al (2003) Complications after gamma knife radiosurgery for benign meningiomas. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:226–230
Kobayashi T, Kida Y, Mori Y (2001) Long-term results of stereotactic gamma radiosurgery of meningiomas. Surg Neurol 55:325–331
Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Perez B (1998) Judicious resection and/or radiosurgery for parasagittal meningiomas: outcomes from a multicenter review–Gamma Knife Meningioma Study Group. Neurosurgery 43:405–414, discussion 413–414
De Salles AA, Hariz M, Bajada CL, et al (1993) Comparison between radiosurgery and stereotactic fractionated radiation for the treatment of brain metastases. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 58:115–118
Acknowledgments
We thank Kristin Kraus for her editorial assistance in preparing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kan, P., Liu, J.K., Wendland, M.M. et al. Peritumoral edema after stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial meningiomas and molecular factors that predict its development. J Neurooncol 83, 33–38 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9294-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-006-9294-y