Abstract
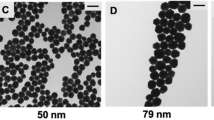
The discovery and development of novel contrast agents for CT imaging could address the current limitations of this non-invasive testing technique, thus improving diagnostic efficiency. Although this approach is significant to clinical research, finding a highly potent and biocompatible contrast agent is challenging. In our study, the homogeneous and monodisperse Au nanospheres were successfully synthesized using chemical reduction. The influence of surfactants, oleylamine (OLA) and sodium oleate (SOA); solvent; and reaction time on the materials’ formation, size, and properties was examined to find the optimal conditions. Investigation showed that using OLA and SOA as surfactants resulted in materials with similar morphology and uniformity. The solvent 1-octadecene (ODE) and reaction time in the 30–60-min range facilitated the formation of uniform and monodisperse gold nanoparticles (GNPs). Characterization indicated that the fabricated Au materials were crystalline and spherical with a face-centered cubic (fcc) structure and an average size of 8.4–20.7 nm. Their maximum surface plasmon resonance (SPR) absorbance varied in the range of 516–531 nm. After surface modification by the poly(maleic anhydride-alt-1-octadecene) (PMAO), the Au NPs were highly stable in a aqueous solution with a zeta potential ranging from − 45.6 to − 42 mV, dynamic light scattering (DLS) size of 17.7 and 26.8 corresponding to the sample size of 8.4 nm and 15.5 nm, respectively. In vitro CT imaging results show that the material Au@PMAO enhanced the CT image contrast signals. Particularly, the smaller GNPs exhibited higher X-ray attenuation than the large ones. At the same investigated concentration, the image contrast performance of the Au@PMAO NPs outweighed that of the commercial product Xenetix, which contained iodine. These outstanding properties prove that the Au@PMAO material is a promising alternative for CT imaging techniques.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on suitable request.
References
Chithrani BD, Ghazani AA, Chan WCW (2006) Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett 6:662–668. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl052396o
Kircher MF, Willmann JK (2012) Molecular body imaging: MR imaging, CT, and US. Part I Principles Radiology 263:633–643. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12102394
Pelc NJ (2014) Recent and future directions in CT imaging. Ann Biomed Eng 42:260–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-0974-z
Reuveni T, Motiei M, Romman Z, Popovtzer A, Popovtzer R (2011) Targeted gold nanoparticles enable molecular CT imaging of cancer: an in vivo study. Int J Nanomedicine 6:2859–2864. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s25446
Lusic H, Grinstaff MW (2013) X-ray-computed tomography contrast agents. Chem Rev 113:1641–1666. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200358s
Bernstein AL, Dhanantwari A, Jurcova M, Cheheltani R, Naha PC, Ivanc T, Shefer E, Cormode DP (2016) Improved sensitivity of computed tomography towards iodine and gold nanoparticle contrast agents via iterative reconstruction methods. Sci Rep 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26177
Cormode DP, Naha PC, Fayad ZA (2014) Nanoparticle contrast agents for computed tomography: a focus on micelles. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 9:37–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmmi.1551
Ashton JR, West JL, Badea CT (2015) In vivo small animal micro-CT using nanoparticle contrast agents. Front Pharmacol 6:1–22. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00256
Ghann WE, Aras O, Fleiter T, Daniel MC (2012) Syntheses and characterization of lisinopril-coated gold nanoparticles as highly stable targeted CT contrast agents in cardiovascular diseases. Langmuir 28:10398–10408. https://doi.org/10.1021/la301694q
Boote E, Fent G, Kattumuri V, Casteel S, Katti K, Chanda N, Kannan R, Katti K, Churchill R (2010) Gold nanoparticle contrast in a phantom and juvenile swine. Acad Radiol 17:410–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2010.01.006
Shilo M, Reuveni T, Motiei M, Popovtzer R (2012) Nanoparticles as computed tomography contrast agents: current status and future perspectives”. Nanomedicine 7:257–269. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.11.190
Daniel MC, Astruc D (2004) Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology. Catalysis, and Nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr030698+
Naha PC, Chhour P, Cormode DP (2015) Systematic in vitro toxicological screening of gold nanoparticles designed for nanomedicine applications. Toxicol Vitr 29:1445–1453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2015.05.022
Dung NT, Linh NTN, Chi DL, Hoa NTH, Hung NP, Ha NT, Nam PH, Phuc NX, Tam LT, Le TLu (2021) Optical properties and stability of small hollow gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv 11:13458–13465. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra09417j
Rabin O, Perez JM, Grimm J, Wojtkiewicz G, Weissleder R (2006) An X-ray computed tomography imaging agent based on long-circulating bismuth sulphide nanoparticles. Nat Mater 5:118–122. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1571
Yu SB, Watson AD (1999) Metal-based X-ray contrast media. Chem Rev 99:2353–2377. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr980441p
Pannu HK, Thompson RE, Phelps J, Magee CA, Fishman EK (2005) Optimal contrast agents for vascular imaging on computed tomography: iodixanol versus iohexol. Acad Radiol 12:576–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2005.01.015
Voert CEM, Kour RYN, Teeffelen BCJ, Ansari N, Stok KS (2020) Contrast-enhanced micro-computed tomography of articular cartilage morphology with ioversol and iomeprol. J Anat 237:1062–1071. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.13271
Oliva MR, Erturk SM, Ichikawa T, Rocha T, Ros PR, Silverman SG, Mortele KJ (2012) Gastrointestinal tract wall visualization and distention during abdominal and pelvic multidetector ct with a neutral barium sulphate suspension: comparison with positive barium sulphate suspension and with water. JBR–BTR. 95, 237–242. https://doi.org/10.5334/jbr-btr.628
Cormode DP, Jarzyna PA, Mulder WJM, Fayad ZA (2012) Modified natural nanoparticles as contrast agents for medical imaging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2009.11.005
Hsu JC, Nieves LM, Betzer O, Sadan T, Noël PB, Popovtzer R, Cormode DP (2021) Nanoparticle contrast agents for X-ray imaging applications. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 12(6):e1642. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1642.Nanoparticle
Cochran ST (2005) Anaphylactoid reactions to radiocontrast media Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep 5:28–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-005-0051-7
Mruk B (2016) Renal safety of iodinated contrast media depending on their osmolarity - current outlooks. Polish J Radiol 81:157–165. https://doi.org/10.12659/PJR.895406
Hainfeld JF, Slatkin DN, Focella TM, Smilowitz HM (2006) Gold nanoparticles: a new X-ray contrast agent. Br J Radiol 79:248–253. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/13169882
Cormode DP, Cormode DP, Skajaa T, Schooneveld MM, Koole R, Jarzyna P, Lobatto ME, Calcagno C, Barazza A, Gordon RE, Zanzonico P, Fisher EA, Fayad ZA, Mulder WJM (2008) Nanocrystal core high-density lipoproteins- a multimodality contrast agent platform. Nano. Lett. 8:3715–3723. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl801958b
Peng C, Zheng L, Chen Q, Shen M, Guo R, Wang H, Cao X, Zhang G, Shi X (2012) PEGylated dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles for in vivo blood pool and tumor imaging by computed tomography. Biomaterials 33:1107–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.10.052
Jackson PA, Rahman WNWA, Wong CJ, Ackerly T, Geso M (2010) Potential dependent superiority of gold nanoparticles in comparison to iodinated contrast agents. Eur J Radiol 75:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.03.057
Lee DE, Koo H, Sun IC, Ryu JH, Kim K, Kwon IC (2012) Multifunctional nanoparticles for multimodal imaging and theragnosis. Chem Soc Rev 41:2656–2672. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs15261d
Cai QY, Kim SH, Choi KS, Kim SY, Byun SJ, Kim KW, Park SH, Juhng SK, Yoon KH (2007) Colloidal gold nanoparticles as a blood-pool contrast agent for x-ray computed tomography in mice. Invest Radiol 42:797–806. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0b013e31811ecdcd
Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC (2014) Long-circulating and target-specific nanoparticles : theory to practice. Pharmacol Rev. 2001, 53, 283–318. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/11980988_Long-Circulating_and_Target-Specific_Nanoparticles_Theory_to_Practice
Eck W, Nicholson AI, Zentgraf H, Semmler W, Bartling S (2010) Anti-CD4-targeted gold nanoparticles induce specific contrast enhancement of peripheral lymph nodes in X-ray computed tomography of live mice. Nano Lett 10:2318–2322. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl101019s
Chenjie X, Tung GA, Shouheng S (2008) Size and concentration effect of gold nanoparticles on X-ray attenuation as measured on computed tomography. Chem Mater 20:4167–4169. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm8008418
Fang Y, Peng C, Guo R, Zheng L, Qin J, Zhou B, Shen M, Lu X, Zhang G, Shi X (2013) Dendrimer-stabilized bismuth sulfide nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and potential computed tomography imaging applications. Analyst 138:3172–3180. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an00237c
**ao YD, Paudel R, Liu J, Ma C, Zhang ZS, Zhou SK (2016) MRI contrast agents: classification and application (Review). Int J Mol Med 38:1319–1326. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2744
Thomsen HS (2006) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a serious late adverse reaction to gadodiamide. Eur Radiol 16:2619–2621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0495-8
Hajfathalian M, Amirshaghaghi A, Naha PC, Chhour P, Hsu JC, Douglas K, Dong Y, Sehgal CM, Tsourkas A, Neretina S, Cormode DP (2018) Wulff in a cage gold nanoparticles as contrast agents for computed tomography and photoacoustic imaging. Nanoscale 10:18749–18757. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr05203d
Cole LE, Ross RD, Tilley JM, Vargo-Gogola T, Roeder RK (2015) Gold nanoparticles as contrast agents in X-ray imaging and computed tomography. Nanomedicine 10:321–341. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.14.171
Oumano M, Russell L, Salehjahromi M, Shanshan L, Sinha N, Ngwa W, Yu H (2021) CT imaging of gold nanoparticles in a human-sized phantom. J Appl Clin Med Phys 22:337–342. https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.13155
Mieszawska AJ, Mulder WJM, Fayad ZA, Cormode DP (2013). Mol. Pharmaceutics. 10, 831–847
Kiessling F, Pichler BJ, Hauff P (2017) Small animal imaging. Springer Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-42202-2
Haiss W, Thanh NTK, Aveyard J, Fernig DG (2007) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-Vis spectra. Anal Chem 79:4215–4221. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac0702084
Dong YC, Hajfathalian M, Maidment PSN, Hsu JC, Naha PC, Si-Mohamed S, Breuilly M, Kim J, Chhour P, Douek P, Litt HI, Cormode DP (2019) Effect of gold nanoparticle size on their properties as contrast agents for computed tomography. Sci. Rep. 9:14912. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50332-8
Chhour P, Kim J, Benardo B, Tovar A, Mian S, Litt HI, Ferrari VA, Cormode DP (2017) Effect of gold nanoparticle size and coating on labeling monocytes for CT tracking. Bioconjugate Chem 28:260–269. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00566
Khademi S, Sarkara S, Kharrazid S, Aminie SM, Zadehf AS, Ay MR, Ghadiri H (2017) Evaluation of size, morphology, concentration, and surface effect of gold nanoparticles on X-ray attenuation in computed tomography. Phys Medica 45:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.12.001
Y Dou Y Guo X Li X Li S Wang L Wang G Lv X Zhang H Wang X Gong and, 2016 J Chang Size-tuning ionization to optimize gold nanoparticles for simultaneous enhanced CT imaging and radiotherapy ACS Nano 10 2536 2548 https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b07473
Ross RD, Cole LE, Tilley JMR, Roeder RK (2014) Effects of functionalized gold nanoparticle size on X-ray attenuation and substrate binding affinity. Chem Mater 26:1187–1194. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm4035616
Hirn S, Behnke MS, Schleh C, Wenk A, Lipka J, Schäffler M, Takenaka S, Möller W, Schmid G, Simon U, Kreyling WG (2011) Particle size-dependent and surface charge-dependent biodistribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 77:407–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2010.12.029
Takeuchi I, Nobata S, Oiri N, Tomoda K, Makino K (2017) Biodistribution and excretion of colloidal gold nanoparticles after intravenous injection: effects of particle size. Biomed Mater Eng 28:315–323. https://doi.org/10.3233/BME-171677
Fratoddi I, Venditti I, Cametti C, Russo MV (2017) Gold nanoparticles and gold nanoparticle-conjugates for delivery of therapeutic molecules. Progress and challenges. J Mater Chem B 2:4204–4220. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tb00383g
Lu LT, Dung NT, Tung LD, Thanh CT, Quy OK, Chuc NV, Maenosono S, Thanh NTK (2015) Synthesis of magnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with controlled morphology, monodispersity and composition: the influence of solvent, surfactant, reductant and synthetic conditions. Nanoscale 7:19596–19610. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr04266f
Yamashita Y, Miyahara R, Sakamoto K (2017) Emulsion and emulsification technology. Elsevier Inc. Chapter 28, 489–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802005-0.00028-8
Fodjo EK, Canlier A, Kong C, Yurtsever A, Guillaume PL, Patrice FT, Abe M, Tohei T, Sakai A (2018) Facile synthesis route of Au-Ag nanostructures soaked in PEG. Adv Nanoparticles 7:37–45. https://doi.org/10.4236/anp.2018.72004
Novak JP, Feldheim DL (2000) Assembly of phenylacetylene-bridged silver and gold nanoparticle arrays. JACS 122:3979–3980. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja000477a
Kalyan Kamal SS, Vimala J, Sahoo PK, Ghosal P, Ram S, Durai L (2014) A green chemical approach for synthesis of shape anisotropic gold nanoparticles. Int Nano Lett 4:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-014-0109-4
Ha Pham TT, Dien ND, Vu XH (2021) Facile synthesis of silver/gold alloy nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive rhodamine B detection. RSC Adv 11:21475–21488. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra02576g
Losso JN, Khachatryan A, Ogawa M, Godber JS, Shih F (2005) Random centroid optimization of phosphatidylglycerol stabilized lutein-enriched oil-in-water emulsions at acidic pH. Food Chem 92:737–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.12.029
Zhao HY, Liu S, He J, Pan CC, Li H, Zhou ZY, Ding Y, Huo D, Hu Y (2015) Synthesis and application of strawberry-like Fe3O4-Au nanoparticles as CT-MR dual-modality contrast agents in accurate detection of the progressive liver disease. Biomaterials 51:194–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.02.019
Chen Q, Li K, Wen S, Liu H, Peng C, Cai H, Shen M, Zhang G, Shi X (2013) Targeted CT/MR dual mode imaging of tumors using multifunctional dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles. Biomaterials 34:5200–5209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.03.009
Liu H, Li K, Wen S, Liu H, Peng C, Cai H, Shen M, Zhang G, Shi X (2013) Targeted tumor computed tomography imaging using low-generation dendrimer-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Chem - A Eur J 19:6409–6416. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201204612
Li J, Zheng L, Cai H, Sun W, Shen M, Zhang G, Shi X (2013) Facile one-pot synthesis of Fe3O4@Au composite nanoparticles for dual-mode MR/CT imaging applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:10357–10366. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4034526
**ao T, Wen S, Wang H, Liu H, Shen M, Zhao J, Zhang G, Shi X (2013) Facile synthesis of acetylated dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles with enhanced gold loading for CT imaging applications. J Mater Chem B 1:2773–2780. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb20399a
Ajeesh M, Francis BF, Annie J, Varma PRH (2010) Nano iron oxide-hydroxyapatite composite ceramics with enhanced radiopacity. J Mater Sci Mater Med 21:1427–1434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-010-4005-9
Rotello V (2004) Nanoparticles building blocks for nanotechnology nanostructure science and technology. Nanostructure Sci. Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9042-6
Acknowledgements
L. T. Tam is thankful to Vinh University. N. T. N. Linh is grateful to Thai Nguyen University of Sciences, Thai Nguyen University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, L.T.N., Van Vu, H. & Le, T.T. Size-controlled synthesis of gold nanoparticles and related molecular imaging contrast for computed tomography. J Nanopart Res 26, 113 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-024-06024-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-024-06024-0