Abstract
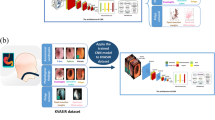
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) recognition is essential for the diagnosis of esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), a highly fatal disease when left untreated at earlier stages of cancer development. General endoscopists often face difficulty in distinguishing BE from reflux esophagitis (RE) due to their resemblance in endoscopic images. This paper proposes a novel framework for the diagnosis of BE and RE in endoscopic images, leveraging deep learning techniques. The proposed framework begins with a localization network that removes interference information and enhances image contrast using histogram equalization. Subsequently, a graph-optimized deep learning (GODL) model is designed for the few-shot classification task. This model consists of two branches: a convolutional neural network (CNN) classification part, incorporating a CNN module for feature representation, and an SVM classifier for classification. Additionally, a graph neural network (GNN) branch is included to capture sample relations and utilize them effectively. The proposed model is trained using a meta-learning strategy and evaluated on endoscopic images obtained from both the **angya Hospital private dataset and the Hyper-Kvasir dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model achieves a 4-classification recognition accuracy of 93.0%, with macro-precision, macro-recall, and macro-F scores of 93.5%, 92.9%, and 93.2%, respectively. Importantly, our model’s performance is comparable to that of experienced endoscopists. These promising results suggest that the proposed GODL model can serve as a valuable supportive tool for detecting esophageal diseases in clinical settings.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to data privacy but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Coleman HG, **e S-H, Lagergren J (2018) The epidemiology of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 154(2):390–405
Hvid-Jensen F, Pedersen L, Drewes AM, Sørensen HT, Funch-Jensen P (2011) Incidence of adenocarcinoma among patients with barrett’s esophagus. N Engl J Med 365(15):1375–1383
Shaheen NJ, Falk GW, Iyer PG, Gerson LB (2016) Acg clinical guideline: diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus. Am Coll Gastroenterol 111(1):30–50
Anaparthy R, Sharma P (2014) Progression of barrett oesophagus: role of endoscopic and histological predictors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(9):525–534
Maret-Ouda J, Markar SR, Lagergren J (2020) Gastroesophageal reflux disease: a review. Jama 324(24):2536–2547
Mastracci L, Grillo F, Parente P, Unti E, Battista S, Spaggiari P, Campora M, Scaglione G, Fassan M, Fiocca R (2020) Gastro-esophageal reflux disease and barrett’s esophagus: an overview with an histologic diagnostic approach. Pathologica 112(3):117
Sebastianelli L, Benois M, Vanbiervliet G, Bailly L, Robert M, Turrin N, Gizard E, Foletto M, Bisello M, Albanese A et al (2019) Systematic endoscopy 5 years after sleeve gastrectomy results in a high rate of barrett’s esophagus: results of a multicenter study. Obes Surg 29(5):1462–1469
de Souza Jr LA, Passos LA, Mendel R, Ebigbo A, Probst A, Messmann H, Palm C, Papa JP (2020) Assisting barrett’s esophagus identification using endoscopic data augmentation based on generative adversarial networks. Comput Biol Med 126:104029
Mendel R, Ebigbo A, Probst A, Messmann H, Palm C (2017) Barrett’s esophagus analysis using convolutional neural networks. In: Bildverarbeitung Für die Medizin 2017. Springer, pp 80– 85
de Souza Jr LA, Palm C, Mendel R, Hook C, Ebigbo A, Probst A, Messmann H, Weber S, Papa JP (2018) A survey on Barrett’s esophagus analysis using machine learning. Comput Biol Med 96:203–213
Takenaka K, Ohtsuka K, Fujii T, Negi M, Suzuki K, Shimizu H, Oshima S, Akiyama S, Motobayashi M, Nagahori M et al (2020) Development and validation of a deep neural network for accurate evaluation of endoscopic images from patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology
Gong EJ, Bang CS, Jung K, Kim SJ, Kim JW, Seo SI, Lee U, Maeng YB, Lee YJ, Lee JI et al (2022) Deep-learning for the diagnosis of esophageal cancers and precursor lesions in endoscopic images: A model establishment and nationwide multicenter performance verification study. J Pers Med 12(7):1052
Kusano C, Singh R, Lee YY, Soh YSA, Sharma P, Ho K-Y, Gotoda T (2022) Global variations in diagnostic guidelines for Barrett’s esophagus. Dig Endosc
Ma H, Wang L, Chen Y, Tian L et al (2022) Convolutional neural network-based artificial intelligence for the diagnosis of early esophageal cancer based on endoscopic images: A meta-analysis. Saudi J Gastroenterol 28(5):332
Ohmori M, Ishihara R, Aoyama K, Nakagawa K, Iwagami H, Matsuura N, Shichijo S, Yamamoto K, Nagaike K, Nakahara M et al (2020) Endoscopic detection and differentiation of esophageal lesions using a deep neural network. Gastrointest Endosc 91(2):301–309
Faghani S, Codipilly DC, Vogelsang D, Moassefi M, Rouzrokh P, Khosravi B, Agarwal S, Dhaliwal L, Katzka DA, Hagen C et al (2022) Development of a deep learning model for the histological diagnosis of dysplasia in barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc
Dumoulin FL, Rodriguez-Monaco FD, Ebigbo A, Steinbrück I (2022) Artificial intelligence in the management of barrett’s esophagus and early esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancers 14(8):1918
Ghatwary N, Ye X, Zolgharni M (2019) Esophageal abnormality detection using densenet based faster r-cnn with gabor features. IEEE Access 7:84374–84385
Struyvenberg MR, De Groof AJ, van der Putten J, van der Sommen F, Baldaque-Silva F, Omae M, Pouw R, Bisschops R, Vieth M, Schoon EJ et al (2021) A computer-assisted algorithm for narrow-band imaging-based tissue characterization in barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 93(1):89–98
Salehi AW, Khan S, Gupta G, Alabduallah BI, Almjally A, Alsolai H, Siddiqui T, Mellit A (2023) A study of cnn and transfer learning in medical imaging: Advantages, challenges, future scope. Sustainability 15(7):5930
Yao X, Wang X, Wang S-H, Zhang Y-D (2022) A comprehensive survey on convolutional neural network in medical image analysis. Multimed Tools Appl 81(29):41361–41405
Ahmed MB (2020) An efficient algorithm for medical image classification using deep convolutional network: Case of cancer pathology. In: NISS2020
Abraham B, Nair MS (2020) Computer-aided detection of covid-19 from x-ray images using multi-cnn and bayesnet classifier. Biocybern Biomed Eng 40(4):1436–1445
Sali R, Moradinasab N, Guleria S, Ehsan L, Fernandes P, Shah TU, Syed S, Brown DE (2020) Deep learning for whole-slide tissue histopathology classification: A comparative study in the identification of dysplastic and non-dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus. J Pers Med 10(4):141
Li Z, Feng X, Wu Z, Yang C, Bai B, Yang Q (2019) Classification of atrial fibrillation recurrence based on a convolution neural network with svm architecture. IEEE Access 7:77849–77856
Wang Z, Meng Y, Weng F, Chen Y, Lu F, Liu X, Hou M, Zhang J (2020) An effective cnn method for fully automated segmenting subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue on ct scans. Ann Biomed Eng 48(5)
Wang Z, **ao Y, Li Y, Zhang J, Lu F, Hou M, Liu X (2020) Automatically discriminating and localizing covid-19 from community-acquired pneumonia on chest x-rays. Pattern Recogn 110:107613
Radak M, Lafta HY, Fallahi H (2023) Machine learning and deep learning techniques for breast cancer diagnosis and classification: a comprehensive review of medical imaging studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 1–19
Wang Z, **ao Y, Weng F, Li X, Meng Y (2021) R-jaunlab: Automatic multi-class recognition of jaundice on photos of subjects with region annotation networks. J Dig Imaging 9
Murata M, Usami H, Iwahori Y, Aili W (2017) Polyp classification using multiple cnn-svm classifiers from endoscope images. In: The Ninth International Conferences on Pervasive Patterns and Applications, pp. 109– 112
Waikhom L, Patgiri R (2023) A survey of graph neural networks in various learning paradigms: methods, applications, and challenges. Artif Intell Rev 56(7):6295–6364
Li X, Yang X, Ma Z, Xue J-H (2023) Deep metric learning for few-shot image classification: A review of recent developments. Pattern Recognit 109381
Yu T, He S, Song Y-Z, **ang T (2022) Hybrid graph neural networks for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol. 36. pp 3179– 3187
Kim J, Kim T, Kim S, Yoo CD (2019) Edge-labeling graph neural network for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 11– 20
Zhao K, Zhang Z, Jiang B, Tang J (2022) Lglnn: Label guided graph learning-neural network for few-shot learning. Neural Netw 155:50–57
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 770– 778
Qilong W, Banggu W, Pengfei Z, Peihua L, Wangmeng Z, Qinghua H (2020) Eca-net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks 2020 ieee. In: CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
Guo Y, Ma Z, Li X, Dong Y (2021) Tlrm: Task-level relation module for gnn-based few-shot learning. In: 2021 International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP). IEEE, pp 1– 5
Borgli H, Thambawita V, Smedsrud PH, Hicks S, Jha D, Eskeland SL, Randel KR, Pogorelov K, Lux M, Nguyen DTD et al (2020) Hyperkvasir, a comprehensive multi-class image and video dataset for gastrointestinal endoscopy. Scientific Data 7(1):1–14
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R (2018) Mask r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp 2961– 2969
Cai L, Long T, Dai Y, Huang Y (2020) Mask r-cnn-based detection and segmentation for pulmonary nodule 3d visualization diagnosis. IEEE Access 8:44400–44409
Yu X, Pang W, Xu Q, Liang M (2020) Mammographic image classification with deep fusion learning. Sci Rep 10(1):1–11
Jenifer S, Parasuraman S, Kadirvelu A (2016) Contrast enhancement and brightness preserving of digital mammograms using fuzzy clipped contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 42:167–177
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. ar**v:1409.1556
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z (2016) Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 2818– 2826
Yang L, Li L, Zhang Z, Zhou X, Zhou E, Liu Y (2020) Dpgn: Distribution propagation graph network for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 13390– 13399
Mubarak D et al (2022) Classification of early stages of esophageal cancer using transfer learning. IRBM 43(4):251–258
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province China under Grants 2022JJ30673.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, M., Wang, J., Liu, T. et al. A graph-optimized deep learning framework for recognition of Barrett’s esophagus and reflux esophagitis. Multimed Tools Appl (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-024-18910-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-024-18910-9