Abstract
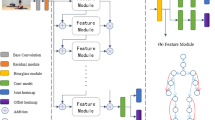
In this paper, we explore multi-level semantic information of human body structure and propose a paradigm for bottom-up multi-person pose estimation. To represent the multi-level semantic body structure, we define a Spatial Hierarchical Body Tree (SHBT) that encodes the location and association information of the body center, parts, and joints for each human instance. This encoding approach assists in associating joints to each human instance, and the multi-level form is suitable for handling cases of partial human body occlusion. To apply the spatial hierarchical body tree to multi-person pose estimation, we build Hierarchical Pose Net(Heap-net) by inheriting the topology of the SHBT. This Heap-net explicitly defines the corresponding output order and the feature fusion aggregation. Furthermore, we propose a shared filters spatial pyramid module, which consists of a multi-branches dilation convolution module with shared filters and a max-out activation, to alleviate the effect of a wide range of human scale. To verify the effectiveness of our model, we conduct experiments on the MSCOCO keypoints detection validation and test set. The experimental results are comparable to the previous bottom-up multi-person pose estimation methods.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Cao Z, Simon T, Wei S-E, Sheikh Y (2016) Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. ar**v:1611.08050 [cs]
Carreira J, Agrawal P, Fragkiadaki K, Malik J (2016) Human pose estimation with iterative error feedback. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 4733–4742
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2017) Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848
Chen Y, Wang Z, Peng Y, Zhang Z, Yu G, Sun J (2017) Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. ar**v:1711.07319 [cs]. Accessed 21 Nov 2017
Chu X, Ouyang W, Li H, Wang X (2016) Structured feature learning for pose estimation. ar**v:1603.09065 [cs]. Accessed 10 Oct 2019
Chu X, Yang W, Ouyang W, Ma C, Yuille AL, Wang X (2017) Multi-context attention for human pose estimation. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 5669–5678
Contributors M (2020) OpenMMLab Pose estimation toolbox and benchmark https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmpose
Corona E, Pumarola A, Alenya G, Moreno-Noguer F (2020) Context-aware human motion prediction, 10
Dai J, Li Y, He K, Sun J (2016) R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks. In: NIPS
Dantone M, Gall J, Leistner C, Gool LV (2013) Human pose estimation using body parts dependent joint regressors. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 3041–3048
Deng J, Zhou Y, Cheng S, Zafeiriou S (2018) Cascade multi-view hourglass model for robust 3d face alignment. 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), 399–403
Fang H, **e S, Tai Y-W, Lu C. (2017) Rmpe: Regional multi-person pose estimation. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) 2353–2362
Fang H, Xu Y, Wang W, Liu X, Zhu S-C (2017) Learning pose grammar to encode human body configuration for 3d pose estimation. ar**v:1710.06513 [cs]. Accessed 10 Sep 2019
Felzenszwalb P, McAllester D, Ramanan D (2008) A discriminatively trained, multiscale, deformable part model. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition. CVPR 2008. IEEE Conference on, pp 1–8. IEEE. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=4587597 Accessed 07 Nov 2015
Fischler MA, Elschlager RA (1973) The representation and matching of pictorial structures. IEEE Trans Comput C-22(1):67–92. https://doi.org/10.1109/T-C.1973.223602
Han J, Pauwels EJ, de Zeeuw PM, de With PHN (2012) Employing a rgb-d sensor for real-time tracking of humans across multiple re-entries in a smart environment. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 58(2):255–263. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2012.6227420
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R (2017) Mask r-CNN. ar**v:1703.06870. Accessed 22 Mar 2017
Hsiao W-L, Katsman I, Wu C-Y, Parikh D, Grauman K (2019) Fashion++: Minimal edits for outfit improvement. ar**v:1904.09261 [cs]. Accessed 13 Oct 2019
Insafutdinov E, Pishchulin L, Andres B, Andriluka M, Schiele B (2016) Deepercut: a deeper, stronger, and faster multi-person pose estimation model. In: ECCV
Kreiss S, Bertoni L, Alahi A (2019) PifPaf: Composite fields for human pose estimation. ar**v:1903.06593 [cs]. Accessed 23 Apr 2019
Lee H-Y, Yang X, Liu M-Y, Wang T-C, Lu Y-D, Yang M-H, Kautz J (2019) Dancing to music. ar**v:1911.02001 [cs]. Accessed 11 Aug 2019
Li W, Wang Z, Yin B, Peng Q, Du Y, **ao T, Yu G, Lu H, Wei Y, Su J (2019) Rethinking on multi-stage networks for human pose estimation. ar**v:1901.00148 [cs]. Accessed 03 Jan 2019
Li J, Wang Y, Zhang S (2023) PolarPose: Single-stage multi-person pose estimation in polar coordinates. IEEE Trans Image Process 32:1108–1119. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2023.3239192
Li C, **e C, Zhang B, Han J, Zhen X, Chen J (2022) Memory attention networks for skeleton-based action recognition. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 33(9):4800–4814. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3061115
Lin T-Y, Dollár P, Girshick RB, He K, Hariharan B, Belongie SJ (2017) Feature pyramid networks for object detection ar**v:1612.03144
Lin T-Y, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollár P, Zitnick CL (2014) Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, pp 740–755
Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed SE, Fu C-Y, Berg AC (2016) SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector. In: ECCV
Liu Z, Yan S, Luo P, Wang X, Tang X (2016) Fashion landmark detection in the wild. ar**v:1608.03049 [cs]. Accessed 16 Jan 2018
Liu Y, Zhang D, Zhang Q, Han J (2022) Part-object relational visual saliency. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(7):3688–3704. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3053577
Ma L, Sun Q, Jia X, Schiele B, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L (2017) Pose guided person image generation. ar**. ar** keypoints for multi-person pose estimation using instance-aware attention. Pattern Recognit 136:109232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2022.109232
Zhang H, Ouyang H, Liu S, Qi X, Shen X, Yang R, Jia J (2019) Human pose estimation with spatial contextual information. ar**v:1901.01760 [cs]. Accessed 09 Jan 2019
Zhang B, Yang Y, Chen C, Yang L, Han J, Shao L (2017) Action recognition using 3d histograms of texture and a multi-class boosting classifier. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(10):4648–4660. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2718189
Zhang J, Zhu Z, Zou W, Li P, Li Y, Su H, Huang G (2019) FastPose: Towards real-time pose estimation and tracking via scale-normalized multi-task networks ar**v:1908.05593 [cs]. Accessed 02 Sep 2019
Zhou X, Wang D, Krähenbühl P (2019) Objects as points. ar**v:1904.07850 [cs]. Accessed 17 Apr 2019
Zhu Z, Huang T, Shi B, Yu M, Wang B, Bai X (2022) Progressive and Aligned Pose Attention Transfer for Person Image Generation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(8):4306–4320. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3068236
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2021ZD0110901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Yao, H. & Hou, Y. Hierarchical pose net: spatial hierarchical body tree driven multi-person pose estimation. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 6373–6392 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15320-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15320-1