Abstract
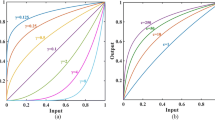
We propose an efficient low-light image enhancement algorithm based on an optimization-based approach for gamma correction parameter estimation. We first separate an input color image into the luminance and chrominance channels, and then normalize the luminance channel using the logarithmic function to make it consistent with the human perception. Then, we divide the luminance image into dark and bright regions, and estimate the optimal gamma correction parameter for each region independently. Specifically, based on the statistical properties of the input image, we formulate a convex optimization problem that maximizes the image contrast subject to the constraint on the gamma value. By efficiently solving the optimization problems using the convex optimization theories, we obtain the optimal gamma parameter for each region. Finally, we obtain an enhanced image by merging the independently enhanced dark and bright regions with the optimal gamma parameters. Experimental results on real-world images demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can provide higher enhancement performance than state-of-the-art algorithms in terms of both subjective and objective evaluations, while providing a substantial improvement in speed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agaian SS, Silver B, Panetta KA (2007) Transform coefficient histogram-based image enhancement algorithms using contrast entropy. IEEE Trans Image Process 16(3):741–758
Arici T, Dikbas S, Altunbasak Y (2009) A histogram modification framework and its application for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans Image Process 18(9):1921–1935
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L (2004) Convex optimization. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge U.K
Cai J, Gu S, Zhang L (2018) Learning a deep single image contrast enhancer from multi-exposure images. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(4):2049–2062
Celik T (2014) Spatial entropy-based global and local image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(12):5298–5308
Celik T (2016) Spatial mutual information and pagerank-based contrast enhancement and quality-aware relative contrast measure. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(10):4719–4728
Chang Y, Jung C, Ke P, Song H, Hwang J (2018) Automatic contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization with dual gamma correction. IEEE Access 6:11782–11792
Chen C, Chen Q, Xu J, Koltun V (2018) Learning to see in the dark. In: Proc. IEEE conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern recognit., pp 3291–3300
Farid H (2001) Blind inverse gamma correction. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(10):1428–1433
Fu Q, Jung C, Xu K (2018) Retinex-based perceptual contrast enhancement in images using luminance adaptation. IEEE Access 6:61277–61286
Gonzalez RC, Woods R (2007) Digital image processing, third edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA
Guo CG, Li C, Guo J, Loy CC, Hou J, Kwong S, Cong R (2020) Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp 1780–1789
Guo X, Li Y, Ling H (2017) LIME: Low-Light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(2):982–993
Hao S, Feng Z, Guo Y (2018) Low-light image enhancement with a refined illumination map. Multimed Tools Appl 77:29639–29650
Huang S, Cheng F, Chiu Y (2013) Efficient contrast enhancement using adaptive gamma correction with weighting distribution. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(3):1032–1041
Ju M, Ding C, Zhang D, Guo YJ (2018) Gamma-correction-based visibility restoration for single hazy images. IEEE Signal Process Lett 25 (7):1084–1088
Kim D, Kim C (2017) Contrast enhancement using combined 1-D and 2-D histogram-based techniques. IEEE Signal Process Lett 24(6):804–808
Kim YT (1997) Contrast enhancement using brightness preserving bi-histogram equalization. IEEE Trans Consum Electron 43(1):1–8
Lee C, Lam EY (2016) Computationally efficient truncated nuclear norm minimization for high dynamic range imaging. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(9):4145–4157
Lee C, Lam EY (2018) Computationally efficient brightness compensation and contrast enhancement for transmissive liquid crystal displays. J Real-Time Image Process 14(4):733–741
Lee C, Lee C, Kim CS (2013) Contrast enhancement based on layered difference representation of 2D histograms. IEEE Trans Image Process 22 (12):5372–5384
Lee C, Lee C, Lee YY, Kim CS (2012) Power-constrained contrast enhancement for emissive displays based on histogram equalization. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(1):80–93
Lim J, Heo M, Lee C, Kim CS (2017) Contrast enhancement of noisy low-light images based on structure-texture-noise decomposition. J Vis Commun Image Represent 45(5):107–121
Loh YP, Chan CS (2019) Getting to know low-light images with the exclusively dark dataset. Comput Vis Image Understand 178:30–42
Loh YP, Liang X, Chan CS (2019) Low-light image enhancement using Gaussian process for features retrieval. Signal Process Image Commun 74:175–190
Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik AC (2013) Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20(3):209–212
Nocedal J, Wright SJ (2006) Numerical optimization, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, Germany
Park S, Yu S, Kim M, Park K, Paik J (2018) Dual autoencoder network for retinex-based low-light image enhancement. IEEE Access 6:22084–22093
Rahman S, Rahman MM, A-Al-Wadud M, Al-Quaderi GD, Shoyaib M (2016) An adaptive gamma correction for image enhancement. EURASIP J. Image Video Process 2016(35)
Reinhard E, Ward G, Debevec P, Pattanaik S, Heidrich W (2010) High dynamic range imaging: acquisition, display, and image-based Lighting, second edn. Morgan Kaufmann
Ren W, Liu S, Ma L, Xu Q, Xu X, Cao X, Du J, Yang MH (2019) Low-light image enhancement via a deep hybrid network. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(9):4364–4375
Ren X, Yang W, Cheng WH, Liu J (2020) LR3M: Robust low-light enhancement via low-rank regularized retinex model. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:5862–5876
Tan SF, Isa NAM (2019) Exposure based multi-histogram equalization contrast enhancement for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Access 7:70842–70861
Tao L, Zhu C, Song J, Lu T, Jia H, **e X (2017) Low-light image enhancement using CNN and bright channel prior. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Image process., pp. 3215–3219
Wang S, Ma K, Yeganeh H, Wang Z, Lin W (2015) A patch-structure representation method for quality assessment of contrast changed images. IEEE Signal Process Lett 22(12):2387–2390
Yang KF, Li H, Kuang H, Li CY, Li YJ (2019) An adaptive method for image dynamic range adjustment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(3):640–652
Yang W, Wang S, Fang Y, Wang Y, Liu J (2020) From fidelity to perceptual quality: a semi-supervised approach for low-light image enhancement. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp 3063–3072
Yue H, Yang J, Sun X, Wu F, Hou C (2017) Contrast enhancement based on intrinsic image decomposition. IEEE Trans Image Process 26 (8):3981–3994
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea Government (MSIT) (No. NRF-2019R1A2C4069806).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, I., Lee, C. An optimization-based approach to gamma correction parameter estimation for low-light image enhancement. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 18027–18042 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10614-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-10614-8