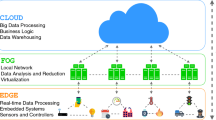
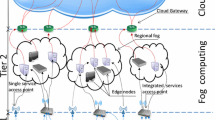
Abstract
In line with digital transformation and the rapid progress on the Internet, technology has led to new hierarchical infrastructures for seamless connectivity. The integrated cloud-fog-edge computing system is a hierarchical infrastructure that provides better operational connectivity for users at all network ends. Lack of mobility management, the requirement for high-speed internet connectivity, limited bandwidth, and security issues are some of the issues that result in poor Quality of Service (QoS) in such environments. Mobility or seamless connectivity of users is one of the main challenging factors in the performance evaluation of an integrated cloud-fog-edge computing system. Hence, to obtain better QoS and support seamless connectivity, new and efficient modelling approaches are necessary. Thus, a stochastic performance model is considered in this paper for QoS analysis. The performance analysis is done to determine the operational space of the proposed model. This gives an idea of how to design and develop more efficient architectures for such systems. The mean queue length, throughput, and mean response time results are examined for performance evaluation. A discrete event simulation is also presented to validate the proposed analytical model.















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not Applicable
References
Qi Q, Tao F (2019) A smart manufacturing service system based on edge computing, fog computing, and cloud computing. IEEE Access 7:86769–86777. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2923610
Wang H, Liu T, Kim B, Lin C-W, Shiraishi S, **e J, Han Z (2020) Architectural design alternatives based on cloud/edge/fog computing for connected vehicles. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 22(4):2349–2377. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2020.3020854
Abbasi M, Yaghoobikia M, Rafiee M, Jolfaei A, Khosravi MR (2020) Efficient resource management and workload allocation in fog-cloud computing paradigm in iot using learning classifier systems. Comput Commun 153:217–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2020.02.017
Yan J, Huang Y, Gupta A, Gupta A, Liu C, Li J, Cheng L (2022) Energy aware systems for real-time job scheduling in cloud data centers: A deep reinforcement learning approach. Comput Electrical Eng 99:107688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.107688
Rahman MA, Tari Z, Zhu D, Piccialli F, Wang X (2020) Ieee access special section editorial: Cloud-fog-edge computing in cyber-physical-socia systems (cpss). IEEE Access 8:222859–222864. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3042584
Rapuzzi R, Repetto M (2018) Building situational awareness for network threats in fog/edge computing: Emerging paradigms beyond the security perimeter model. Future Generation Comput Syst 85:235–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.04.007
Rathi S, Nagpal R, Mehrotra D, Srivastava G (2022) A metric focused performance assessment of fog computing environments: A critical review. Comput Electric Eng 103:108350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.108350
Murtaza F, Akhunzada A, ul Islam S, Boudjadar J, Buyya R, (2020) Qos-aware service provisioning in fog computing. J Netw Comput Appl 165:102674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102674
Jha DN, Alwasel K, Alshoshan A, Huang X, Naha RK, Battula SK, Garg S, Puthal D, James P, Zomaya A, Dustdar S, Ranjan R (2020) Iotsim-edge: A simulation framework for modeling the behavior of internet of things and edge computing environments. Software: Practice and Experience 50(6):844–867. https://arxiv.org/abs/https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/spe.2787. https://doi.org/10.1002/spe.2787
Cavalieri d’Oro E, Colombo S, Gribaudo M, Iacono M, Manca D, Piaz-zolla P (2019) Modeling and evaluating a complex edge computing based systems: An emergency management support system case study. Int Things 6:100054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2019.100054
Ferrández-Pastor F-J, Mora H, Jimeno-Morenilla A, Volckaert B (2018) Deploy-ment of iot edge and fog computing technologies to develop smart building services. Sustainability 10(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/su10113832
Qiu M, Kung S-Y, Gai K (2020) Intelligent security and optimization in edge/-fog computing. Future Generation Comput Syst 107:1140–1142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.06.002
Petrovic N, Tosic M (2020) Smada-fog: Semantic model driven approach to deployment and adaptivity in fog computing. Simul Model Pract Theory 101:102033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2019.102033
Mutlag AA, Abd Ghani MK, Arunkumar N, Mohammed MA, Mohd O (2019) Enabling technologies for fog computing in healthcare iot systems. Future Generation Comput Syst 90:62–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.07.049
Haverkort BR, Marie R, Rubino G, Trivedi KS (2001) Performability Modelling: Techniques and Tools. Wiley, England
Lera I, Guerrero C, Juiz C (2019) Yafs: A simulator for iot scenarios in fog computing. IEEE Access 7:91745–91758
Mechalikh C, Taktak H, Moussa F (2019) Pureedgesim: A simulation toolkit for performance evaluation of cloud, fog, and pure edge computing environments. In: 2019 International Conference on High Performance Computing and Simulation (HPCS), pp. 700–707. https://doi.org/10.1109/HPCS48598.2019.9188059
Puliafito C, Gonçalves DM, Lopes MM, Martins LL, Madeira E, Mingozzi E, Rana O, Bittencourt LF (2020) Mobfogsim: Simulation of mobility and migration for fog computing. Simul Model Pract and Theory 101:102062
Mohan N, Kangasharju J (2016) Edge-fog cloud: A distributed cloud for internet of things computations. In: 2016 Cloudification of the Internet of Things (CIoT), pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/CIOT.2016.7872914
Gupta H, Vahid Dastjerdi A, Ghosh SK, Buyya R (2017) ifogsim: A toolkit for modeling and simulation of resource management techniques in the internet of things, edge and fog computing environments. Softw: Pract Exp 47(9):1275–1296
Gupta H, Vahid Dastjerdi A, Ghosh SK, Buyya R (2017) ifogsim: A toolkit for modeling and simulation of resource management techniques in the internet of things, edge and fog computing environments. Softw: Pract Exp 47(9):1275–1296
Kirsal Y (2018) Analytical modelling and optimization analysis of large-scale communication systems and networks with repairmen policy. Computing 100(5):503–527
Kirsal Y, Ever K, Y, Mapp GE, Raza M, (2021) 3d analytical modelling and iterative solution for high performance computing clusters. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCC.2021.3055119
Fantacci R, Picano B (2020) Performance analysis of a delay constrained data offloading scheme in an integrated cloud-fog-edge computing system. IEEE Trans Vehic Technol 69(10):12004–12014. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2020.3008926
Vilaplana J, Solsona F, Teixidó I, Mateo J, Abella F, Rius J (2015) A queuing model considering resources sharing for cloud service performance. J Supercomput 71(11):4042–4055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-015-1503-z
Battula SK, O’Reilly MM, Garg S, Montgomery J (2021) A generic stochastic model for resource availability in fog computing environments. IEEE Trans Parallel Distributed Syst 32(4):960–974. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2020.3037247
Banks J, Carson II JS, Automation B, Nelson BL, Nicol DM (2004) Discrete-event system simulation fourth edition
Jafarnejad Ghomi E, Rahmani AM, Qader NN (2019) Applying queue theory for modeling of cloud computing: A systematic review. Concurrency Comput: Pract Exp 31(17):51–86
Liu X, Li S, Tong W (2015) A queuing model considering resources sharing for cloud service performance.J Supercomput 71(11):4042–4055. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-015-1503-z
Suresh S, Sakthivel S (2017) A novel performance constrained power management framework for cloud computing using an adaptive node scaling approach. Comput Electrical Eng 60:30–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2017.04.018
Mas L, Vilaplana J, Mateo J (2022) A queuing theory model for fog computing. J Supercomput 78(8):11138–11155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04328-3
Tadakamalla U, Menascé D (2018) Fogqn: An analytic model for fog/cloud computing. In: 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing Companion (UCC Companion), pp. 307–313. https://doi.org/10.1109/UCC-Companion.2018.00073
El Kafhali S, Salah K, Ben Alla S (2018) Performance evaluation of iot-fog-cloud deployment for healthcare services. In: 2018 4th International Conference on Cloud Computing Technologies and Applications (Cloudtech), pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/CloudTech.2018.8713355
Chakka R (1998) Spectral expansion solution for some finite capacity queues. Annals Operations Res 79:27–44
Ever E (2007) Performability modelling of homogenous and heterogeneous multiserver systems with breakdowns and repairs. PhD thesis, Middlesex University
Aldag M, Kirsal Y, Ülker S (2022) An analytical modelling and qos evaluation of fault-tolerant load balancer and web servers in fog computing. J Supercomput 78(10):12136–12158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04345-2
Firouzi F, Farahani B, Marinšek A (2022) The convergence and interplay of edge, fog, and cloud in the ai-driven internet of things (iot). Inf Syst 107:101840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2021.101840
Ma X, Xu H, Gao H, Bian M, Hussain W (2023) Real-time virtual machine scheduling in industry iot network: A reinforcement learning method. IEEE Trans Industrial Informatics 19(2):2129–2139. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2022.3211622
Gao H, Huang W, Liu T, Yin Y, Li Y (2022) Ppo2: Location privacy-oriented task offloading to edge computing using reinforcement learning for intelligent autonomous transport systems. IEEE Trans Intell Transportation Syst 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3169421
Xu Y, Lin J, Gao H, Li R, Jiang Z, Yin Y, Wu Y (2022) Machine learning-driven apps recommendation for energy optimization in green communication and networking for connected and autonomous vehicles. IEEE Trans Green Commun Netw 6(3):543–1552. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGCN.2022.3165262
Gao Y, Guan H, Qi Z, Song T, Huan F, Liu L (2014) Service level agreement based energy-efficient resource management in cloud data centers. Comput Electrical Eng 40(5):1621–1633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2013.11.001
Leontiou N, Dechouniotis D, Denazis S, Papavassiliou S (2018) A hierarchical control framework of load balancing and resource allocation of cloud computing services. Comput Electrical Eng 67:235–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2018.03.035
Outamazirt A, Barkaoui K, Aïssani D (2018) Maximizing profit in cloud computing using m/g/c/k queuing model. In: 2018 International Symposium on Programming and Systems (ISPS), pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISPS.2018.8379008
Adhikari S, Hutaihit M, Chakraborty M, Mahmood S, Durakovic B, Pal S, Akila D, Obaid A (2021) Analysis of average waiting time and server utilization factor using queueing theory in cloud computing environment. Int J Nonlinear Anal Appl 12(Special Issue):1259–1267
Li W, Karthik C, Rajalakshmi M (2022) Big data visualization for in-situ data exploration for sportsperson. Comput Electrical Eng 99:107829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2022.107829
Ghosh S, Mukherjee A, Ghosh SK, Buyya R (2020) Mobi-iost: Mobility-aware cloud-fog-edge-iot collaborative framework for time-critical applications. IEEE Trans Netw Sci Eng 7(4):2271–2285. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSE.2019.2941754
Funding
Not Applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest/Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Appendix A
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kırsal, Y. A Stochastic Performance Model and Mobility Analysis in the Integrated Cloud-Fog-Edge Computing System. Mobile Netw Appl (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-023-02202-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-023-02202-x