Abstract
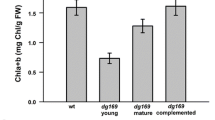
The plastid inner envelope membrane-bond nucleotide triphosphate transporter (NTT) transports cytosolic adenosine triphosphate (ATP) into plastid, which is necessary for the biochemical activities in plastid. We identified a chloroplast-localized BnaC08.NTT2 and obtained the overexpressed lines of BnaC08.NTT2 and CRISPR/Cas9 edited double mutant lines of BnaC08.NTT2 and BnaA08.NTT2 in B. napus. Further studies certified that overexpression (OE) of BnaC08.NTT2 could help transport ATP into chloroplast and exchange adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and this process was inhibited in BnaNTT2 mutants. Additional results showed that the thylakoid was abnormal in a8 c8 double mutants, which also had lower photosynthetic efficiency, leading to retarded plant growth. The BnaC08.NTT2 OE plants had higher photosynthetic efficiency and better growth compared to WT. OE of BnaC08.NTT2 could improve carbon flowing into protein and oil synthesis from glycolysis both in leaves and seeds. Lipid profile analysis showed that the contents of main chloroplast membrane lipids, including monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG), digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG), and phosphatidylglycerol (PG), were significantly reduced in mutants, while there were no differences in OE lines compared to WT. These results suggest that BnaNTT2 is involved in the regulation of ATP/ADP homeostasis in plastid to impact plant growth and seed oil accumulation in B. napus.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article and its supplementary information files.
Not applicable.
References
Andersson M, Turesson H, Arrivault S, Zhang Y, Falt AS, Fernie AR, Hofvander P (2018) Inhibition of plastid PPase and NTT leads to major changes in starch and tuber formation in potato. J Exp Bot 69(8):1913–1924. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery051
Baud S, Mendoza MS, To A, Harscoet E, Lepiniec L, Dubreucq B (2007) WRINKLED1 specifies the regulatory action of LEAFY COTYLEDON2 towards fatty acid metabolism during seed maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 50(5):825–838. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03092.x
Baud S, WuillÃme S, To A, Rochat C, Lepiniec LC (2009) Role of WRINKLED1 in the transcriptional regulation of glycolytic and fatty acid biosynthetic genes in Arabidopsis. Plant J 60(6):933–947. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04011.x
Block MA (2018) Isolation of inner and outer membranes of the chloroplast envelope from Spinach and Pea. Methods Mol Biol 1829:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8654-5_9
Bourgis F, Kilaru A, Cao X, Ngando-Ebongue GF, Drira N, Ohlrogge JB, Arondel V (2011) Comparative transcriptome and metabolite analysis of oil palm and date palm mesocarp that differ dramatically in carbon partitioning. P Natl Acad Sci USA 108(30):12527–12532. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1106502108
Cai Y, Goodman JM, Pyc M, Mullen RT, Dyer JM, Chapman KD (2015) Arabidopsis SEIPIN proteins modulate triacylglycerol accumulation and influence lipid droplet proliferation. Plant Cell 27(9):2616–2636. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00588
Cernac A, Benning C (2004) WRINKLED1 encodes an AP2/EREB domain protein involved in the control of storage compound biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 40(4):575–585. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02235.x
Chow PS, Landhausser SM (2004) A method for routine measurements of total sugar and starch content in woody plant tissues. Tree Physiol 24(10):1129–1136. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/24.10.1129
Dai C, Li Y, Li L, Du Z, Lu S (2020) An efficient agrobacterium-mediated transformation method using hypocotyl as explants for Brassica napus. Mol Breeding 40(10):96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-020-01174-0
Fan K, Rawsthorne S (1994) Starch and fatty acid synthesis in plastids from develo** embryos of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Plant J 6(6):795–805. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1994.6060795.x
Flugge UI, Hausler RE, Ludewig F, Gierth M (2011) The role of transporters in supplying energy to plant plastids. J Exp Bot 62(7):2381–2392. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq361
Geigenberger P, Stamme C, Tjaden J, Schulz A, Quick PW, Betsche T, Kersting HJ, Neuhaus HE (2001) Tuber physiology and properties of starch from tubers of transgenic potato plants with altered plastidic adenylate transporter activity. Plant Physiol 125(4):1667–1678. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.125.4.1667
Guo L, Ma F, Wei F, Fanella B, Allen DK, Wang X (2014) Cytosolic phosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases affect Arabidopsis cellular metabolism and promote seed oil accumulation. Plant Cell 26(7):3023–3035. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.126946
Haferkamp I, Hackstein JH, Voncken FG, Schmit G, Tjaden J (2002) Functional integration of mitochondrial and hydrogenosomal ADP/ATP carriers in the Escherichia coli membrane reveals different biochemical characteristics for plants, mammals and anaerobic chytrids. Eur J Biochem 269(13):3172–3181. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02991.x
Hattori M, Hibbs RE, Gouaux E (2012) A fluorescence-detection size-exclusion chromatography-based thermostability assay for membrane protein precrystallization screening. Structure 20(8):1293–1299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.06.009
Hong Y, **a H, Li X, Fan R, Li Q, Ouyang Z, Tang S, Guo L (2022) Brassica napus BnaNTT1 modulates ATP homeostasis in plastids to sustain metabolism and growth. Cell Rep 40(2):111060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111060
Hong Y, Yuan S, Sun L, Wang X, Hong Y (2018) Cytidinediphosphate-diacylglycerol synthase 5 is required for phospholipid homeostasis and is negatively involved in hyperosmotic stress tolerance. Plant J 94(6):1038–1050. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13916
Kong Q, Ma W (2018) WRINKLED1 as a novel 14–3-3 client: function of 14–3-3 proteins in plant lipid metabolism. Plant Signal Behav 13(8):e1482176. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2018.1482176
Kong Q, Yang Y, Guo L, Yuan L, Ma W (2020) Molecular basis of plant oil biosynthesis: insights gained from studying the WRINKLED1 transcription factor. Front Plant Sci 11:24. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00024
Kusumi K, Yara A, Mitsui N, Tozawa Y, Iba K (2004) Characterization of a rice nuclear-encoded plastid RNA polymerase gene OsRpoTp. Plant Cell Physiol 45(9):1194–1201. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pch133
Lee EJ, Oh M, Hwang JU, Li-Beisson Y, Nishida I, Lee Y (2017) Seed-specific overexpression of the pyruvate transporter BASS2 increases oil content in Arabidopsis seeds. Front Plant Sci 8(194):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00194
Li-Beisson Y, Shorrosh B, Beisson F, Andersson MX, Arondel V, Bates PD, Baud S, Bird D, Debono A, Durrett TP, Franke RB, Graham IA, Katayama K, Kelly AA, Larson T, Markham JE, Miquel M, Molina I, Nishida I, Rowland O, Samuels L, Schmid KM, Wada H, Welti R, Xu C, Zallot R, Ohlrogge J (2013) Acyl-Lipid Metabolism. Arabidopsis Book 11:e0161. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0161
Li D, Guo Y, Zhang D, He S, Gong J, Ma H, Gao X, Wang Z, Jiang L, Dun X, Hu S, Chen M (2020) Melatonin represses oil and anthocyanin accumulation in seeds. Plant Physiol 183(3):898–914. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.20.00117
Li N, Gugel IL, Giavalisco P, Zeisler V, Schreiber L, Soll J, Philippar K (2015) FAX1, a novel membrane protein mediating plastid fatty acid export. PLoS Biol 13(2):e1002053. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002053
Linka N, Hurka H, Lang BF, Burger G, Winkler HH, Stamme C, Urbany C, Seil I, Kusch J, Neuhaus HE (2003) Phylogenetic relationships of non-mitochondrial nucleotide transport proteins in bacteria and eukaryotes. Gene 306:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1119(03)00429-3
Lu S, Bahn SC, Qu G, Qin H, Hong Y, Xu Q, Zhou Y, Hong Y, Wang X (2013) Increased expression of phospholipase Dα1 in guard cells decreases water loss with improved seed production under drought in Brassica napus. Plant Biotechnol J 11(3):380–389. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12028
Lu S, Liu H, ** C, Li Q, Guo L (2019) An efficient and comprehensive plant glycerolipids analysis approach based on high‐performance liquid chromatography–quadrupole time‐of‐flight mass spectrometer. Plant Direct 3(11):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/pld3.183
Lyu J, Wang Y, Liu L, Wang C, Ren Y, Peng C, Liu F, Wang Y, Niu M, Wang D, Zheng M, Zhou K, Zhao S, Wu F, Wang H, Wan J (2017) A putative plastidial adenine nucleotide transporter, BRITTLE1-3, plays an essential role in regulating chloroplast development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Plant Biol 60(5):493–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-017-0063-6
Möhlmann T, Neuhaus RSE (1994) Interaction between fatty-acid and starch synthesis in isolated amyloplasts from cauliflower floral buds. Planta 194(4):492–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00714461
Maeo K, Tokuda T, Ayame A, Mitsui N, Kawai T, Tsukagoshi H, Ishiguro S, Nakamura K (2009) An AP2-type transcription factor, WRINKLED1, of Arabidopsis thaliana binds to the AW-box sequence conserved among proximal upstream regions of genes involved in fatty acid synthesis. Plant J 60(3):476–487. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03967.x
Mohlmann T, Tjaden J, Schwoppe C, Winkler HH, Kampfenkel K, Neuhaus HE (1998) Occurrence of two plastidic ATP/ADP transporters in Arabidopsis thaliana L.–molecular characterisation and comparative structural analysis of similar ATP/ADP translocators from plastids and Rickettsia prowazekii. Eur J Biochem 252(3):353–359. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2520353.x
Moreira D, Le Guyader H, Philippe H (2000) The origin of red algae and the evolution of chloroplasts. Nature 405(6782):69–72. https://doi.org/10.1038/35011054
Mullet JE (1993) Dynamic regulation of chloroplast transcription. Plant Physiol 103(2):309–313. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.2.309
Neuhaus H, Maass U (1996) Unidirectional transport of orthophosphate across the envelope of isolated cauliflower-bud amyloplasts. Planta 198(4):542–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262640
Neuhaus HE, Emes MJ (2000) Nonphotosynthetic metabolism in plastids. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:111–140. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.51.1.111
Qi Q, Klep**er-Sparace KF, Sparace SA (1994) The role of the triose-phosphate shuttle and glycolytic intermediates in fatty-acid and glycerolipid biosynthesis in pea root plastids. Planta 194(2):193–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01101678
Reiser J, Linka N, Lemke L, Jeblick W, Neuhaus HE (2004) Molecular physiological analysis of the two plastidic ATP/ADP transporters from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 136(3):3524–3536. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.049502
Reynolds KB, Taylor MC, Zhou XR, Vanhercke T, Wood CC, Blanchard CL, Singh SP, Petrie JR (2015) Metabolic engineering of medium-chain fatty acid biosynthesis in Nicotiana benthamiana plant leaf lipids. Front Plant Sci 6:164. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00164
Rieder B, Neuhaus HE (2011) Identification of an Arabidopsis plasma membrane-located ATP transporter important for anther development. Plant Cell 23(5):1932–1944. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.084574
Roux SJ, Steinebrunner I (2007) Extracellular ATP: an unexpected role as a signaler in plants. Trends Plant Sci 12(11):522–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2007.09.003
Sanjaya DTP, Weise SE, Benning C (2011) Increasing the energy density of vegetative tissues by diverting carbon from starch to oil biosynthesis in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol J 9(8):874–883. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00599.x
Schmitz-Esser S, Linka N, Collingro A, Beier CL, Neuhaus HE, Wagner M, Horn M (2004) ATP/ADP translocases: a common feature of obligate intracellular amoebal symbionts related to Chlamydiae and Rickettsiae. J Bacteriol 186(3):683–691. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.3.683-691.2004
Slabas AR, Fawcett T (1992) The biochemistry and molecular biology of plant lipid biosynthesis. Plant Mol Biol 19(1):169–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00015613
Song CJ, Steinebrunner I, Wang X, Stout SC, Roux SJ (2006) Extracellular ATP induces the accumulation of superoxide via NADPH oxidases in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 140(4):1222–1232. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.073072
Steinebrunner I, Wu J, Sun Y, Corbett A, Roux SJ (2003) Disruption of apyrases inhibits pollen germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 131(4):1638–1647. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.014308
Tang T, Yu X, Yang H, Gao Q, Ji H, Wang Y, Yan G, Peng Y, Luo H, Liu K, Li X, Ma C, Kang C, Dai C (2018) Development and validation of an effective CRISPR/Cas9 vector for efficiently isolating positive transformants and transgene-free mutants in a wide range of plant species. Front Plant Sci 9:1533. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01533
Tang W, Brady SR, Sun Y, Muday GK, Roux SJ (2003) Extracellular ATP inhibits root gravitropism at concentrations that inhibit polar auxin transport. Plant Physiol 131(1):147–154. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.013672
Tjaden J, Schwoppe C, Mohlmann T, Quick PW, Neuhaus HE (1998) Expression of a plastidic ATP/ADP transporter gene in Escherichia coli leads to a functional adenine nucleotide transport system in the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. J Biol Chem 273(16):9630–9636. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.16.9630
To A, Joubes J, Barthole G, Lecureuil A, Scagnelli A, Jasinski S, Lepiniec L, Baud S (2012) WRINKLED transcription factors orchestrate tissue-specific regulation of fatty acid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24(12):5007–5023. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.106120
Trentmann O, Jung B, Neuhaus HE, Haferkamp I (2008) Nonmitochondrial ATP/ADP transporters accept phosphate as third substrate. J Biol Chem 283(52):36486–36493. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M806903200
van Erp H, Kelly AA, Menard G, Eastmond PJ (2014) Multigene engineering of triacylglycerol metabolism boosts seed oil content in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 165(1):30–36. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.236430
Vanhercke T, El Tahchy A, Shrestha P, Zhou XR, Singh SP, Petrie JR (2013) Synergistic effect of WRI1 and DGAT1 coexpression on triacylglycerol biosynthesis in plants. FEBS Lett 587(4):364–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.12.018
Voon CP, Lim BL (2019) ATP translocation and chloroplast biology. Natl Sci Rev 6(6):1073–1076. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwz089
Weber AP (2004) Solute transporters as connecting elements between cytosol and plastid stroma. Curr Opin Plant Bio 7(3):247–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2004.03.008
Weber APM, Linka N (2011) Connecting the plastid: transporters of the plastid envelope and their role in linking plastidial with cytosolic metabolism. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62(1):53–77. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103903
Welti R, Li W, Li M, Sang Y, Biesiada H, Zhou HE, Rajashekar CB, Williams TD, Wang X (2002) Profiling membrane lipids in plant stress responses. Role of phospholipase D alpha in freezing-induced lipid changes in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277(35):31994–32002. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M205375200
Winkler HH, Neuhaus HE (1999) Non-mitochondrial ATP transport. Trends Biochem Sci 24(2):64–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0004(98)01334-6
Xu C, Shanklin J (2016) Triacylglycerol metabolism, function, and accumulation in plant vegetative tissues. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:179–206. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-111641
Zhai Z, Keereetaweep J, Liu H, Xu C, Shanklin J (2021) The role of sugar signaling in regulating plant fatty acid synthesis. Front Plant Sci 12:643843. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.643843
Zhou Z, Dun X, **a S, Shi D, Qin M, Yi B, Wen J, Shen J, Ma C, Tu J, Fu T (2012) BnMs3 is required for tapetal differentiation and degradation, microspore separation, and pollen-wall biosynthesis in Brassica napus. J Exp Bot 63(5):2041–2058. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err405
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Open Sharing Platform at Huazhong Agricultural University for the help with TEM and confocal laser scanning scope in this research.
Funding
The work was supported by grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31900908, 31871658).
Author information
Contributions
S.T. and L.G. designed this study. Y.H., H.X., X.L., R.F., Q.L., and Z.O. performed the experiments. Y.H. analyzed the data. Y.H. wrote the manuscript. S.T., L.G., S.L., X.L., and X.Y. revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
The authors are consented to participate.
Consent for publication
The authors are consented for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
**a, H., Hong, Y., Li, X. et al. BnaNTT2 regulates ATP homeostasis in plastid to sustain lipid metabolism and plant growth in Brassica napus. Mol Breeding 42, 54 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01322-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01322-8