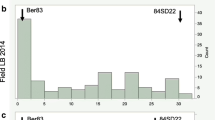
Abstract
Leptosphaeria maculans L. causing blackleg is a highly evolved fungal pathogen that damages the rapeseed industry in Canada, Australia, and Europe. Advanced backcross populations segregating for intermediate resistance (BLMR2) and susceptible (blmr2) alleles were planted and inoculated using cotyledons. Near iso-genic lines (NILs) containing the intermediate blackleg resistance locus along with the parent lines and other controls were planted in a blackleg nursery at the University of Manitoba. ANOVA indicated a correlated significant difference between the genotypes with BLMR2 and blmr2 alleles at the seedling and adult plant stages. Heterozygous plants with both BLMR2 and blmr2 alleles showed relatively lower disease severity index (DSI) while other plants with only the blmr2 allele induced a higher DSI at seedling and adult plant stages, respectively, on a scale of 0–9. In the field, the NILs with the BLMR2 alleles consistently showed lower stem canker severity index similar to the resistant parent Surpass 400 in three consecutive years. In comparison, lines with known R genes (BLMR1 and Rlm2) showed relatively higher DSI in the field test. This demonstrated that the intermediate resistance locus performed well under severe blackleg disease pressure in the field while the NIL lines with single dominant R genes were ineffective. Because a group of isolates carrying various Avr/avr alleles was used in the field evaluation, our results suggest that the intermediate resistance locus confers horizontal resistance and has excellent potential in blackleg management in western Canadian canola production regions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansal VK, Kharbanda PD, Stringam GR, Thiagarajah MR, Tewari JP (1994) A comparison of greenhouse and field screening methods for blackleg resistance in doubled haploid lines of Brassica napus. Plant Dis. 78: 276-281
Brun H, Chèvre AM, Fitt BD, Powers S, Besnard AL, Ermel M, Huteau V, Marquer B, Eber F, Renard M, Andrivon D (2010) Quantitative resistance increases the durability of qualitative resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica napus. New Phytol 185:285–299. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03049.x
Chen Y, Fernando WGD (2006) Prevalence of pathogenicity groups of Leptosphaeria maculans in western Canada and North Dakota, USA. Can J Plant Pathol 28:533–539. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060660609507331
Crouch JH, Lewis BG, Mithen RF (1994) The effect of A genome substitution on the resistance of Brassica napus to infection by Leptosphaeria maculans. Plant Breed 112:265–278. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.1994.tb00684.x
Delourme R, Pilet-Nayel ML, Archipiano M, Horvais R, Tanguy X, Rouxel T, Brun H, Renard M, Balesdent MH (2004) A cluster of major specific resistance genes to Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica napus. Phytopathology 94:578–583. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.6.578
Delourme R, Chèvre AM, Brun H, Rouxel T, Balesdent MH, Dias JS, Salisbury P, Renard M, Rimmer SR (2006) Major gene and polygenic resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Eur J Plant Pathol 114:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-005-2108-9
Delourme R, Brun H, Ermel M, Lucas MO, Vallee P, Domin C, Walton G, Li H, Sivasithamparam K, Barbetti MJ (2008a) Expression of resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica napus double haploid lines in France and Australia is influenced by location. Ann Appl Biol 153:259–269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2008.00258.x
Delourme R, Piel N, Horvais R, Pouilly N, Domin C, Vallée P, Falentin C, Manzanares-Dauleux MJ, Renard M (2008b) Molecular and phenotypic characterization of near isogenic lines at QTL for quantitative resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 117:1055–1067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0844-x
Dilmaghani A, Balesdent MH, Didier JP, Wu C, Davey J, Barbetti MJ, Li H, Moreno-Rico O, Phillips D, Despeghel JP, Vincenot L, Gout L, Rouxel T (2009) The Leptosphaeria maculans - Leptosphaeria biglobosa species complex in the American continent. Plant Pathol 58:1044–1058. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2009.02149.x
Dion Y, Gugel RK, Rakow GFW, Séguin-Swartz G, Landry BS (1995) RFLP map** of resistance to the blackleg disease [causal agent, Leptosphaeria maculans (Desm.) Ces. et de Not.] in canola (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 91:1190–1194. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220928
Easton A (2001) Blackleg tested 9. Where does it come from and what does it mean. In: Marcroft SJ (ed) Proceedings of the 12th Australian Research Assembly on Brassicas, Geelong, Victoria, 2–5 October 2001, pp 47–49
Elliott VL, Marcroft SJ, Howlett BJ, Van de Wouw AP (2016) Gene-for-gene resistance is expressed in cotyledons, leaves and pods, but not during late stages of stem colonization in the Leptosphaeria maculans-Brassica napus pathosystem. Plant Breed 135:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12343
Gugel RK, Petrie GA (1992) History, occurrence, impact, and control of blackleg of rapeseed. Can J Plant Pathol 14:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060669209500904
Hammond KE, Lewis BG (1987a) Differential responses of oilseed rape leaves to Leptosphaeria maculans. Trans Br Mycol Soc 88:329–333. British Mycological Society. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1536(87)80006-2
Hammond KE, Lewis BG (1987b) The establishment of systemic infection in leaves of oilseed rape by Leptosphaeria maculans. Plant Pathol 36:135–147. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.1987.tb02213.x
Hammond KE, LEWIS BG, MUSA TM (1985) A systemic pathway in the infection of oilseed rape plants by Leptosphaeria maculans. Plant Pathol 34:557–565. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.1985.tb01407.x
Huang YJ, Evans N, Li ZQ, Eckert M, Chèvre AM, Renard M, Fitt BDL (2006) Temperature and leaf wetness duration affect phenotypic expression of Rlm6-mediated resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica napus. New Phytol 170:129–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01651.x
Huang YJ, Pirie EJ, Evans N, Delourme R, King GJ, Fitt BDL (2009) Quantitative resistance to symptomless growth of Leptosphaeria maculans (phoma stem canker) in Brassica napus (oilseed rape). Plant Pathol 58:314–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2008.01957.x
Huang YJ, Qi A, King GJ, Fitt BDL (2014) Assessing quantitative resistance against Leptosphaeria maculans (phoma stem canker) in Brassica napus (oilseed rape) in young plants. PLoS One 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084924
Kutcher HR, Keri M, McLaren DL, Rimmer SR (2007) Pathogenic variability of Leptosphaeria maculans in western Canada. Can J Plant Pathol 29:388–393. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060660709507484
Kutcher HR, Balesdent MH, Rimmer SR, Rouxel T, Chèvre AM, Delourme R, Brun H (2010) Frequency of avirulence genes in Leptosphaeria maculans in western Canada. Can J Plant Pathol 32:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060661003594109
Larkan NJ, Lydiate DJ, Parkin IAP, Nelson MN, Epp DJ, Cowling WA, Rimmer SR, Borhan MH (2013) The Brassica napus blackleg resistance gene LepR3 encodes a receptor-like protein triggered by the Leptosphaeria maculans effector AVRLM1. New Phytol 197:595–605. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12043
Larkan NJ, Lydiate DJ, Yu F, Rimmer SR, Borhan MH (2014) Co-localisation of the blackleg resistance genes Rlm2 and LepR3 on Brassica napus chromosome A10. BMC Plant Biol 14:387. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0387-z
Larkan NJ, Ma L, Borhan MH (2015) The Brassica napus receptor-like protein RLM2 is encoded by a second allele of the LepR3/Rlm2 blackleg resistance locus. Plant Biotechnol J 13:983–992. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12341
Larkan NJ, Raman H, Lydiate DJ, Robinson SJ, Yu F, Barbulescu DM, Raman R, Luckett DJ, Burton W, Wratten N, Salisbury PA, Rimmer SR, Borhan MH (2016a) Multi-environment QTL studies suggest a role for cysteine-rich protein kinase genes in quantitative resistance to blackleg disease in Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biol 16:183. BMC Plant Biology. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0877-2
Larkan NJ, Yu F, Lydiate DJ, Rimmer SR, Borhan MH (2016b) Single R gene introgression lines for accurate dissection of the Brassica - Leptosphaeria pathosystem. Front Plant Sci 7:1771. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01771
Li CX, Cowling WA (2003) Identification of a single dominant allele for resistance to blackleg in Brassica napus “Surpass 400”. Plant Breed 122:485–488. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2003.00863.x
Li H, Barbetti MJ, Sivasithamparam K 2003 Field isolates of Leptosphaeria maculans from Western Australia overcome a single dominant resistance gene in Brassica napus cv. Surpass 400. Thirteen. Bienn. Aust. Res. Assem. Brassicas. Proc. a Conf. Tamworth, New South Wales, Aust. 8-12 Sept. 2003: pp 136-137
Li H, Sivasithamparam K, Barbetti MJ, Kuo J (2004) Germination and invasion by ascospores and pycnidiospores of Leptosphaeria maculans on spring-type Brassica napus canola varieties with varying susceptibility to blackleg. J Gen Plant Pathol 70:261–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-004-0125-8
Li H, Barbetti MJ, Sivasithamparam K (2005) Hazard from reliance on cruciferous hosts as sources of major gene-based resistance for managing blackleg (Leptosphaeria maculans) disease. Field Crop Res 91:185–t198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2004.06.006
Li CX, Wratten N, Salisbury PA, Burton WA, Potter TD, Walton G, Li H, Sivasithamparam K, Banga SS, Banga S, Singh D, Liu SY, Fu TD, Barbetti MJ (2008a) Response of Brassica napus and B. juncea germplasm from Australia, China and India to Australian populations of Leptosphaeria maculans. Australas Plant Pathol 37:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1071/AP08005
Li H, Sivasithamparam K, Barbetti MJ, Wylie SJ, Kuo J (2008b) Cytological responses in the hypersensitive reaction in cotyledon and stem tissues of Brassica napus after infection by Leptosphaeria maculans. J Gen Plant Pathol 74:120–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-007-0067-z
Liban SH, Cross DJ, Kutcher HR, Peng G, Fernando WGD (2016) Race structure and frequency of avirulence genes in the western Canadian Leptosphaeria maculans pathogen population, the causal agent of blackleg in Brassica species. Plant Pathol 65:1161–1169. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12489
Long Y, Wang Z, Sun Z, Fernando DWG, McVetty PBE, Li G (2011) Identification of two blackleg resistance genes and fine map** of one of these two genes in a Brassica napus canola cultivar “Surpass 400”. Theor Appl Genet 122:1223–1231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1526-z
Marcroft SJ, Elliott VL, Cozijnsen AJ, Salisbury PA, Howlett BJ, Van De Wouw AP (2012) Identifying resistance genes to Leptosphaeria maculans in Australian Brassica napus cultivars based on reactions to isolates with known avirulence genotypes. Crop Pasture Sci 63:338–350. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP11341
Mayerhofer R, Bansal VK, Thiagarajah MR, Stringam GR, Good AG (1997) Molecular map** of resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in Australian cultivars of Brassica napus. Genome 40:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1139/g97-041
McNabb WM, van den Berg CGJ, Rimmer SR (1993) Comparison of inoculation methods for selection of plants resistant to Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica napus. Can J Plant Sci 73:1199–1207
Mengistu A, Rimmer SR, Koch E, Williams PH 1991 Pathogenicity grou** of isolates of Leptosphaeria maculans on Brassica napus cultivars and their disease reaction profiles on rapid-cycling Brassicas. Plant Disease 75:1279–82
Pang ECK, Halloran GM (1996) The genetics of blackleg Leptosphaeria maculans (Desm) Ces et De Not resistance in rapeseed (Brassica napus L). 1. Adult-plant resistance in F-2 and first-backcross populations. Theor Appl Genet 93:932–940. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00224096
Pilet ML, Delourme R, Foisset N, Renard M (1998) Identification of loci contributing to quantitative field resistance to blackleg disease, causal agent Leptosphaeria maculans (Desm.) Ces. et de Not., in Winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 96:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050704
Pilet ML, Duplan G, Archipiano M, Barret P, Baron C, Horvais R, Tanguy X, Lucas MO, Renard M, Delourme R (2001) Stability of QTL for field resistance to blackleg across two genetic backgrounds in oilseed rape. Crop Sci 41:197–205. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2001.411197x
Raman R, Taylor B, Marcroft S, Stiller J, Eckermann P, Coombes N, Rehman A, Lindbeck K, Luckett D, Wratten N, Batley J, Edwards D, Wang X, Raman H (2012) Molecular map** of qualitative and quantitative loci for resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans causing blackleg disease in canola (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 125:405–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1842-6
Raman H, Raman R, Coombes N, Song J, Diffey S, Kilian A, Lindbeck K, Barbulescu DM, Batley J, Edwards D, Salisbury PA, Marcroft S (2016) Genome-wide association study identifies new loci for resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in Canola. Front Plant Sci 7:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01513
Rimmer SR (2006) Resistance genes to Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica napus. Can J Plant Pathol 297:288–297
Rouxel T, Penaud A, Pinochet X, Brun H, Gout L, Delourme R, Schmit J, Balesdent MH (2003) A 10-year survey of populations of Leptosphaeria maculans in France indicates a rapid adaptation towards the Rlm1 resistance gene of oilseed rape. Eur J Plant Pathol 109:871–881. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026189225466
Salisbury PA, Ballinger DJ, Wratten N, Plummer KM, Howlett BJ 1995 Blackleg disease on oilseed Brassica in Australia a review. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture 35(5):665–672
Sprague SJ, Balesdent MH, Brun H, Hayden HL, Marcroft SJ, Pinochet X, Rouxel T, Howlett BJ (2006) Major gene resistance in Brassica napus (oilseed rape) is overcome by changes in virulence of populations of Leptosphaeria maculans in France and Australia. Eur J Plant Pathol 114:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-005-3683-5
Travadon R, Marquer B, Ribulé A, Sache I, Masson JP, Brun H, Delourme R, Bousset L (2009) Systemic growth of Leptosphaeria maculans from cotyledons to hypocotyls in oilseed rape: influence of number of infection sites, competitive growth and host polygenic resistance. Plant Pathol 58:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2008.02014.x
Van De Wouw AP, Marcroft SJ, Barbetti MJ, Hua L, Salisbury PA, Gout L, Rouxel T, Howlett BJ, Balesdent MH (2009) Dual control of avirulence in Leptosphaeria maculans towards a Brassica napus cultivar with “sylvestris-derived” resistance suggests involvement of two resistance genes. Plant Pathol 58:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2008.01982.x
Van de Wouw AP, Marcroft SJ, Ware A, Lindbeck K, Khangura R, Howlett BJ (2014) Breakdown of resistance to the fungal disease, blackleg, is averted in commercial canola (Brassica napus) crops in Australia. Field Crop Res 166:144–151. Elsevier B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2014.06.023
West JS, Kharbanda PD, Barbetti MJ, Fitt BDL (2001) Epidemiology and management of Leptosphaeria maculans (phoma stem canker) on oilseed rape in Australia, Canada and Europe. Plant Pathol 50:10–27. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3059.2001.00546.x
Williams and Delwiche P.A. (1979) Screening for resistance to blackleg of crucifers in the seedling stage.Eucarpia Cruciferae, Conference Proceedings. Wageningen, The Netherlands 1-3 Oct. 1979, pp 164-170
Yu F, Lydiate DJ, Rimmer SR (2005) Identification of two novel genes for blackleg resistance in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 110:969–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1919-y
Yu F, Lydiate DJ, Rimmer SR (2008) Identification and map** of a third blackleg resistance locus in Brassica napus derived from B. rapa subsp. sylvestris. Genome 51:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1139/g07-103
Zhang X, Peng G, Kutcher HR, Balesdent MH, Delourme R, Fernando WGD (2016) Breakdown of Rlm3 resistance in the Brassica napus–Leptosphaeria maculans pathosystem in western Canada. Eur J Plant Pathol 145:659–674. European Journal of Plant Pathology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0819-0
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Growing Forward 2, SaskCanola for isolate characterizations and field setup with inoculum.
Funding
Financial support was from NSERC CRD and Discovery projects, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada and SasKcanola Growing Forward 2 project, Bunge Canada and DL Seeds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dandena, H.B., Zhang, Q., Zhou, T. et al. Analysis of quantitative adult plant resistance to blackleg in Brassica napus. Mol Breeding 39, 124 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-019-1035-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-019-1035-y