Abstract
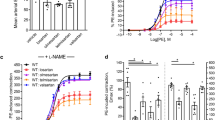
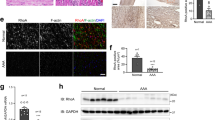
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a major cause of global mortality. The proper functioning of the endothelial layer of arteries is crucial to cardiovascular health. Retinoblastoma protein (Rb), encoded by the Rb1 gene, has been shown to offer vasoprotective effects. Herein, we investigated endothelial Rb’s effects on arterial function using an endothelial-specific conditional Rb1 knockout (Rb cKO) mouse model. We found that Rb deficiency reduced dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) activity and downstream NO production in mouse aortic endothelial cells and blocked arterial vasodilation in an endothelial DHFR-dependent manner. Rb deficiency also increased phenylephrine-triggered arterial vasoconstriction, BP levels, and pathological aortic remodeling without significantly affecting prostanoid synthesis. Employing an angiotensin II (AngII)-stimulated apolipoprotein E knockout (apoE −/−) mice fed a standard, non-atherogenic diet, Rb deficiency increased aortic diameter, stimulated abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) development, and reduced survival. These pathological responses to Rb deficiency in AngII-stimulated apoE−/− mice were rescued by DHFR overexpression. Cumulatively, our findings reveal that endothelial Rb positively impacts arterial function by supporting vasoprotective endothelial DHFR/NO pathway activity, leading to reduced AAA development.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joseph P, Leong D, Mckee M, Anand SS, Schwalm J-D, Teo K, Mente A, Yusuf S (2017) Reducing the global burden of cardiovascular disease, part 1: the epidemiology and risk factors. Circ Res 121:677–694
Leong DP, Joseph PG, McKee M, Anand SS, Teo KK, Schwalm J-D, Yusuf S (2017) Reducing the global burden of cardiovascular disease, part 2: prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 121:695–710
Gatica D, Chiong M, Lavandero S, Klionsky DJ (2015) Molecular mechanisms of autophagy in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res 116:456–467
Hua Y, Nair S (2015) Proteases in cardiometabolic diseases: pathophysiology, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1852:195–208
Vásquez-Trincado C, García-Carvajal I, Pennanen C, Parra V, Hill JA, Rothermel BA, Lavandero S (2016) Mitochondrial dynamics, mitophagy and cardiovascular disease. J Physiol 594:509–525
Gao J, Xu W, Wang J, Wang K, Li P (2017) The role and molecular mechanism of non-coding RNAs in pathological cardiac remodeling. Int J Mol Sci 18:608
Pober JS, Sessa WC (2007) Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 7:803
Lamalice L, Le Boeuf F, Huot J (2007) Endothelial cell migration during angiogenesis. Circ Res 100:782–794
van Hinsbergh VW (2012) Endothelium—role in regulation of coagulation and inflammation. Semin Immunopathol 34(1):93–106
Félétou M (2011) The endothelium, Part I: Multiple functions of the endothelial cells–focus on endothelium-derived vasoactive mediators. In: Granger JP, Neil Granger D (eds) Colloquium series on integrated systems physiology: from molecule to function, vol 3. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences, San Rafael, pp 1–306
Puddu P, Puddu GM, Zaca F, Muscari A (2000) Endothelial dysfunction in hypertension. Acta Cardiol 55:221–232
Dharmashankar K, Widlansky ME (2010) Vascular endothelial function and hypertension: insights and directions. Curr Hypertens Rep 12:448–455
Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK (2011) Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 473:317
O’Rourke M (1995) Mechanical principles in arterial disease. Hypertension 26:2–9
Boesten LS, Zadelaar ASM, van Nieuwkoop A, Hu L, Jonkers J, van de Water B, Gijbels MJ, van der Made I, de Winther MP, Havekes LM (2006) Macrophage retinoblastoma deficiency leads to enhanced atherosclerosis development in ApoE-deficient mice. FASEB J 20:953–955
Lee W-H, Shew J-Y, Hong FD, Sery TW, Donoso LA, Young L-J, Bookstein R, Eva Y-HL (1987) The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein associated with DNA binding activity. Nature 329:642
Weinberg RA (1995) The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 81(3):323–330
Chellappan SP, Hiebert S, Mudryj M, Horowitz JM, Nevins JR (1991) The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell 65:1053–1061
Schwartz LB, Moawad J, Svensson EC, Tufts RL, Meyerson SL, Baunoch D, Leiden JM (1999) Adenoviral-mediated gene transfer of a constitutively active form of the retinoblastoma gene product attenuates neointimal thickening in experimental vein grafts. J Vasc Surg 29:874–883
Pillai S, Kovacs M, Chellappan S (2010) Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors by Rb and E2F1: role of acetylation. Can Res 70:4931–4940
Reynolds MR, Lane AN, Robertson B, Kemp S, Liu Y, Hill BG, Dean DC, Clem BF (2014) Control of glutamine metabolism by the tumor suppressor Rb. Oncogene 33:556
Genovese C, Trani D, Caputi M, Claudio P (2006) Cell cycle control and beyond: emerging roles for the retinoblastoma gene family. Oncogene 25:5201
Slansky JE, Li Y, Kaelin WG, Farnham PJ (1993) A protein synthesis-dependent increase in E2F1 mRNA correlates with growth regulation of the dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Mol Cell Biol 13:1610–1618
Li H, Li Q, Zhang Y, Liu W, Gu B, Narumi T, Siu KL, Youn JY, Liu P, Yang X (2019) Novel treatment of hypertension by specifically targeting E2F for restoration of endothelial dihydrofolate reductase and eNOS function under oxidative stress. Hypertension 73:179–189
Santhanam AVR, d’Uscio LV, Smith LA, Katusic ZS (2012) Uncoupling of eNOS causes superoxide anion production and impairs NO signaling in the cerebral microvessels of hph-1 mice. J Neurochem 122:1211–1218
Rhoden A, Speiser J, Geertz B, Uebeler J, Kjestine S, de Wit C, Eschenhagen T (2019) Preserved cardiovascular homeostasis despite blunted acetylcholine-induced dilation in mice with endothelial muscarinic M3 receptor deletion. Acta Physiol 226(1):e13262
Zuccolo E, Laforenza U, Negri S, Botta L, Berra-Romani R, Faris P, Scarpellino G, Forcaia G, Pellavio G, Sancini G (2019) Muscarinic M5 receptors trigger acetylcholine-induced Ca2+ signals and nitric oxide release in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 234:4540–4562
Tangsucharit P, Takatori S, Zamami Y, Goda M, Pakdeechote P, Kawasaki H, Takayama F (2016) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1 and M3 subtypes mediate acetylcholine-induced endothelium-independent vasodilatation in rat mesenteric arteries. J pharmacol sci 130:24–32
Mitchell JA, Ali F, Bailey L, Moreno L, Harrington LS (2008) Role of nitric oxide and prostacyclin as vasoactive hormones released by the endothelium. Exp Physiol 93:141–147
Swierkosz TA, Mitchell JA, Warner TD, Botting RM, Vane JR (1995) Co-induction of nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase: interactions between nitric oxide and prostanoids. Br J Pharmacol 114:1335–1342
Aguado A, Rodríguez C, Martínez-Revelles S, Avendaño M, Zhenyukh O, Orriols M, Martínez-González J, Alonso M, Briones A, Dixon D (2015) HuR mediates the synergistic effects of angiotensin II and IL-1β on vascular COX-2 expression and cell migration. Br J Pharmacol 172:3028–3042
Curci JA, Thompson RW (2004) Adaptive cellular immunity in aortic aneurysms: cause, consequence, or context? J Clin Investig 114:168–171
Forsdahl SH, Singh K, Solberg S, Jacobsen BK (2009) Risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Circulation 119:2202–2208
Siu KL, Miao XN, Cai H (2014) Recoupling of eNOS with folic acid prevents abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in angiotensin II-infused apolipoprotein E null mice. PLoS ONE 9:e88899
Gao L, Siu KL, Chalupsky K, Nguyen A, Chen P, Weintraub NL, Galis Z, Cai H (2012) Role of uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase in abdominal aortic aneurysm formation: treatment with folic acid. Hypertension 59:158–166
Förstermann U, **a N, Li H (2017) Roles of vascular oxidative stress and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ Res 120:713–735
Martinez-Lemus LA, Hill MA, Meininger GA (2009) The plastic nature of the vascular wall: a continuum of remodeling events contributing to control of arteriolar diameter and structure. Physiology 24:45–57
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81760059, 81560060) and The YunLing Scholars and Special Joint Program of Yunnan Province (Grant No. 2018FE001-181). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Contributions
YC and DX conceived and designed the study; RK, GLD, and MHZ performed the experimental procedures; LL, JPZ, LHJ, and HRL analyzed the data; LHJ and HRL drafted the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Lihong Jiang and Hongrong Li are co corresponding authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Y., **ong, D., Kong, R. et al. Endothelial retinoblastoma protein reduces abdominal aortic aneurysm development via promoting DHFR/NO pathway-mediated vasoprotection. Mol Cell Biochem 460, 29–36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03567-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03567-y