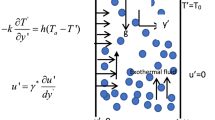
Abstract
The study investigates the transient dynamics of a third-grade fluid, capable of undergoing exothermic reactions, in a two-dimensional rectangular micro-channel. The combined effects of the adverse pressure gradients and electro-osmotic forces constitute the primary flow drivers. In addition to exothermic reactions, the system if also subjected to joule heating and convective cooling at the micro-channel boundaries. Newton’s law of cooling and Arrhenius kinetics are employed to model the boundary-cooling and exothermic-reactions respectively. The temperature-dependent fluid viscosity is modelled via a Nahme-type law. It is assumed that the area in between the micro-channels is a porous material with constant permeability. Computational solutions (implemented on the MATLAB software) are employed for the non-homogeneous partial differential equations for temperature and velocity. These computational solutions are developed from efficient, convergent, and unconditionally stable, semi-implicit finite difference methods. In contrast, the linearized Poisson–Boltzmann equation is solved analytically. The sensitivity of the field variables to variations in the various flow parameters are explored graphically and discussed qualitatively.







































Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are however available upon reasonable request from the corresponding authors.
References
Bruus H. Hydraulic resistance and compliance, theoretical microfluidics. New York: Oxford University Press; 2008. p. 71–88.
Hanna WT, Osterle JF. Transient electro-osmosis in capillary tubes. J Chem Phys. 1968;49(9):4062–8.
Ivory CF. Transient electroosmosis: the momentum transfer coefficient. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1983;96(1):296–8.
Keh HJ, Tseng HC. Transient electrokinetic flow in fine capillaries. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2001;242(2):450–9.
Santiago JG. Electroosmotic flows in microchannels with finite inertial and pressure forces. Anal Chem. 2001;73(10):2353–65.
Kang Y, Yang C, Huang X. Dynamic aspects of electroosmotic flow in a cylindrical microcapillary. Int J Eng Sci. 2002;40(20):2203–21.
Chakraborty S, Ray S. Mass flow-rate control through time periodic electro-osmotic flows in circular microchannels. Phys Fluids. 2008;20(8):083602.
Chakraborty S, Srivastava AK. A generalized model for time periodic electroosmotic flows with overlap** electrical double layers. Langmuir. 2007;23:12421–8.
Qu W, Li D. A model for overlapped EDL fields. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2000;224(2):397–407.
Das S, Chakraborty S. Analytical solutions for velocity, temperature and concentration distribution in electroosmotic microchannel flows of a non-Newtonian bio-fluid. Anal Chim Acta. 2006;559(1):15–24.
Chakraborty S. Electroosmotically driven capillary transport of typical non-Newtonian biofluids in rectangular microchannels. Anal Chim Acta. 2007;605(2):175–84.
Zhao C, Yang C. Electroosmotic flow of power-law fluids in a slit microchannel. In: International conference on nanochannels, microchannels, and minichannels, vol 43499, pp 211–218 (2009).
Park HM, Lee WM. Helmholtz–Smoluchowski velocity for viscoelastic electroosmotic flows. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2008;317(2):631–6.
Park HM, Lee WM. Effect of viscoelasticity on the flow pattern and the volumetric flow rate in electroosmotic flows through a microchannel. Lab Chip. 2008;8(7):1163–70.
Bird RB, Dotson PJ, Johnson NL. Polymer solution rheology based on a finitely extensible bead-spring chain model. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech. 1980;7(2–3):213–35.
Afonso AM, Alves MA, Pinho FT. Analytical solution of mixed electro-osmotic/pressure driven flows of viscoelastic fluids in microchannels. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech. 2009;159(1–3):50–63.
Wang X, Xu H, Qi H. Numerical analysis for rotating electro-osmotic flow of fractional Maxwell fluids. Appl Math Lett. 2020;103:106179.
Yang C, Jian Y, **e Z, Li F. Electromagnetohydrodynamic Electroosmotic flow and entropy generation of third-grade fluids in a parallel microchannel. Micromachines. 2020;11(4):418.
Akgül MB, Pakdemirli M. Analytical and numerical solutions of electro-osmotically driven flow of a third grade fluid between micro-parallel plates. Int J Non-Linear Mech. 2008;43(9):985–92.
Nazeer M, Ali N, Ahmad F, Ali W, Saleem A, Ali Z, Sarfraz A. Effects of radiative heat flux and joule heating on electro-osmotically flow of non-Newtonian fluid: analytical approach. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer. 2020;117:104744.
Nazeer M, Hussain F, Khan MI, El-Zahar ER, Chu YM, Malik MY. Theoretical study of MHD electro-osmotically flow of third-grade fluid in micro channel. Appl Math Comput. 2022;420:126868.
Pengra DB, et al. Experimental study of electrokinetics in porous media. MRS Proc. 1994;366:201.
Li B, Zhou WN, Yan YY, Tian C. Evaluation of electro-osmotic pum** effect on microporous media flow. Appl Therm Eng. 2013;60(1–2):449–55.
Obliger A, Jardat M, Coelho D, Bekri S, Rotenberg B. Pore network model of electrokinetic transport through charged porous media. Phys Rev E. 2014;89(4):043013.
Di Fraia S, Massarotti N, Nithiarasu P. Finite Element Modelling of Electro-Osmotic Flow in Porous Media. Momentum. 2016;1:3.
Tripathi D, Bhushan S, Beg OA. Electro-osmotic flow in a microchannel containing a porous medium with complex wavy walls. J Porous Media. 2020;23(5):477–95.
Chinyoka T, Makinde OD. Numerical analysis of the transient and non-isothermal channel flow of a third-grade fluid with convective cooling. Eng Trans. 2020;68(4):335–51.
Fosdick RL, Rajagopal KR. Thermodynamics and stability of fluids of third grade. Proc R Soc Lond A Math Phys Sci. 1980;369(1738):351–77.
Nazeer M, Ali N, Ahmad F, Latif M. Numerical and perturbation solutions of third-grade fluid in a porous channel: boundary and thermal slip effects. Pramana. 2020;94(1):1–15.
Gao Y, Wong TN, Yang C, Ooi KT. Two-fluid electroosmotic flow in microchannels. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;284(1):306–14.
Blazek J. Computational fluid dynamics: principles and applications. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2015.
Khan Idrees, Chinyoka Tiri, Gill Andrew. Computational analysis of the dynamics of generalized-viscoelastic-fluid-based nanofluids subject to exothermic-reaction in shear-flow. J Nanofluids. 2022;11:487–99.
Khan I, Chinyoka T, Gill A. Dynamics of non-isothermal pressure-driven flow of generalized viscoelastic-fluid-based nanofluids in a channel. Math Probl Eng 2022, Article ID 9080009, 17 pages (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/9080009.
Khan I, Chinyoka T, Gill A. Computational analysis of shear banding in simple shear flow of viscoelastic fluid-based nanofluids subject to exothermic reactions. Energies. 2022;15:1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15051719.
Khan I, Chinyoka T, Gill A. Computational-analysis of the non-isothermal dynamics of gravity-driven flows of viscoelastic-fluid-based nanofluids down an inclined plane. FDMP-Fluid Dyn Mater Process (in press) (2022)
Chinyoka T. Computational dynamics of a thermally decomposable viscoelastic lubricant under shear. J Fluids Eng. 2008;130(12).
Khan I, Chinyoka T, Ismail EA, Awwad FA, Ahmad Z. MHD flow of third-grade fluid through a vertical micro-channel filled with porous media using semi implicit finite difference method. Alex Eng J. 2024;86:513–24.
Okoya SS. Computational study of thermal influence in axial annular flow of a reactive third grade fluid with non-linear viscosity. Alex Eng J. 2019;58(1):401–11.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the KKU research unit for the financial and administrative support under Grant Number 574 for year 44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflict of interest is in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, I., Chinyoka, T., Gul, T. et al. Unsteady electro-osmotic thermal convection of a reactive third-grade fluid with exothermic reaction in a porous medium saturated micro-channel. J Therm Anal Calorim 149, 5457–5481 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13116-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-024-13116-5