Abstract
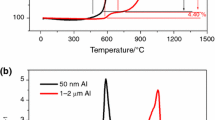
This article reports an investigation on the thermal reactivity of nano-aluminum powder (NAP) in the air. We performed tests on the metallic powder in synchronous thermal analysis at four heating rates of 5, 10, 15, and 20 °C min−1. Given the polymorphic phase change of aluminum, the oxidation process of NAP was divided into four stages. The results showed a notable effect from the heating rate on the oxidation of NAP. The mass gain decreased at stage II and increased at stage IV as the rate of heating increased. The maximum mass gain rate at 5, 10, 15, and 20 °C min−1 was 2.38, 4.70, 33.79, and 53.38% min−1, respectively, while the thermal release was 35,126, 27,955, 15,608, and 16,336 J g−1, respectively. Furthermore, the average apparent activation energy, preexponential factor, and mechanism function were obtained by the kinetic integral method.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meda L, Marra G, Galfetti L, Severini F, Luca LD. Nano-aluminum as energetic material for rocket propellants. Mater Sci Eng. 2007;27:1393–6.
Pourmortazavi SM, Hajimirsadeghi SS, Kohsari I, Fathollahi M, Hosseini SG. Thermal decomposition of pyrotechnic mixtures containing either aluminum or magnesium powder as fuel. Fuel. 2008;87:244–51.
Marmo L, Piccinini N, Danzi E. Small magnitude explosion of aluminium powder in an abatement plant: a telling case. Process Saf Environ Prot. 2015;98:221–30.
Li G, Yang HX, Yuan CM, Eckhoff RK. A catastrophic aluminium-alloy dust explosion in china. J Loss Prevent Proc. 2016;39:121–30.
Deng J, Qu J, Wang QH, Zhai XW, **ao Y, Cheng Y, Shu CM. Minimum ignition temperature of aluminium dust clouds via the Godbert-Greenwald furnace. Process Saf Environ Prot. 2019;129:176–83.
Li QZ, Lin BQ, Li WX, Zhai C, Zhu CJ. Explosion characteristics of nano-aluminum powder–air mixtures in 20 L spherical vessels. Powder Technol. 2011;212:303–9.
Bernard S, Gillard P, Frascati F. Ignition and explosibility of aluminium alloys used in additive layer manufacturing. J Loss Prevent Proc. 2017;49:888–95.
Wu HC, Ou HJ, Peng DJ, Hsiao HC, Gau CY, Shih TS. Dust explosion characteristics of agglomerated 35 nm and 100 nm aluminum particles. Int J Chem Eng. 2010;9:1–6.
Wu HC, Ou HJ, Hsiao HC, Shih TS. Explosion characteristics of aluminum nanopowders. Aerosol Air Qual Res. 2010;10:38–42.
Denkevits A, Hoess B. Hybrid H2/Al dust explosions in Siwek sphere. J Loss Prevent Proc. 2015;36:509–21.
Liu XL, Zhang Q. Influence of turbulent flow on the explosion parameters of micro- and nano-aluminum powder–air mixtures. J Hazard Mater. 2015;299:603–17.
Zhang Q, Liu LJ, Shen SL. Effect of turbulence on explosion of aluminum dust at various concentrations in air. Powder Technol. 2018;325:467–75.
Castellanos D, Carreto-Vazquez VH, Mashuga CV, Trottier R, Mejia AF, Mannan MS. The effect of particle size polydispersity on the explosibility characteristics of aluminum dust. Powder Technol. 2014;254:331–7.
Huang Y, Risha GA, Yang V, Yetter RA. Combustion of bimodal nano/micron-sized aluminum particle dust in air. Proc Combust Inst. 2007;31:2001–9.
Yuasa S, Sogo S, Isoda H. Ignition and combustion of aluminum in carbon dioxide streams. Symp Combust. 1992;24:1817–25.
Bidabadi M, Moallemi N, Shabani A, Abdous MA. Analysis of size distribution and ignition temperature effects on flame speeds in aluminium dust clouds. J Aerosp Eng. 2010;224:113–9.
Zhu Y, Yuasa S. Effects of oxygen concentration on combustion of aluminum in oxygen/nitrogen mixture streams. Combust Flame. 1998;115:327–34.
Li LB, Chen X, Musa O, Zhou CS, Zhu M. The effect of pressure and oxygen concentration on the ignition and combustion of aluminum–magnesium fuel–rich propellant. Aerosp Sci Technol. 2018;76:394–401.
Gao W, Zhang XY, Zhang DW, Peng QK, Zhang Q, Dobashi R. Flame propagation behaviours in nano-metal dust explosions. Powder Technol. 2017;321:154–62.
Qu J, Deng J, Luo ZM, **ao Y, Shu C-M. Thermal reaction characteristics and microstructure evolution of aluminium nano-powder in various mixtures of oxygen and nitrogen atmosphere. Process Saf Environ Prot. 2023;170:45–53.
Tseng JM, Huang ST, Duh YS, Hsieh TY, Sun YY, Lin JZ, et al. Thermal analysis and safety information for metal nanopowders by DSC. Thermochim Acta. 2013;566:257–60.
Zhu BZ, Wang Q, Sun YL, Jia T. Thermal reaction characterization of micron–sized aluminum powders in CO2. Russ J Phys Chem. 2016;10:644–50.
Johnson CE, Fallis S, Chafin AP, Groshens TJ, Higa KT. Characterization of nanometer- to micron-sized aluminum powders: Size distribution from thermogravimetric analysis. J Propul Power. 2007;23:669–82.
Vlaskin MS, Shkolnikov EI, Bersh AV. Oxidation kinetics of micron-sized aluminum powder in high–temperature boiling water. Int J Hydrogen Energ. 2011;36:6484–95.
Feng JQ, Hays DA. Relative importance of electrostatic forces on powder particles. Powder Technol. 2003;135:65–75.
Hu B, Yi Y, Liang C, Yuan ZL, Szczepan R, Yang LJ. Experimental study on particles agglomeration by chemical and turbulent agglomeration before electrostatic precipitators. Powder Technol. 2018;335:186–94.
Hu RZ, Gao SL, Zhao FQ, et al. Thermal analysis kinetics. 2nd ed. Science Press; 2008.
Rufino B, Coulet MV, Bouchet R, Isnard O, Denoyel R. Structural changes and thermal properties of aluminium micro- and nano-powders. Acta Mater. 2010;58:4224–32.
Sun J, Simon SL. The melting behavior of aluminum nanoparticles. Thermochim Acta. 2007;463:32–40.
Schoenitz M, Patel B, Agboh O, Dreizin EL. Oxidation of aluminum powders at high heating rates. Thermochim Acta. 2010;507:115–22.
Jones DEG, Brousseau P, Fouchard RC, Turcotte AM, Kwok QSM. Thermal characterization of passivated nanometer size aluminium powders. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2000;61:805–18.
Sun YL, Sun R, Zhu BZ, Mao KK, Wu YX. Thermal reaction mechanisms of nano- and micro- scale aluminum powders in carbon dioxide at low heating rate. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124:1727–34.
Hasani S, Panjepour M, Shamanian M. Non-isothermal kinetic analysis of oxidation of pure aluminium powder particles. Oxid Met. 2013;81:299–313.
Zeng W, Liu JC, Chen XX, Ma HA. A new reduced reaction mechanism of a surrogate fuel for kerosene. Can J Chem Eng. 2013;91:483–9.
Tognotti L, Malotti A, Petarca L, Zanelli S. Measurement of Ignition Temperature of Coal Particles Using a Thermogravimetric Technique. Combust Sci Tech. 1985;44:15–28.
Trunov MA, Schoenitz M, Zhu XY, Dreizin EL. Effect of polymorphic phase transformations in Al2O3 film on oxidation kinetics of aluminum powders. Combust Flame. 2005;140:310–8.
Trunov MA, Schoenitz M, Dreizin EL. Effect of polymorphic phase transformations in alumina layer on ignition of aluminum particles. Combust Theor Model. 2006;10:603–24.
Rai A, Park K, Zhou L, Zachariah MR. Understanding the mechanism of aluminum nanoparticle oxidation. Combust Theor Model. 2006;10:843–59.
Hasani S, Panjepour M, Shamanian M. The oxidation mechanism of pure aluminium powder particles. Oxid Met. 2012;78:179–95.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support by National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFB4000905), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52104214), and the Youth Innovation Team of Shaanxi Universities, China (No. 22JP049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, J., Deng, J., Luo, ZM. et al. Thermal reaction characterization of nano-aluminum powder at different heating rates by synchronous thermal analysis. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 4937–4947 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11900-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11900-9