Abstract
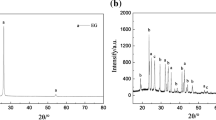
The sodium acetate trihydrate (SAT)/expanded graphite (EG) composite phase change material (PCM) was firstly prepared by absorbing liquid SAT into a porous network of EG, in which SAT acted as the PCM. EG prepared at microwave irradiation power of 800 W for 30 s with maximum volumes has the largest sorption capacity for SAT. At the mass fraction of SAT <95 %, SAT uniformly disperse in the pores of EG without liquid leakage evidenced from scanning electron microscopy characterization. X-ray diffraction results further show that PCM is just a combination between SAT and EG without any chemical reaction. Differential scanning calorimeter measurements indicate that the melting temperature and latent heat of the composite PCM are 59.5 °C and 202 J g−1, respectively, close to those of pure SAT. The thermal conductivity of the composite PCM can be as high as 1.589 W m−1 K−1.The form-stable SAT/EG composite with SAT mass fraction of 95 % has great potential in thermal energy storage due to its moderate melting point, significant latent heat storage capacity, form-stable property, direct usability without need for an extra storage container, and high thermal conductivity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma A, Tyagi VV, Chen CR, Buddhi D. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change materials and applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2009;13(2):318–45.
Zalba B. Maŕin JM, Cabeza LF, Mehling H. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change: materials, heat transfer analysis and applications. Appl Therm Eng. 2003;23(3):251–83.
Karaman S, Karaipekli A, Sari A, Bicer A. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)/diatomite composite as a novel form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2011;95(7):1647–53.
**ao JB, Huang J, Zhu PP, Wang CH, Li XX. Preparation, characterization and thermal properties of binary nitrate salts/expanded graphite as composite phase change material. Thermochim Acta. 2014;587:52–8.
**ao X, Zhang P, Li M. Preparation and thermal characterization of paraffin/metal foam composite phase change material. Appl Energy. 2013;112(SI):1357–66.
Xu BW, Li ZJ. Paraffin/diatomite composite phase change material incorporated cement-based composite for thermal energy storage. Appl Energy. 2013;105:229–37.
Kim T, France DM, Yu WH, Zhao WH, Singh D. Heat transfer analysis of a latent heat thermal energy storage system using graphite foam for concentrated solar power. Sol Energy. 2014;103:438–47.
Stritih U, Osterman E, Evliya H, Butala V, Paksoy H. Exploiting solar energy potential through thermal energy storage in Slovenia and Turkey. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2013;25:442–61.
Kong LB, Li T, Hng HH, Boey F, Zhang TS, Li S. Waste thermal energy harvesting (III): storage with phase change materials. In: Waste energy harvesting. Berlin: Springer; 2014. p. 481–592.
López-Sabirón AM, Royo P, Ferreira VJ, Aranda-Usón A, Ferreira G. Carbon footprint of a thermal energy storage system using phase change materials for industrial energy recovery to reduce the fossil fuel consumption. Appl Energy. 2014;135:616–24.
Cabeza LF, Castell A, Barreneche C, De Gracia A, Fernández AI. Materials used as PCM in thermal energy storage in buildings: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2011;15(3):1675–95.
Tyagi VV, Buddhi D, Kothari R, Tyagi SK. Phase change material (PCM) based thermal management system for cool energy storage application in building: an experimental study. Energy Build. 2012;51:248–54.
Yuan YG, Yuan YP, Zhang N, Du YX, Cao XL. Preparation and thermal characterization of capric–myristic–palmitic acid/expanded graphite composite as phase change material for energy storage. Mater Lett. 2014;125:154–7.
Mesalhy O, Lafdi K, Elgafy A. Carbon foam matrices saturated with PCM for thermal protection purposes. Carbon. 2006;44(10):2080–8.
Li WQ, Qu ZG, He YL, Tao WQ. Experimental and numerical studies on melting phase change heat transfer in open-cell metallic foams filled with paraffin. Appl Therm Eng. 2012;37:1–9.
Karaipekli A, Sarı A. Capric–myristic acid/expanded perlite composite as form-stable phase change material for latent heat thermal energy storage. Renew Energy. 2008;33(12):2599–605.
Karaipekli A, Sarı A. Capric–myristic acid/vermiculite composite as form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy. 2009;83(3):323–32.
Li M, Wu ZS, Kao HT. Study on preparation, structure and thermal energy storage property of capric–palmitic acid/attapulgite composite phase change materials. Appl Energy. 2011;88(9):3125–32.
Sarier N, Onder E, Ozay S, Ozkilic Y. Preparation of phase change material–montmorillonite composites suitable for thermal energy storage. Thermochim Acta. 2011;524(1):39–46.
Zhang N, Yuan YP, Wang X, Cao XL, Yang XJ, Hu SC. Preparation and characterization of lauric-myristic-palmitic acid ternary eutectic mixtures/expanded graphite composite phase change material for thermal energy storage. Chem Eng J. 2013;231:214–9.
**a L, Zhang P, Wang RZ. Preparation and thermal characterization of expanded graphite/paraffin composite phase change material. Carbon. 2010;48(9):2538–48.
Zhang ZG, Shi GQ, Wang SP, Fang XM, Liu XH. Thermal energy storage cement mortar containing n-octadecane/expanded graphite composite phase change material. Renew Energy. 2013;50:670–5.
Zhong LM, Zhang XW, Luan Y, Wang G, Feng YH, Feng DL. Preparation and thermal properties of porous heterogeneous composite phase change materials based on molten salts/expanded graphite. Sol Energy. 2014;107:63–73.
**a L, Zhang P. Thermal property measurement and heat transfer analysis of acetamide and acetamide/expanded graphite composite phase change material for solar heat storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2011;95(8SI):2246–54.
Kim S, Drzal LT. High latent heat storage and high thermal conductive phase change materials using exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2009;93(1):136–42.
Zhang ZG, Fang XM. Study on paraffin/expanded graphite composite phase change thermal energy storage material. Energ Convers Manag. 2006;47(3):303–10.
Zeng JL, Gan J, Zhu FR, Yu SB, **ao ZL, Yan WP, Zhu L, Liu ZQ, Sun LX, Cao Z. Tetradecanol/expanded graphite composite form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2014;127:122–8.
Shi JN, Ger MD, Liu YM, Fan YC, Wen NT, Lin CK, Pu NW. Improving the thermal conductivity and shape-stabilization of phase change materials using nanographite additives. Carbon. 2013;51:365–72.
Wang XL, Guo QG, Zhong YJ, Wei XH, Liu L. Heat transfer enhancement of neopentyl glycol using compressed expanded natural graphite for thermal energy storage. Renew Energy. 2013;51:241–6.
Yuan YP, Li TY, Zhang N, Cao XL, Yang XJ. Investigation on thermal properties of capric-palmitic –stearic acid/activated carbon composite phase change materials for high-temperature cooling application. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;. doi:10.1007/s1097301551730.
Liu SY, Yang HM. Stearic acid hybridizing coal-series kaolin composite phase change material for thermal energy storage. Appl Clay Sci. 2014;101:277–81.
Mills A, Farid M, Selman JR, Al-Hallaj S. Thermal conductivity enhancement of phase change materials using a graphite matrix. Appl Therm Eng. 2006;26(14–15):1652–61.
Sari A, Karaipekli A. Thermal conductivity and latent heat thermal energy storage characteristics of paraffin/expanded graphite composite as phase change material. Appl Therm Eng. 2007;27(8–9):1271–7.
Sari A, Karaipekli A. Preparation, thermal properties and thermal reliability of palmitic acid/expanded graphite composite as form-stable PCM for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2009;93(5):571–6.
Zhang ZG, Zhang N, Peng J, Fang XM, Gao XN, Fang YT. Preparation and thermal energy storage properties of paraffin/expanded graphite composite phase change material. Appl Energy. 2012;91(1):426–31.
Wang WL, Yang XX, Fang YT, Ding J, Yan JY. Preparation and thermal properties of polyethylene glycol/expanded graphite blends for energy storage. Appl Energy. 2009;86(9):1479–83.
Fang GY, Li H, Chen Z, Liu X. Preparation and characterization of stearic acid/expanded graphite composites as thermal energy storage materials. Energy. 2010;35(12):4622–6.
Yang XJ, Yuan YP, Zhang N, Cao XL, Liu C. Preparation and properties of myristic-palmitic-stearic acid/expanded graphite composites as phase change materials for energy storage. Sol Energy. 2014;99:259–66.
Acknowledgements
This study is financially supported by Bei**g Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2132024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, X., Qin, S., Wu, X. et al. Preparation and thermal characterization of sodium acetate trihydrate/expanded graphite composite phase change material. J Therm Anal Calorim 125, 831–838 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5444-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5444-4