Abstract
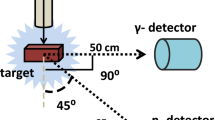
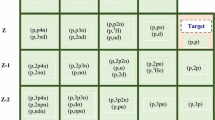
The quantification of induced activity in the accelerator structures and their decay profiles are required to be studied for planning the maintenance operations and the disposal procedures. This paper studies in detail the yield of radioactivity generated in the common beam dump materials, like copper and tantalum irradiated with proton beams of 10 and 20 MeV and their decay profiles using Fluka Monte Carlo simulations. The neutron yields and ambient dose equivalent rates generated from the target materials are also estimated using Fluka Monte Carlo code and are presented. Few of the estimated neutron ambient dose equivalent rates are experimentally validated.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bungau C, Bungau A, Robert C, Roger B, Thomas RE (2014) Induced activation in accelerator components. Phys Rev Spec Top Accel Beams 17:084701-1-12
Fasso A, Silari M, Ulrici L (1999) Predicting induced radioactivity at high energy accelerators, 244 SLAC-PUB-8215:1−9
Torre FL (2014) Study of induced radioactivity in proton accelerator facilities, 252 Universität Bern CERN-THESIS-2014-009. Ph.D. dissertation
Stevenson GR (2001) Induced activity in accelerator structures, air and water. Radiat Prot Dosim 96:373–380
Keshavkumar B, Anand S, Singh KD, Bandyopadhyay T (2017) Estimation of induced air activity in 30 MeV proton accelerator: comparative study of Monte Carlo simulations and analytical calculations. Radiat Prot Environ 40:84–89
National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (2003) Radiation protection for particle accelerator facilities, NCRP Report No. 144
Singh P, Rao SVLS, Pande R, Basak T, Roy S, Aslam M, Jain P, Srivastava SCL, Kumar R, Nema PK, Kailas S, Sahni VC (2007) Accelerator development in India for ADS programme. Pramana J Phys 68:331–342
Ferrari A, Sala PR, Fasso A, Ranft J (2005) CERN-2005-10, INFN/TC_05/11, SLAC-R-773 FLUKA
Böhlen TT, Cerutti F, Chin MPW, Fasso A, Ferrari A, Ortega PG, Mairani A, Sala PA, Smirnov G, Vlachoudis V (2014) The FLUKA code: developments and challenges for high energy and medical applications. Nuclear Data Sheets 120:211–214
Biju K, Vitisha S, Paul S, Sahoo GS, Tripathy SP, Shanbhag AA, Joshi DS, Bandyopadhyay T (2019) Monte Carlo simulation of neutron and photon ambientdose equivalent rates by proton beam irradiation on copper. In: 14th Biennial DAE BRNS symposium on nuclear and radiochemistry (NUCAR-2019), p 174
http://nucleardata.nuclear.lu.se/toi/listnuc.asp?sql=. Last visited 25 Dec 2019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keshavkumar, B., Suman, V., Joshi, D.S. et al. Proton induced radioactivity and neutron yields in tantalum and copper using Monte Carlo simulation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 325, 869–873 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07221-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07221-6