Abstract
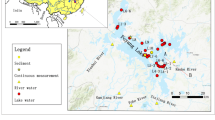
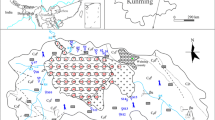
A latest thermokarst lake sampling program was carried out in the Source Area of the Yellow River in September, 2019. Isotopic signatures in water including δ18O, δ2H and 222Rn activities in thermokarst lakes and groundwater were systematically reported. Furthermore, lake water balance metrics and groundwater contributions to lakes were quantified via two isotope mass balance models. Results showed the robust but complex hydrological responses driven by progressive permafrost thaw. Further quantifying the relations between water volumes and other observed biogeochemical impacts to understand the mechanisms in geochemical feedbacks driven by permafrost degradation was needed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan X, You Y, Roth K, Guo L, Wang X, Yu Q (2014) Map** permafrost features that influence the hydrological processes of a thermokarst lake on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Permafr Periglac Process 25(1):60–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp.1797
Lei Y, Yao T, Yang K, Bird BW, Tian L, Zhang X et al (2018) An integrated investigation of lake storage and water level changes in the Paiku Co basin, central Himalayas. J Hydrol 562(May):599–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.05.040
Mao D, Wang Z, Yang H, Li H, Thompson JR, Li L et al (2018) Impacts of climate change on Tibetan lakes: patterns and processes. Remote Sens 10(3):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030358
** H, He R, Cheng G, Wu Q, Wang S, Lü L, Chang X (2009) Changes in frozen ground in the source area of the yellow river on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China, and their eco-environmental impacts. Environ Res Lett 4(4):045206. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/4/4/045206
Ran Y, Li X, Cheng G (2017) Climate warming has led to the degradation of permafrost stability in the past half century over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Cryosphere Discuss. https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-2017-120
Keil A, Berking J, Mügler I, Schütt B, Schwalb A, Steeb P (2010) Hydrological and geomorphological basin and catchment characteristics of lake Nam co, south-central Tibet. Quatern Int 218(1):118–130
Wrozyna C, Frenzel P, Steeb P, Zhu L, Geldern RV, Mackensen A et al (2010) Stable isotope and ostracode species assemblage evidence for lake level changes of Nam co, southern Tibet, during the past 600 years. Quatern Int 212(1):2–13
Chu D, Qiong PU, Wang D, Ciren M, Zhuoma L, Zhang X et al (2012) Water level variations of Yamzho Yumco Lake in Tibet and the main driving forces. J Mt Sci 30(2):239–247
Lin Z, Niu F, Liu H, Lu J (2011) Hydrothermal processes of Alpine Tundra Lakes, Beiluhe Basin, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Cold Reg Sci Technol 65(3):446–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2010.10.013
Jiao JJ, Zhang X, Liu Y, Kuang X (2015) Increased water storage in the Qaidam Basin, the North Tibet Plateau from grace gravity data. PLoS ONE 10(10):e0141442
Séjourné A, Costard F, Fedorov A, Gargani J, Skorve J, Massé M, Mège D (2015) Evolution of the banks of thermokarst lakes in Central Yakutia (Central Siberia) due to retrogressive thaw slump activity controlled by insolation. Geomorphology 241:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.03.033
Turner KW, Wolfe BB, Edwards TWD (2010) Characterizing the role of hydrological processes on lake water balances in the Old Crow Flats, Yukon Territory, Canada, using water isotope tracers. J Hydrol 386(1–4):103–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.03.012
Kokelj SV, Jorgenson MT (2013) Advances in thermokarst research. Permafr Periglac Process 24(2):108–119. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp.1779
Niu F, Lin Z, Liu H, Lu J (2011) Characteristics of thermokarst lakes and their influence on permafrost in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Geomorphology 132(3–4):222–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.05.011
Wan C, Gibson JJ, Shen S, Yi Y, Yi P, Yu Z (2019) Using stable isotopes paired with tritium analysis to assess thermokarst lake water balances in the Source Area of the Yellow River, northeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, China. Sci Total Environ 689:1276–1292
Wan C, Li K, Shen S, Gibson JJ, Ji K, Yi P, Yu Z (2019) Using tritium and 222Rn to estimate groundwater discharge and thawing permafrost contributing to surface water in permafrost regions on Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 322(2):561–578
Yi P, Luo H, Chen L, Yu Z, ** H, Chen X et al (2018) Evaluation of groundwater discharge into surface water by using Radon-222 in the Source Area of the Yellow River, Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. J Environ Radioact 192(November 2017):257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2018.07.003
Luo D, ** H, ** X, He R, Li X, Muskett RR et al (2018) Elevation-dependent thermal regime and dynamics of frozen ground in the Bayan Har Mountains, northeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, southwest China. Permafr Periglac Process 29(4):257–270. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp.1988
Luo D, ** H, Bense VF (2019) Ground surface temperature and the detection of permafrost in the rugged topography on NE Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Geoderma 333(March 2018):57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.07.011
Yi P, Wan C, ** H, Luo D, Yang Y, Wang Q et al (2018) Hydrological insights from hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in Source Area of the Yellow River, east-northern part of Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 317(1):131–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-5864-7
Ren W, Yao T, Yang X, Joswiak DR (2013) Implications of variations in δ18O and δD in precipitation at Madoi in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Quatern Int 313–314:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2013.05.026
Craig H, Gordon LI (1965) Deuterium and oxygen-18 in the ocean and marine atmosphere. In: Tongiorgi E (ed) Stable isotopes in oceanographic studies and paleotemperatures, Spoleto, pp 9–130
MacDonald LA, Wolfe BB, Turner KW, Anderson L, Arp CD, Birks SJ et al (2016) A synthesis of thermokarst lake water balance in high-latitude regions of North America from isotope tracers. Arct Sci 3(2):118–149. https://doi.org/10.1139/as-2016-0019
Gilfedder BS, Frei S, Hofmann H, Cartwright I (2015) Groundwater discharge to wetlands driven by storm and flood events: quantification using continuous Radon-222 and electrical conductivity measurements and dynamic mass-balance modelling. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 165:161–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2015.05.037
MacIntyre S, Fram J, Kushner P, O’brien WJ, Hobbie J, Kling GR, Wanninkhof, Chanton JP (1995) Trace gas exchange across the air-water interface in freshwater and coastal marine environments. In: Biogenic trace gases: measuring emission from soil and water. Blackwell, pp 52–97
Gibson JJ, Birks SJ, Yi Y (2016) Stable isotope mass balance of lakes: a contemporary perspective. Quatern Sci Rev 131:316–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.04.013
Gibson JJ, Birks SJ, Jeffries D, Yi Y (2017) Regional trends in evaporation loss and water yield based on stable isotope mass balance of lakes: the Ontario Precambrian Shield surveys. J Hydrol 544:500–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.11.016
Prakash R, Srinivasamoorthy K, Gopinath S, Saravanan K (2018) Measurement of submarine groundwater discharge using diverse methods in Coleroon Estuary, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl Water Sci 8(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0659-0
Prakash R, Srinivasamoorthy K, Gopinath S, Saravanan K, Vinnarasi F, Ponnumani G et al (2018) Radon isotope assessment of submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) in Coleroon River Estuary, Tamil Nadu, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 317(1):25–36
Srinivasamoorthy K, Ponnumani G, Prakash R, Gopinath S, Saravanan K, Vinnarasi F (2019) Tracing groundwater inputs to Bay of Bengal from Sankarabarani River Basin, Pondicherry, India, using continuous radon monitoring. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(10):5513–5524
Gopinath S, Srinivasamoorthy K, Saravanan K, Prakash R (2019) Tracing groundwater salinization using geochemical and isotopic signature in Southeastern coastal Tamilnadu, India. Chemosphere 236:124305
Lamhonwah D, Lafrenière MJ, Lamoureux SF, Wolfe BB (2017) Evaluating the hydrological and hydrochemical responses of a High Arctic catchment during an exceptionally warm summer. Hydrol Process 31(12):2296–2313. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11191
Rudy ACA, Lamoureux SF, Kokelj SV, Smith IR, England JH (2017) Accelerating thermokarst transforms ice-cored terrain triggering a downstream cascade to the ocean
Luo D, ** H, Lü L, Wu Q (2014) Spatiotemporal characteristics of freezing and thawing of the active layer in the source areas of the Yellow River (SAYR). Chin Sci Bull 59(24):3034–3045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-014-0189-6
Lafrenière MJ, Lamoureux SF (2019) Effects of changing permafrost conditions on hydrological processes and fluvial fluxes. Earth Sci Rev 191(June 2018):212–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.02.018
Finger Higgens RA, Chipman JW, Lutz DA, Culler LE, Virginia RA, Ogden LA (2019) Changing lake dynamics indicate a drier Arctic in Western Greenland. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 124(4):870–883. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JG004879
Balasubramaniam AM, Hall RI, Wolfe BB, Sweetman JN, Wang X (2015) Source water inputs and catchment characteristics regulate limnological conditions of shallow subarctic lakes (Old Crow Flats, Yukon, Canada). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 72(7):1058–1072. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfas-2014-0340
Johansson M, Åkerman HJ (2008) Thawing permafrost and thicker active layers in Sub-arctic Sweden. Permafr Periglac Process 19(January):279–292. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.51979072) and the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA2010010307).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, J. Quantifying the influence of groundwater discharge induced by permafrost degradation on lake water budget in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: using 222Rn and stable isotopes. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 323, 1125–1134 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07025-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07025-8