Abstract
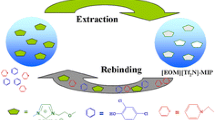
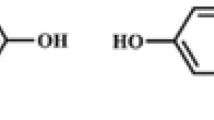
Deep eutectic solvent molecularly imprinted polymer (DES-MIP) was synthesized by bulk polymerization via free radical polymerization using bisphenol A (BPA) as a template, DES as a functional monomer, ethylene glycol dimethyl acrylate (EGDMA) as a crosslinker and benzoyl peroxide as initiator. DES functional monomer was prepared by the combination of choline chloride methacrylic acid (ChCl-MAA). The synthesized DES-MIP was then compared with conventional molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) synthesized using methacrylic acid (MAA) as a functional monomer. The DES-MIP has a higher selectivity for BPA (17.72 mg/g) than competing chemicals, including bisphenol AP (9.78 mg/g), 2-naphthol (8.25), and 4-tertiary butyl-phenol (6.98 mg/g). The optimization parameters include the effects of pH, adsorption kinetics, adsorption isotherm, and thermodynamic studies were investigated. DES-MIP showed the highest binding capacity at pH 7. The kinetic and isotherm studies demonstrated good agreement with a pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm models, respectively. The thermodynamic study proved that the adsorption of BPA on DES-MIP was exothermic and spontaneous with ΔH0 (-23.734 × kJ/mol) and ΔG0 (-2.929 kJ/mol−). Reusability experiments show that the DES-MIP can be recycled five times without significantly diminishing its adsorption capacity. As a result, it proved that the contribution of DES as a functional monomer alternative in MIP synthesis considerably improved the recognition of BPA adsorption.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from authors upon reasonable request.
References
Sikder MT, Rahman MM, Jakariya M, Hosokawa T, Kurasaki M, Saito T (2019) Remediation of water pollution with native cyclodextrins and modified cyclodextrins: A comparative overview and perspectives. Chem Eng J 355:920–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.218
Hahladakis JN, Velis CA, Weber R, Iacovidou E, Purnell P (2018) An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J Hazard Mater 344:179–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.014
Wu YT et al (2014) Selective and simultaneous determination of trace bisphenol A and tebuconazole in vegetable and juice samples by membrane-based molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and HPLC. Food Chem 164:527–535
Almeida S, Raposo A, Almeida-González M, Carrascosa C (2018) Bisphenol A: Food Exposure and Impact on Human Health. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 17(6):1503–1517
Reyes-Gallardo EM, Lucena R, Cárdenas S, Valcárcel M (2016) Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction of bisphenol A from milk using magnetic nylon 6 composite and its final determination by HPLC-UV. Microchem J 124:751–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2015.10.025
Kamel AH, Jiang X, Li P, Liang R (2018) A paper-based potentiometric sensing platform based on molecularly imprinted nanobeads for determination of bisphenol A. Anal Methods 10(31):3890–3895
Sousa JCG, Barbosa MO, Ribeiro ARL, Ratola N, Pereira MFR, Silva AMT (2020) Distribution of micropollutants in estuarine and sea water along the Portuguese coast. Mar Pollut Bull 154:111120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111120
Ćwiek-Ludwicka K (2015) Bisphenol A (BPA) in food contact materials - new scientific opinion from EFSA regarding public health risk. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig 66(4):299–307
Lin Y et al (2008) Removal of phenolic estrogen pollutants from different sources of water using molecularly imprinted polymeric microspheres. Environ Pollut 153(2):483–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.08.001
Fu N et al (2017) Specific recognition of polyphenols by molecularly imprinted polymers based on a ternary deep eutectic solvent. J Chromatogr A 1530:23–34
Yamanaka H, Moriyoshi K, Ohmoto T, Ohe T, Sakai K (2008) Efficient microbial degradation of bisphenol a in the presence of activated carbon. J Biosci Bioeng 105(2):157–160. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.105.157
Villegas LGC, Mashhadi N, Chen M, Mukherjee D, Taylor KE, Biswas N (2016) A short review of techniques for phenol removal from wastewater. Curr Pollut Rep 2(3):157–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-016-0035-3
Tursi A, Chatzisymeon E, Chidichimo F, Beneduci A, Chidichimo G (2018) Removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals from water: Adsorption of bisphenol-a by biobased hydrophobic functionalized cellulose. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15112419
Kyzas GZ et al (2018) Nanobubbles effect on heavy metal ions adsorption by activated carbon. Chem Eng J 356:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.019
Ndagijimana P, Liu X, Li Z, Yu G, Wang Y (2019) Optimized synthesis of a core-shell structure activated carbon and its adsorption performance for Bisphenol A. Sci Total Environ 689:457–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.235
Li G, Dai Y, Wang X, Row KH (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymers modified by deep eutectic solvents and ionic liquids with two templates for the simultaneous solid-phase extraction of Fucoidan and Laminarin from Marine Kelp. Anal Lett 52(3):511–525
Sarafraz-yazdi A, Razavi N (2015) Application of molecularly-imprinted polymers in solid-phase microextraction techniques. Trends Anal Chem 73:81–90
Oh DK, Yang JC, Hong SW, Park J (2020) Molecular imprinting of polymer films on 2D silica inverse opal via thermal graft copolymerization for bisphenol A detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 323(July):128670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128670
Tiwari MP, Prasad A (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymer based enantioselective sensing devices: A review. Anal Chim Acta 853(1):1–18
Song X, Xu S, Chen L, Wei Y, **ong H (2014) Recent advances in molecularly imprinted polymers in food analysis. J Appl Polym Sci 131(16):1–18
Kweinor Tetteh E, Rathilal S, Amankwa Opoku M, Amoah ID, Chollom MN (2021) Molecular imprinting technology: a new approach for antibacterial materials. In: Ahamed MI, Prasad R (eds) Advanced Antimicrobial Materials and Applications Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2021, pp 393–421
Ardekani R, Borhani S, Rezaei B (2020) Selective molecularly imprinted polymer nanofiber sorbent for the extraction of bisphenol A in a water sample. Polym Int 69(9):780–793
Tian Y, Wang Y, Wu S, Sun Z, Gong B (2018) Preparation of ampicillin surface molecularly imprinted polymers for its selective recognition of ampicillin in eggs samples. Int J Anal Chem 11
Viveiros R, Rebocho S, Casimiro T (2018) Green strategies for molecularly imprinted polymer development. Polymers (Basel) 10(3)
Yang T et al (2017) Improving whole-cell biocatalysis by addition of deep eutectic solvents and natural deep eutectic solvents. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(7):5713–5722
López-Porfiri P, Brennecke JF, Gonzalez-Miquel M (2016) Excess molar enthalpies of deep eutectic solvents (DESs) composed of quaternary ammonium salts and glycerol or ethylene glycol. J Chem Eng Data 61(12):4245–4251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.6b00608
Fu N et al (2019) A choline chloride-acrylic acid deep eutectic solvent polymer based on Fe 3 O 4 particles and MoS 2 sheets ( poly ( ChCl-AA DES )@ Fe 3 O 4 @ MoS 2) with specific recognition and good antibacterial properties for β-lactoglobulin in milk. Talanta 197(1):567–577
van der Merwe D, Gehring R, Buur JL (2018) Toxicokinetics in Veterinary Toxicology, Third Edit. Elsevier Inc
Abu-Alsoud GF, Hawboldt KA, Bottaro CS (2020) Comparison of four adsorption isotherm models for characterizing molecular recognition of individual phenolic compounds in porous tailor-made molecularly imprinted polymer films. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(10):11998–12009
Mohamed Idris Z, Hameed BH, Ye L, Hajizadeh S, Mattiasson B, Mohd Din AT (2020) Amino-functionalised silica-grafted molecularly imprinted polymers for chloramphenicol adsorption. J Environ Chem Eng 8(5)
Balayan S, Chauhan N, Chandra R, Jain U (2022) Electrochemical based c-reactive protein (Crp) sensing through molecularly imprinted polymer (mip) pore structure coupled with bi-metallic tuned screen-printed electrode. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 12(6):7697–7714
Mohebali A, Abdouss M, Kazemi Y, Daneshnia S (2021) Fabrication and characterization of pH-responsive poly (methacrylic acid)-based molecularly imprinted polymers nanosphere for controlled release of amitriptyline hydrochloride. Polym Adv Technol 32(11):4386–4396
Ezzati R (2020) Derivation of pseudo-first-order, pseudo-second-order and modified pseudo-first-order rate equations from Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms for adsorption. Chem Eng J 392(September 2019):123705
Ahmed MJ, Dhedan SK (2012) Equilibrium isotherms and kinetics modeling of methylene blue adsorption on agricultural wastes-based activated carbons. Fluid Phase Equilib 317:9–14
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Process Saf Environ Prot 76(2):183–191
Arabi M et al (2021) Molecular imprinting: green perspectives and strategies. Adv Mater 33(30):1–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202100543
Asman S, Mohamad S, Sarih NM (2016) Study of the morphology and the adsorption behavior of molecularly imprinted polymers prepared by reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization process based on two functionalized β-cyclodextrin as monomers. J Mol Liq 214:59–69
Weber TW, Chakravorti RK (1974) Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed-bed adsorbers. AIChE J 20(2):228–238
Surikumaran H, Mohamad S, Sarih NM (2014) Molecular imprinted polymer of methacrylic acid functionalised β-Cyclodextrin for selective removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Int J Mol Sci 15(4):6111–6136
Kavci E (2021) Malachite green adsorption onto modified pine cone: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics mechanism. Chem Eng Commun 208(3):318–327
Rojas G, Silva J, Flores JA, Rodriguez A, Ly M, Maldonado H (2005) Adsorption of chromium onto cross-linked chitosan. Sep Purif Technol 44(1):31–36
Ayankojo AG, Reut J, Ciocan V, Öpik A, Syritski V (2019) Talanta Molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensor for electrochemical detection of erythromycin. Talanta 120502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120502
Piletsky SA et al (1996) A biomimetic receptor system for sialic acid based on molecular imprinting. Anal Lett 29(2):157–170
Yuan X, Liu T, Gao L, **ng L, Zhu Y, Li S (2018) A convenient separation method for di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate by novel superparamagnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. RSC Adv 8(63):36191–36199
Asman S, Mohamad S, Sarih NM (2015) Effects of RAFT agent on the selective approach of molecularly imprinted polymers. Polymers (Basel) 7(3):484–503
Chen W et al (2021) Magnetic-graphene oxide based molecular imprinted polymers for selective extraction of glycoprotein at physiological pH. Polymer (Guildf) 215(October 2020):123384
Mobasherpour I, Salahi E, Ebrahimi M (2014) Thermodynamics and kinetics of adsorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J Saudi Chem Soc 18(6):792–801
Orimi SMH, Khavarpour M, Kazemi S (2020) Removal of bisphenol a from water solution using molecularly imprinted nanopolymers: Isotherm and kinetic studies. J Water Environ Nanotechnol 5(1):56–67
Pazhoor MT, Gautam PK, Samanta S, Suman, Bangotra P, Banerjee S (2021) Performance assessment of Zn–Sn bimetal oxides for the removal of inorganic arsenic in groundwater. Groundw Sustain Dev 14(April):100600
Tomé LIN, Baião V, da Silva W, Brett CMA (2018) Deep eutectic solvents for the production and application of new materials. Appl Mater Today 10:30–50
Acosta R et al (2018) Adsorption of Bisphenol A on KOH-activated tyre pyrolysis char. J Environ Chem Eng 6(1):823–833
Özcan A, Öncü EM, Özcan AS (2006) Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Acid Blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto natural sepiolite. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 277(1–3):90–97
Xu K, Wang Y, Wei X, Chen J, Xu P, Zhou Y (2018) Preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on a deep eutectic solvent as the functional monomer for specific recognition of lysozyme. Microchim Acta 185(2)
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) through Fundamental Research Grant Scheme for Research Acculturation of Early Career Research (FRGS-Racer) RACER/1/2019/STG01/UTHM//2 and assistance support from Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have no conflict of interest including any financial, personal, or other relationships with other people or organizations.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, S.A.H., Asman, S. Evaluation of deep eutectic solvent as a new monomer for molecularly imprinted polymers for removal of bisphenol A. J Polym Res 30, 205 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03581-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03581-1