Abstract
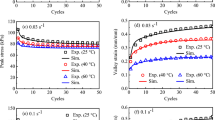
The cyclic deformation of VHB 4910 dielectric elastomer is experimentally investigated by performing a series of strain-controlled and stress-controlled pure-shear-like cyclic tests at room temperature. In the strain-controlled cyclic tests, obvious Mullins effect is observed in the first cycle, and continuous stress softening is characterized in the subsequent cycles; the Mullins effect and continuous stress softening are intensified by prescribing larger peak strains and higher strain rates. In the stress-controlled cyclic tests, remarkable ratchetting takes place, and its evolution becomes more significant if higher stress levels, lower stress rates and longer hold time at peak stress are prescribed. Moreover, a partial recovery of residual strain indicates that, besides obvious hyper-elasticity, the VHB 4910 dielectric elastomer also exhibits both recoverable viscoelasticity and measurable irrecoverable visco-plasticity during the cyclic tests.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pelrine R, Kornbluh R, Pei QB, Joseph J (2000) High-speed electrically actuated elastomers with strain greater than 100%. Science 287(5454):836–839
Carpi F, De Rossi D, Kornbluh R, Pelrine RE, Sommer-Larsen P (2008) Dielectric elastomers as electromechanical transducers: fundamentals, materials, devices, models and applications of an emerging electroactive polymer technology. Elsevier
Li T, Keplinger C, Baumgartner R, Bauer S, Yang W, Suo Z (2013) Giant voltage-induced deformation in dielectric elastomers near the verge of snap-through instability. J Mech Phys Solids 61(2):611–628
Gu G-Y, Zhu J, Zhu L-M, Zhu X (2017) A survey on dielectric elastomer actuators for soft robots. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics 12(1)
Li T, Li G, Liang Y, Cheng T, Dai J, Yang X, Liu B, Zeng Z, Huang Z, Luo Y, **e T, Yang W (2017) Fast-moving soft electronic fish. Sci Adv 3(4):e1602045
Wissler M, Mazza E (2005) Modeling of a pre-strained circular actuator made of dielectric elastomers. Sensors Actuators A Phys 120(1):184–192
Kofod G (2001) Dielectric elastomer actuators: Ph. D. Thesis. The Technical University of Denmark
Gao Z, Tuncer A, Cuitiño AM (2011) Modeling and simulation of the coupled mechanical–electrical response of soft solids. Int J Plast 27(10):1459–1470
Boyce MC, Arruda EM (2000) Constitutive models of rubber elasticity: a review. Rubber Chem Technol 73(3):504–523
Treloar L (1944) Stress-strain data for vulcanised rubber under various types of deformation. Trans Faraday Soc 40:59–70
Schmidt A, Rothemund P, Mazza E (2012) Multiaxial deformation and failure of acrylic elastomer membranes. Sensors Actuators A Phys 174:133–138
Wissler M, Mazza E (2007) Mechanical behavior of an acrylic elastomer used in dielectric elastomer actuators. Sensors Actuators A Phys 134(2):494–504
Sahu RK, Patra K (2016) Rate-dependent mechanical behavior of VHB 4910 elastomer. Mech Adv Mater Struct 23(2):170–179
Sahu RK, Patra K, Szpunar J (2015) Experimental study and numerical modelling of creep and stress relaxation of dielectric elastomers. Strain 51(1):43–54
Michel S, Zhang XQ, Wissler M, Löwe C, Kovacs G (2010) A comparison between silicone and acrylic elastomers as dielectric materials in electroactive polymer actuators. Polym Int 59(3):391–399
Hossain M, Vu DK, Steinmann P (2012) Experimental study and numerical modelling of VHB 4910 polymer. Comput Mater Sci 59:65–74
Qu S, Li K, Li T, Jiang H, Wang M, Li Z (2012) Rate dependent stress-stretch relation of dielectric elastomers subjected to pure shear like loading and electric field. Acta Mech Solida Sin 25(5):542–549
Hossain M, Vu DK, Steinmann P (2015) A comprehensive characterization of the electro-mechanically coupled properties of VHB 4910 polymer. Arch Appl Mech 85(4):523–537
Fan W, Wang Y, Cai S (2017) Fatigue fracture of a highly stretchable acrylic elastomer. Polym Test 61:373–377
Yu W, Chen X, Wang Y, Yan L, Bai N (2008) Uniaxial ratchetting behavior of vulcanized natural rubber. Polym Eng Sci 48(1):191–197
Chen K, Kang G, Lu F, Jiang H (2015) Uniaxial cyclic deformation and internal heat production of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. J Polym Res 22(11)
Chen Y, Kang G, Yuan J, Yu C (2018) Uniaxial ratchetting of filled rubber: experiments and damage-coupled hyper-viscoelastic-plastic constitutive model. J Appl Mech 85(6):061013
Treloar L (1943) The elasticity of a network of long-chain molecules—II. Trans Faraday Soc 39:241–246
Yeoh O (2001) Analysis of deformation and fracture of ‘pure shear’rubber testpiece. Plast Rubber Compos 30(8):389–397
Federico C, Iain A, Siegfried B, Gabriele F, Giuseppe G, Massimiliano G, Christian G, Claire J-M, William K, Guggi K, Matthias K, Roy K, Benny L, Marc M, Silvain M, Stephan N, Benjamin OB, Qibing P, Ron P, Björn R, Samuel R, Herbert S (2015) Standards for dielectric elastomer transducers. Smart Mater Struct 24(10):105025
Vertechy R, Fontana M, Stiubianu G, Cazacu M (2014) Open-access dielectric elastomer material database. In electroactive polymer actuators and devices. Proc of SPIE, San Diego, California. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2045053
Zhou J, Jiang L, Khayat RE (2018) A micro–macro constitutive model for finite-deformation viscoelasticity of elastomers with nonlinear viscosity. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 110:137–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2017.09.016
Diani J, Fayolle B, Gilormini P (2009) A review on the Mullins effect. Eur Polym J 45(3):601–612
Mullins L (1969) Softening of rubber by deformation. Rubber Chem Technol 42(1):339–362
Qi HJ, Boyce MC (2005) Stress–strain behavior of thermoplastic polyurethanes. Mech Mater 37(8):817–839
Lu T, Wang J, Yang R, Wang T (2017) A constitutive model for soft materials incorporating viscoelasticity and Mullins effect. J Appl Mech 84(2):021010
Kang G (2008) Ratchetting: recent progresses in phenomenon observation, constitutive modeling and application. Int J Fatigue 30(8):1448–1472
Fan F, Szpunar J (2015) Characterization of viscoelasticity and self-healing ability of VHB 4910. Macromol Mater Eng 300(1):99–106
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (11272269 and 11572265), the Opening Project of Applied Mechanics and Structure Safety Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, China (SZDLH-1702) and Doctoral Innovation Fund Program of Southwest Jiaotong University (D-CX201837).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Kang, G., Yuan, J. et al. Experimental study on pure-shear-like cyclic deformation of VHB 4910 dielectric elastomer. J Polym Res 26, 186 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1858-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1858-6