Abstract
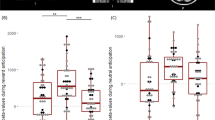
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a heterogeneous disorder. Data on the role of transdiagnostic, intermediate phenotypes in ADHD-relevant characteristics and outcomes are needed to advance conceptual understanding and approaches to precision psychiatry. Specifically, the extent to which the association between neural response to reward and ADHD-associated affective, externalizing, internalizing, and substance use problems differ depending on ADHD status is unknown. Aims were to examine, in 129 adolescents, whether concurrent and prospective associations of fMRI-measured initial response to reward attainment (relative to loss) with affectivity and externalizing, internalizing, and alcohol use problems differs between youth at-risk for (i.e., subclinical) (n = 50) and not at-risk for ADHD. Adolescents were, on average, 15.29 years old (SD = 1.00; 38% female), 50 were at-risk for (Mage = 15.18 years, SD = 1.04; 22% female) and 79 not at-risk for (Mage = 15.37 years, SD = 0.98; 48.1% female) ADHD. Both concurrent and prospective relations differed given ADHD risk: across analyses, in at-risk youth, greater superior frontal gyrus response was associated with lower concurrent depressive problems but in not at-risk youth, these characteristics were not related. Controlling for baseline use, in at-risk youth, greater putamen response was associated with greater 18-month hazardous alcohol use, whereas in not at-risk youth, greater putamen response was associated with lower use. Where in brain and for which outcomes modulate (direction of) observed relations: superior frontal gyrus response is relevant for depressive problems whereas putamen response is relevant for alcohol problems and greater neural responsivity is linked to less depressive but to more alcohol problems in adolescents at-risk for ADHD and less alcohol problems in adolescents not at-risk. Differences in neural response to reward differentially confer vulnerability for adolescent depressive and alcohol problems depending on ADHD risk.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T., & Rescorla, L. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms & Profiles. University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families.
Allen, J. P., Litten, R. Z., Fertig, J. B., & Babor, T. (1997). A Review of Research on the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT). Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000374-199706000-00008.
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). A DSM-5 referencia-kézikönyv a DSM-5 diagnosztikai kritériumaihoz. Oriold és Társai Kft.
American Psychiatric Association. (2022). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision (DSM-5-TR). American Psychiatric Association.
Armstrong, D., Lycett, K., Hiscock, H., Care, E., & Sciberras, E. (2015). Longitudinal Associations Between Internalizing and Externalizing Comorbidities and Functional Outcomes for Children with ADHD. Child Psychiatry and Human Development. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-014-0515-x.
Ayer, L., Rettew, D., Althoff, R. R., Willemsen, G., Ligthart, L., Hudziak, J. J., & Boomsma, D. I. (2011). Adolescent personality profiles, neighborhood income, and young adult alcohol use: A longitudinal study. Addictive Behaviors. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2011.07.004.
Belsky, J. (1997). Variation in Susceptibility to Environmental Influence: An Evolutionary Argument. Psychological Inquiry. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327965pli0803_3.
Bjork, J. M., Chen, G., Smith, A. R., & Hommer, D. W. (2010). Incentive-elicited mesolimbic activation and externalizing symptomatology in adolescents. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 51(7), 827–837. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02201.x.
Bowirrat, A., & Oscar-Berman, M. (2005). Relationship between dopaminergic neurotransmission, alcoholism, and reward deficiency syndrome. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics, 132(1), 29–37. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.30080.
Bunford, N., Hámori, G., Nemoda, Z., Angyal, N., Fiáth, R., Sebők-Welker, T. É., Pászthy, B., Ulbert, I., & Réthelyi, J. M. (2023). The domain-variant indirect association between electrophysiological response to reward and ADHD presentations is moderated by dopaminergic polymorphisms. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 124, 152389 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2023.152389.
Bunford, N., Wymbs, B. T., Dawson, A. E., & Shorey, R. C. (2017). Childhood Maltreatment, Emotional Lability, and Alcohol Problems in Young Adults At-Risk for ADHD: Testing Moderation and Moderated Moderation. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 49(4), 316–325. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2017.1325031.
Burrows, K., Stewart, J. L., Kuplicki, R., Figueroa-Hall, L., Spechler, P. A., Zheng, H., Guinjoan, S. M., Savitz, J. B., Kent Teague, T., & Paulus, M. P. (2021). Elevated peripheral inflammation is associated with attenuated striatal reward anticipation in major depressive disorder. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 93, 214–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2021.01.016.
Campez, M., Raiker, J. S., Sarver, D. E., Friedman, L. M., Orban, S. A., & Rapport, M. D. (2020). Working Memory Capacity and ADHD Symptoms in Boys: Examining the Heterogeneity of Working Memory Functioning Using Latent Profile Analysis. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-019-09762-x.
Corr, P. J., & McNaughton, N. (2012). Neuroscience and approach/avoidance personality traits: A two stage (valuation-motivation) approach. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 36, 2339–2354.
Cremers, H. R., Veer, I. M., Spinhoven, P., Rombouts, S. A. R. B., & Roelofs, K. (2015). Neural sensitivity to social reward and punishment anticipation in social anxiety disorder. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 8, 439 https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00439.
Derryberry, D., & Rothbart, M. K. (1997). Reactive and effortful processes in the organization of temperament. Development and Psychopathology, 9(4), 633–652. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579497001375.
DuPaul, G. J., Power, T. J., Anastopoulos, A. D., & Reid, R. (2016). ADHD Rating Scale-5 for Children and Adolescents. The Guilford Press.
Durazzo, T. C., Tosun, D., Buckley, S., Gazdzinski, S., Mon, A., Fryer, S. L., & Meyerhoff, D. J. (2011). Cortical thickness, surface area, and volume of the brain reward system in alcohol dependence: Relationships to relapse and extended abstinence. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 35(6), 1187–1200. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01452.x.
Erdman, A., Abend, R., Jalon, I., Artzi, M., Gazit, T., Avirame, K., Ais, E. D., Levokovitz, H., Gilboa-Schechtman, E., Hendler, T., & Harel, E. V. (2020). Ruminative Tendency Relates to Ventral Striatum Functionality: Evidence From Task and Resting-State fMRI. Frontiers in Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00067.
Fair, D. A., Bathula, D., Nikolas, M. A., Nigg, J. T., Iyer, S., Bathula, D., Mills, K. L., Dosenbach, N. U. F., Schlaggar, B. L., Mennes, M., Gutman, D., Bangaru, S., Buitelaar, J. K., Dickstein, D. P., Di Martino, A., Kennedy, D. N., Kelly, C., Luna, B., Schweitzer, J. B., & Milham, M. P. (2012). Distinct neuropsychological subgroups in typically develo** youth inform heterogeneity in children with ADHD. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 6, 80 https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1115365109.
Faraone, S. V., Biederman, J., & Mick, E. (2006). The age-dependent decline of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analysis of follow-up studies. Psychological Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1017/s003329170500471x.
Forbes, E. E., Christopher May, J., Siegle, G. J., Ladouceur, C. D., Ryan, N. D., Carter, C. S., Birmaher, B., Axelson, D. A., & Dahl, R. E. (2006). Reward-related decision-making in pediatric major depressive disorder: An fMRI study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 47(10), 1031–1040. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01673.x.
Gerevich, J., Bácskai, E., & Rózsa, S. (2006). Prevalence of hazardous alcohol use. Psychiatria Hungarica: A Magyar Pszichiátriai Társaság Tudományos Folyóirata, 21(1), 45–56.
Gregory, S., Blair, R. J., ffytche, D., Simmons, A., Kumari, V., Hodgins, S., & Blackwood, N. (2015). Punishment and psychopathy: A case-control functional MRI investigation of reinforcement learning in violent antisocial personality disordered men. The Lancet Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(14)00071-6.
Grimm, O., van Rooij, D., Tshagharyan, A., Yildiz, D., Leonards, J., Elgohary, A., Buitelaar, J., & Reif, A. (2021). Effects of comorbid disorders on reward processing and connectivity in adults with ADHD. Translational Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01758-0.
Gyollai, Á., Simor, P., Köteles, F., & Demetrovics, Z. (2011). Psychometric properties of the Hungarian version of the original and the short form of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS). Neuropsychopharmacologia Hungarica: A Magyar Pszichofarmakologiai Egyesulet Lapja = Official Journal of the Hungarian Association of Psychopharmacology, 13(2), 73–79.
Haber, S. N. (2011). Frontiers in Neuroscience Neuroanatomy of Reward: A View from the Ventral Striatum. In Neurobiology of Sensation and Reward. CRC Press (Taylor and Francis Group).
Hai, T., Swansburg, R., Kahl, C. K., Frank, H., Stone, K., Lemay, J., & McMaster, F. P. (2022). Right Superior Frontal Gyrus Cortical Thickness in Pediatric ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1177/10870547221110918.
Hámori, G., File, B., Fiáth, R., Pászthy, B., Réthelyi, J. M., Ulbert, I., & Bunford, N. (2023). Adolescent ADHD and electrophysiological reward responsiveness: A machine learning approach to evaluate classification accuracy and prognosis. Psychiatry Research, 323, 115139 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2023.115139.
Hámori, G., Rádosi, A., Pászthy, B., Réthelyi, J. M., Ulbert, I., Fiáth, R., & Bunford, N. (2022). Reliability of reward ERPs in middle‐late adolescents using a custom and a standardized preprocessing pipeline. Psychophysiology, 59(8), e14043.
Hartman, S., & Belsky, J. (2018). Prenatal stress and enhanced developmental plasticity. Journal of Neural Transmission, 125(12), 1759–1779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-018-1926-9.
Hasler, B. P., Sitnick, S. L., Shaw, D. S., & Forbes, E. E. (2013). An altered neural response to reward may contribute to alcohol problems among late adolescents with an evening chronotype. Psychiatry Research - Neuroimaging, 214(3), 357–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2013.08.005.
Hayes, A. F. (2022). Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: Third Edition: A Regression-Based Approach (3rd ed.). https://www.guilford.com/books/Introduction-to-Mediation-Moderation-and-Conditional-Process-Analysis/Andrew-Hayes/9781462549030.
Horváth, Z., Paksi, B., Felvinczi, K., Griffiths, M. D., Demetrovics, Z., & Urbán, R. (2019). An empirically based typology of alcohol users in a community sample using latent class analysis. European Addiction Research. https://doi.org/10.1159/000501516.
Hungarian Central Statistical Office. (2011). Nemzetiségi adatok. Népszámlálás, 2011. https://www.ksh.hu/nepszamlalas/tablak_nemzetiseg.
Hungarian Central Statistical Office. (2020). 147 247 Ft volt az egy főre eső nettó havi átlagjövedelem. Egy Főre Jutó Bruttó És Nettó Jövedelem Régió És Településtípus Szerint [Forint/Fő/Év]. https://www.ksh.hu/stadat_files/jov/hu/jov0045.html.
Ivanov, I., Parvaz, M. A., Velthorst, E., Shaik, R. B., Sandin, S., Gan, G., Spechler, P., Albaugh, M. D., Chaarani, B., Mackey, S., Banaschewski, T., Bokde, A. L. W., Bromberg, U., Büchel, C., Quinlan, E. B., Desrivières, S., Flor, H., Grigis, A., Gowland, P., & Stedman, A. (2021). Substance Use Initiation, Particularly Alcohol, in Drug-Naive Adolescents: Possible Predictors and Consequences From a Large Cohort Naturalistic Study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 60(5), 623–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2020.08.443.
Kieling, C., Kieling, R. R., Rohde, L. A., Frick, P. J., Moffitt, T., Nigg, J. T., Tannock, R., & Castellanos, F. X. (2010). The Age at Onset of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09060796.
Kopala-Sibley, D. C., Cyr, M., Finsaas, M. C., Orawe, J., Huang, A., Tottenham, N., & Klein, D. N. (2020). Early Childhood Parenting Predicts Late Childhood Brain Functional Connectivity During Emotion Perception and Reward Processing. Child Development. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.13126.
Kujawa, A., Carroll, A., Mumper, E., Mukherjee, D., Kessel, E. M. E. M., Olino, T., Hajcak, G., & Klein, D. N. D. N. (2018). A longitudinal examination of event-related potentials sensitive to monetary reward and loss feedback from late childhood to middle adolescence. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 132(Nov), 323–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2017.11.001.
Liskola, J., Haravuori, H., Lindberg, N., Niemelä, S., Karlsson, L., Kiviruusu, O., & Marttunen, M. (2018). AUDIT and AUDIT-C as screening instruments for alcohol problem use in adolescents. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 188, 266–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2018.04.015.
Luking, K. R., Infantolino, Z. P., Nelson, B. D., & Hajcak, G. (2019). Age-typical changes in neural reward response are moderated by maternal anhedonia. Psychophysiology. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.13358.
Luking, K. R., Nelson, B. D., Infantolino, Z. P., Sauder, C. L., & Hajcak, G. (2017). Internal Consistency of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Electroencephalography Measures of Reward in Late Childhood and Early Adolescence. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2016.12.004.
Luking, K. R., Nelson, B. D., Infantolino, Z. P., Sauder, C. L., & Hajcak, G. (2018). Ventral Striatal Function Interacts With Positive and Negative Life Events to Predict Concurrent Youth Depressive Symptoms. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2018.07.007.
Maldjian, J. A., Laurienti, P. J., & Burdette, J. H. (2004). Precentral gyrus discrepancy in electronic versions of the Talairach atlas. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.09.032.
Maldjian, J. A., Laurienti, P. J., Kraft, R. A., & Burdette, J. H. (2003). An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00169-1.
Maresh, E. L., Allen, J. P., & Coan, J. A. (2014). Increased default mode network activity in socially anxious individuals during reward processing. Biology of Mood and Anxiety Disorders, 4(7), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-5380-4-7.
Martins, J. S., Joyner, K. J., McCarthy, D. M., Morris, D. H., Patrick, C. J., & Bartholow, B. D. (2022). Differential brain responses to alcohol-related and natural rewards are associated with alcohol use and problems: Evidence for reward dysregulation. Addiction Biology, 27(2), e13118 https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.13118.
Matthys, W., Van Goozen, S. H. M., Snoek, H., & Van Engeland, H. (2004). Response perseveration and sensitivity to reward and punishment in boys with oppositional defiant disorder. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 13, 362–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-004-0395-x.
Mikita, N., Simonoff, E., Pine, D. S., Goodman, R., Artiges, E., Banaschewski, T., Bokde, A. L., Bromberg, U., Büchel, C., Cattrell, A., Conrod, P. J., Desrivières, S., Flor, H., Frouin, V., Gallinat, J., Garavan, H., Heinz, A., Ittermann, B., Jurk, S., & Stringaris, A. (2016). Disentangling the autism—Anxiety overlap: FMRI of reward processing in a community-based longitudinal study. Translational Psychiatry, 6(6), e845–e845. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.107.
Muench, C., Schwandt, M., Jung, J., Cortes, C. R., Momenan, R., & Lohoff, F. W. (2018). The major depressive disorder GWAS-supported variant rs10514299 in TMEM161B-MEF2C predicts putamen activation during reward processing in alcohol dependence. Translational Psychiatry, 8(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0184-9.
Perner, J., Kain, W., & Barchfeld, P. (2002). Executive control and higher-order theory of mind in children at risk of ADHD. Infant and Child Development, 11(2), 141–158. https://doi.org/10.1002/icd.302.
Pillow, D. R., Pelham, W. E., Hoza, B., Molina, B. S. G., & Stultz, C. H. (1998). Confirmatory factor analyses examining attention deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms and other childhood disruptive behaviors. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 26(4), 293–309. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022658618368.
Plichta, M. M., & Scheres, A. (2014). Ventral-striatal responsiveness during reward anticipation in ADHD and its relation to trait impulsivity in the healthy population: A meta-analytic review of the fMRI literature. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 38, 125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.07.012.
Rádosi, A., Pászthy, B., Welker, T., Zubovics, E. A., Réthelyi, J. M., Ulbert, I., & Bunford, N. (2021). The association between reinforcement sensitivity and substance use is mediated by individual differences in dispositional affectivity in adolescents. Addictive Behaviors. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106719.
Reinert, D. F., & Allen, J. P. (2002). The alcohol use disorders identification test (AUDIT): A review of recent research. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 26(2), 272–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2002.tb02534.x.
Rosen, P. J., Walerius, D. M., Fogleman, N. D., & Factor, P. I. (2015). The association of emotional lability and emotional and behavioral difficulties among children with and without ADHD. ADHD Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorders, 7(4), 281–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-015-0175-0.
Roy, A., Hechtman, L., Roy, A., Arnold, L. E., Sibley, M. H., Molina, B. S. G., Swanson, J. M., Howard, A. L., Vitiello, B., Severe, J. B., Jensen, P. S., Arnold, L. E., Hoagwood, K., Richters, J., Vereen, D., Hinshaw, S. P., Elliott, G. R., Wells, K. C., Epstein, J. N., & Stern, K. (2016). Childhood Factors Affecting Persistence and Desistence of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms in Adulthood: Results From the MTA. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2016.05.027.
Scarpelli, S., Gorgoni, M., D’atri, A., Reda, F., & De Gennaro, L. (2019). Advances in understanding the relationship between sleep and attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Journal of Clinical Medicine. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101737.
Scheres, A., Lee, A., & Sumiya, M. (2008). Temporal reward discounting and ADHD: Task and symptom specific effects. Journal of Neural Transmission, 115(2), 221–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-007-0813-6.
Schwenck, C., Ciaramidaro, A., Selivanova, M., Tournay, J., Freitag, C. M., & Siniatchkin, M. (2017). Neural correlates of affective empathy and reinforcement learning in boys with conduct problems: FMRI evidence from a gambling task. Behavioural Brain Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.11.037.
Sebők-Welker, T., Posta, E., Ágrez, K., Rádosi, A., Zubovics, E., Réthelyi, J. M., Ulbert, I., Pászthy, B., & Bunford, N. (2023). The association between prenatal maternal stress and adolescent affective outcomes is mediated by childhood maltreatment and adolescent behavioral inhibition system sensitivity. Child Psychiatry and Human Development. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-023-01499-9.
Shaw, P., Eckstrand, K., Sharp, W., Blumenthal, J., Lerch, J. P., Greenstein, D., Clasen, L., Evans, A., Giedd, J., & Rapoport, J. L. (2007). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is characterized by a delay in cortical maturation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0707741104.
Sonuga-Barke, E. J. S., Sergeant, J. A., Nigg, J., & Willcutt, E. (2008). Executive Dysfunction and Delay Aversion in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Nosologic and Diagnostic Implications. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 17(2), 367–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2007.11.008.
Spechler, P. A., Stewart, J. L., Kuplicki, R., Aupperle, R., Bodurka, J., Feinstein, J., Khalsa, S. S., Paulus, M. P., Savitz, J., Stewart, J., & Victor, T. A. (2020). Attenuated reward activations associated with cannabis use in anxious/depressed individuals. Translational Psychiatry, 10(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-0807-9.
Stoet, G. (2017). PsyToolkit: A Novel Web-Based Method for Running Online Questionnaires and Reaction-Time Experiments. Teaching of Psychology, 44(1), 24–31. https://doi.org/10.1177/0098628316677643.
Ströhle, A., Stoy, M., Wrase, J., Schwarzer, S., Schlagenhauf, F., Huss, M., Hein, J., Nedderhut, A., Neumann, B., Gregor, A., Juckel, G., Knutson, B., Lehmkuhl, U., Bauer, M., Heinz, A., Strohle, A., Stoy, M., Wrase, J., Schwarzer, S., & Heinz, A. (2008). Reward anticipation and outcomes in adult males with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. NeuroImage, 39(3), 966–972. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.09.044.
Talati, A., van Dijk, M., Pan, L., Hao, X., Wang, Z., Gameroff, M., Dong, Z., Kayser, J., Shankman, S., Wickramaratne, P., Posner, J., & Weissman, M. (2022). Putamen structure and function in familial risk for depression: A multimodal imaging study. Biological Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2022.06.035.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., Mazoyer, B., & Joliot, M. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage, 15, 273–289.
van Eck, K., Finney, S. J., & Evans, S. W. (2010). Parent report of adhd symptoms of early adolescents: A confirmatory factor analysis of the disruptive behavior disorders scale. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 70, 1042–1059. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164410378093.
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54, 1063–1070. https://doi.org/10.1521/soco_2012_1006.
Wechsler, D. (2003). Wechsler intelligence scale for children–Fourth Edition (WISC-IV). San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation.
Wechsler, D. (2008). Wechsler adult intelligence scale–Fourth Edition (WAIS–IV). APA PsycTests.
Wellington, T. M., Semrud-Clikeman, M., Gregory, A. L., Murphy, J. M., & Lancaster, J. L. (2006). Magnetic resonance imaging volumetric analysis of the putamen in children with ADHD. Combined type versus control. Journal of Attention Disorders, 10(2), 171–180. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054705284242.
Wimberley, T., Agerbo, E., Horsdal, H. T., Ottosen, C., Brikell, I., Als, T. D., Demontis, D., Børglum, A. D., Nordentoft, M., Mors, O., Werge, T., Hougaard, D., Bybjerg-Grauholm, J., Hansen, M. B., Mortensen, P. B., Thapar, A., Riglin, L., Langley, K., & Dalsgaard, S. (2020). Genetic liability to ADHD and substance use disorders in individuals with ADHD. Addiction. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.14910.
Zhang, B., Qi, S., Liu, S., Liu, X., Wei, X., & Ming, D. (2021). Altered spontaneous neural activity in the precuneus, middle and superior frontal gyri, and hippocampus in college students with subclinical depression. BMC Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-021-03292-1.
Zhang, D. W., Li, H., Wu, Z., Zhao, Q., Song, Y., Liu, L., Qian, Q., Wang, Y., Roodenrys, S., Johnstone, S. J., De Blasio, F. M., & Sun, L. (2019). Electroencephalogram Theta/Beta Ratio and Spectral Power Correlates of Executive Functions in Children and Adolescents With AD/HD. Journal of Attention Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054717718263.
Authors’ Contributions
A.R. conceived the study, developed and designed the methodology, participated in data curation, carried out formal analysis and data visualization, took part in project administration and investigation, and participated in writing the original draft and in editing and review; K.Á. participated in data curation, carried out formal analysis, took part in project administration and investigation, and participated in writing the original draft and in editing and review; B.P. took part in conceptualization and participated in reviewing and editing the original draft; J.R. took part in conceptualization and participated in reviewing and editing the original draft; I.U. took part in conceptualization and participated in reviewing and editing the original draft; N.B. conceived the study, developed and designed the methodology, carried out formal analysis, obtained funds for the study and supervised the study, and participated in writing the original draft and in editing and review. All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a Hungarian Academy of Sciences Momentum (“MTA Lendület”) Grant awarded to N.B. (#LP2018-3/2018). During the preparation of this article, A.R. was supported by New National Excellence Programme (ÚNKP-21-3-II-SE-53) and SE250+ (EFOP-3.6.3-VEKOP-16-2017-00009) fellowships.
Data Sharing and Declaration
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the github repository, https://github.com/agrezk/Radosi_et_al_JOYO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
This research was approved by the National Institute of Pharmacy and Nutrition (OGYÉI/17089-8/2019). This research was performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed Consent
The parents of all participants gave informed consent and all participants gave informed assent prior to participation.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rádosi, A., Ágrez, K., Pászthy, B. et al. Concurrent and Prospective Associations of Reward Response with Affective and Alcohol Problems: ADHD-Related Differential Vulnerability. J Youth Adolescence 52, 1856–1872 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-023-01794-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-023-01794-7