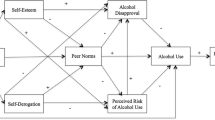
Abstract
Exposure to alcohol content in the media, especially in movies, is a demonstrated risk factor for adolescent alcohol use. This paper examines processes underlying this association and whether parenting mitigates such harms. A mediational model of parental restriction of mature media (W1), alcohol content exposure (W2), alcohol expectancies, peer norms (W3), and alcohol outcomes (W4) was tested using annual assessments from a study of adolescent drinking (N = 879; 52% female; 21% Non-White; 12% Hispanic). When restrictions are not in place, adolescents report greater exposure to alcohol content, leading to higher perceived peer drinking. Parental monitoring did not buffer the link between exposure and peer norms. Parental media restriction and perceptions about peers comprise mechanisms by which alcohol-saturated media influences youth drinking.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abar, C., & Turrisi, R. (2008). How important are parents during the college years? A longitudinal perspective of indirect influences parents yield on their college teens’ alcohol use. Addictive Behaviors. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2008.06.010.
Anderson, P., De Bruijn, A., Angus, K., Gordon, R., & Hastings, G. (2009). Special issue: the message and the media: Impact of alcohol advertising and media exposure on adolescent alcohol use: a systematic review of longitudinal studies. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 44(3), 229–243. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agn115.
Arthur, M. W., Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., & Pollard, J. A. (2000). Student Survey of Risk and Protective Factors and Prevalence of Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drug Use. Seattle: University of Washington, Social Development Research Group.
Babor, T., Higgins-Biddle, J. C., Saunders, J. B., & Monteiro, M. G. (2001). The alcohol use disorders identification test: guidelines for use in primary care. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Bandura, A. (1971). Social learning theory. Social Learning Theory. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-2466.1978.tb01621.x.
Bauer, D. J., Preacher, K. J., & Gil, K. M. (2006). Conceptualizing and testing random indirect effects and moderated mediation in multilevel models: New procedures and recommendations. Psychological Methods, 11, 142–163.
Boyle, S. C., LaBrie, J. W., Froidevaux, N. M., & Witkovic, Y. D. (2016). Different digital paths to the keg? How exposure to peers’ alcohol-related social media content influences drinking among male and female first-year college students. Addictive Behaviors, 57, 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.01.011.
Brown, K. G., Stautz, K., Hollands, G. J., Winpenny, E. M., & Marteau, T. M. (2016). The cognitive and behavioural impact of alcohol promoting and alcoholwarning advertisements: An experimental study. Alcohol Alcohol, 51(3), 354–362. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agv104.
Buckingham, D. (2013). Is there a digital generation. Digital generations: children, young people and the new media. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004.
Chassin, L., Presson, C. C., Todd, M.M., Rose, J. S., & Sherman, S. J. (1998). Maternal socialization of adolescent smoking: The intergenerational transmission of parenting and smoking. Developmental Psychology, 34, 1189–1201.1.
Clark, D. B., Thatcher, D. L., & Tapert, S. F. (2008). Alcohol, psychological dysregulation, and adolescent brain development. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 32(3), 375–385. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00601.x.
Clark, L. S. (2011). Parental mediation theory for the digital age. Communication Theory, 21(4), 323–343. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2885.2011.01391.x.
Cleveland, M. J., Feinberg, M. E., Wayne Osgood, D., & Moody, J. (2012). Do peers’ parents matter? A new link between positive parenting and adolescent substance use. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 73(3), 423–433. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsad.2012.73.423.
Collins, R. L, Martino, S. C., & Shaw, R. (2011). Influence of new media on adolescent sexual health: evidence and opportunities (Working paper WR-761). Santa Monica, CA: RAND Health.
Collins, R. L., Martino, S. C., Kovalchik, S. A., D’Amico, E. J., Shadel, W. G., Becker, K. M., & Tolpadi, A. (2017). Exposure to alcohol advertising and adolescents’ drinking beliefs: Role of message interpretation. Health psychology, 36(9), 890.
Cox, M. J., DiBello, A. M., Meisel, M. K., Ott, M. Q., Kenney, S. R., Clark, M. A., & Barnett, N. P. (2019). Do misperceptions of peer drinking influence personal drinking behavior? results from a complete social network of first-year college students. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 33(3), 297–303. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000455.
Cox, M. J., Gabrielli, J., Janssen, T., & Jackson, K. M. (2018). Parental restriction of movie viewing prospectively predicts adolescent alcohol and marijuana initiation: implications for media literacy programs. Prevention Science, 19(7), 914–926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-018-0891-8.
Curtis, B. L., Lookatch, S. J., Ramo, D. E., McKay, J. R., Feinn, R. S., & Kranzler, H. R. (2018). Meta-analysis of the association of alcohol-related social media use with alcohol consumption and alcohol-related problems in adolescents and young adults. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 42(6), 978–986. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.13642.
Dal Cin, S., Worth, K. A., Gerrard, M., Gibbons, F. X., Stoolmiller, M., Wills, T. A., & Sargent, J. D. (2009). Watching and drinking: expectancies, prototypes, and friends’ alcohol use mediate the effect of exposure to alcohol use in movies on adolescent drinking. Health Psychology, 28(4), 473–483. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014777.
Dalton, M. A., Adachi-Mejia, A. M., Longacre, M. R., Titus-Ernstoff, L. T., Gibson, J. J., Martin, S. K., & Beach, M. L. (2006). Parental rules and monitoring of children’s movie viewing associated with children’s risk for smoking and drinking. Pediatrics, 118(5), 1932–1942. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2005-3082.
Dishion, T. J., & McMahon, R. J. (1998). Parental monitoring and the prevention of child and adolescent problem behavior: a conceptual and empirical formulation. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 1(1), 61–75. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021800432380.
Elmore, K. C., Scull, T. M., & Kupersmidt, J. B. (2017). Media as a “super peer”: how adolescents interpret media messages predicts their perception of alcohol and tobacco use norms. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 46(2), 376–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-016-0609-9.
Festinger, L. (1954). A theory of social comparison processes. Human Relations, 7(2), 117–140. https://doi.org/10.1177/001872675400700202.
Frissell, K. C., McCarthy, D. M., D’Amico, E. J., Metrik, J., Ellingstad, T. P., & Brown, S. A. (2004). Impact of consent procedures on reported levels of adolescent alcohol use. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 18, 307–315.
Gabrielli, J., Marsch, L., & Tanski, S. (2018). TECH parenting to promote effective media management. Pediatrics, 142(1). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2017-3718.
Geusens, F., & Beullens, K. (2018). The association between social networking sites and alcohol abuse among belgian adolescents: the role of attitudes and social norms. Journal of Media Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1027/1864-1105/a000196.
Gibbons, F. X., Kingsbury, J. H., Wills, T. A., Finneran, S. D., Cin, S. D., & Gerrard, M. (2016). Impulsivity moderates the effects of movie alcohol portrayals on adolescents’ willingness to drink. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 30(3), 325–334. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000178.
Gibbons, F. X., Pomery, E. A., Gerrard, M., Sargent, J. D., Weng, C. Y., Wills, T. A., & Yeh, H. C. (2010). Media as social influence: racial differences in the effects of peers and media on adolescent alcohol cognitions and consumption. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 24(4), 649–659. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020768.
Giles, D. C., & Maltby, J. (2004). The role of media figures in adolescent development: Relations between autonomy, attachment, and interest in celebrities. Personality and Individual Differences, 36(4), 813–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8869(03)00154-5.
Goldman, M. S., Del Boca, F. K., & Darkes, J. (1999). Alcohol expectancy theory: The application of cognitive neuroscience. In K. E. Leonard & H. T. Blane (Eds), The Guilford substance abuse series. Psychological theories of drinking and alcoholism (pp. 203–246). The Guilford Press.
Hingson, R. W., Heeren, T., Jamanka, A., & Howland, J. (2000). Age of drinking onset and unintentional injury involvement after drinking. Journal of the American Medical Association, 284(12), 1527–1533. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.284.12.1527.
Jackson, K. M., & Bartholow, B. D. (2020). Psychological Processes Underlying Effects of Alcohol Marketing on Youth Drinking. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs. Supplement, 81–96. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsads.2020.s19.81.
Jackson, K. M., Janssen, T., Barnett, N. P., Rogers, M. L., Hayes, K. L., & Sargent, J. (2018). Exposure to alcohol content in movies and initiation of early drinking milestones. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 42(1), 184–194. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.13536.
Janssen, T., Cox, M. J., Merrill, J. E., Barnett, N. P., Sargent, J. D., & Jackson, K. M. (2018). Peer norms and susceptibility mediate the effect of movie alcohol exposure on alcohol initiation in adolescents. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors. https://doi.org/10.1037/adb0000338.
Janssen, T., Larsen, H., Peeters, M., Pronk, T., Vollebergh, W. A. M., & Wiers, R. W. (2014). Interactions between parental alcohol-specific rules and risk personalities in the prediction of adolescent alcohol use. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 49(5), 579–585. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/agu039.
Kenney, S. R., Ott, M., Meise, M. K., & Barnett, N. P. (2017). Alcohol perceptions and behavior in a residential peer social network. Addictive Behaviors, 64, 143–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.08.047.
Kerr, M., & Stattin, H. (2000). What parents know, how they know it, and several forms of adolescent adjustment: further support for a reinterpretation of monitoring. Developmental Psychology, 36(3), 366–380. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.36.3.366.
Koordeman, R., Anschutz, D. J., & Engels, R. C. M. E. (2012). Alcohol portrayals in movies, music videos and soap operas and alcohol use of young people: current status and future challenges. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 47(5), 612–623. https://doi.org/10.1093/alcalc/ags073.
Krosnick, J. A., & Alwin, D. F. (1989). Aging and susceptibility to attitude change. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 57(3), 416–425. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.57.3.416.
Liu, C., Cox, R. B. Jr., Washburn, I. J., Croff, J. M., & Crethar, H. C. (2017). The effects of requiring parental consent for research on adolescents’ risk behaviors: a meta-analysis. Journal of Adolescent Health, 61(1), 45–52.
Madden, M., Lenhart, A., Cortesi, S., Gasser, U., Duggan, M., Smith, A., & Beaton, M. (2013). Teens, social media, and privacy. Pew Research Center, 21(1055), 2–86.
Marschall-Lévesque, S., Castellanos-Ryan, N., Vitaro, F., & Séguin, J. R. (2014). Moderators of the association between peer and target adolescent substance use. Addictive Behaviors, 39(1), 48–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.09.025.
Martino, S. C., Collins, R. L., Ellickson, P. L., Schell, T. L., & McCaffrey, D. (2006). Socio-environmental influences on adolescents’ alcohol outcome expectancies: a prospective analysis. Addiction, 101(7), 971–983. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1360-0443.2006.01445.x.
Martino, S. C., Kovalchik, S. A., Collins, R. L., Becker, K. M., Shadel, W. G., & D’Amico, E. J. (2016). Ecological momentary assessment of the association between exposure to alcohol advertising and early adolescents’ beliefs about alcohol. Journal of Adolescent Health, 58(1), 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2015.08.010.
McCreanor, T., Barnes, H. M., Kaiwai, H., Borell, S., & Gregory, A. (2008). Creating intoxigenic environments: Marketing alcohol to young people in Aotearoa New Zealand. Social Science and Medicine, 67(6), 938–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2008.05.027.
McGue, M., Iacono, W. G., Legrand, L. N., & Elkins, I. (2001). Origins and consequences of age at first drink. II. Familial risk and heritability. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 25(8), 1166–1173. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2001.tb02331.x.
Mejia, R., Pérez, A., Peña, L., Morello, P., Kollath-Cattano, C., Braun, S., & Sargent, J. D. (2016). Parental Restriction of Mature-rated Media and Its Association with Substance Use among Argentinean Adolescents. Academic Pediatrics, 16(3), 282–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acap.2015.11.004.
Miech, R. A., Johnston, L. D., O’Malley, P. M., Bachman, J. G., Schulenberg, J. E., & Patrick, M. E. (2018). Monitoring the Future national survey results on drug use, 1975-2017: Volume I, secondary school students. Monitoring the Future national survey results on drug use, 1975–2017: Volume I, secondary school students. https://doi.org/10.3998/2027.42/146530.
Miller, D. T., & Prentice, D. A. (2016). Changing norms to change behavior. Annual Review of Psychology, 67, 339–361. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010814-015013.
Moreno, M. A., D’Angelo, J., & Whitehill, J. (2016). Social Media and Alcohol: Summary of Research. Intervention Ideas and Future Study Directions. Media and Communication, 4(3), 50 https://doi.org/10.17645/mac.v4i3.529.
Moreno, O., Janssen, T., Cox, M. J., Colby, S., & Jackson, K. M. (2017). Parent-adolescent relationships in Hispanic versus Caucasian families: associations with alcohol and marijuana use onset. Addictive Behaviors, 74, 74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2017.05.029.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2017). MPlus User’s Guide: Eighth Edition. Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0447.2011.01711.x
Nesi, J., Rothenberg, W. A., Hussong, A. M., & Jackson, K. M. (2017a). Friends’ alcohol-related social networking site activity predicts escalations in adolescent drinking: mediation by peer norms. Journal of Adolescent Health, 60(6), 641–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2017.01.009.
Nesi, J., Rothenberg, W. A., Hussong, A. M., & Jackson, K. M. (2017b). Friends’ alcohol-related social networking site activity predicts escalations in adolescent drinking: mediation by peer norms. Journal of Adolescent Health, 60(6), 641–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2017.01.009.
Osberg, T. M., Billingsley, K., Eggert, M., & Insana, M. (2012). From animal house to old school: A multiple mediation analysis of the association between college drinking movie exposure and freshman drinking and its consequences. Addictive Behaviors, 37(8), 922–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2012.03.030.
Ouellette, J. A., Gerrard, M., Gibbons, F. X., & Reis-Bergan, M. (1999). Parents, peers, and prototypes: Antecedents of adolescent alcohol expectancies, alcohol consumption, and alcohol-related life problems in rural youth. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 13(3), 183–197. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-164X.13.3.183.
Anderson, M., & Jiang, J. (2018). Teens, social media & technology 2018. Pew Research Center, 31, 2018.
Preacher, K. J., Rucker, D. D., & Hayes, A. F. (2007). Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivariate behavioral research, 42(1), 185–227.
Rojas, N. L., Sherrit, L., Harris, S., & Knight, J. R. (2008). The role of parental consent in adolescent substance use research. Journal of Adolescent Health, 42(2), 192–197.
Ross, C. S., Maple, E., Siegel, M., Dejong, W., Naimi, T. S., Ostroff, J., & Jernigan, D. H. (2014). The relationship between brand-specific alcohol advertising on television and brand-specific consumption among underage youth. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 38(8), 2234–2242. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12488.
Ryan, M., Jorm, F., & Lubman, I. (2010). Parenting factors associated with reduced adolescent alcohol use: A systematic review of longitudinal studies. The Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 44(9), 774–783. https://doi.org/10.1080/00048674.2010.501759.
Sargent, J. D., Worth, K. A., Beach, M., Gerrard, M., & Heatherton, T. F. (2008). Population-based assessment of exposure to risk behaviors in motion pictures. Communication Methods and Measures, 2(1–2), 134–151. https://doi.org/10.1080/19312450802063404.Population-Based.
Sargent, JamesD., Wills, T. A., Stoolmiller, M., Gibson, J., & Gibbons, F. X. (2006). Alcohol use in motion pictures and its relation with early-onset teen drinking. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 67(1), 54–65. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsa.2006.67.54.
Schell, T. L., Martino, S. C., Ellickson, P. L., Collins, R. L., & McCaffrey, D. (2005). Measuring developmental changes in alcohol expectancies. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 19(2), 217–220. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-164X.19.2.217.
Shin, W., & Ismail, N. (2014). Exploring the role of parents and peers in young adolescents’ risk taking on social networking sites. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2014.0095
Smith, L. A., & Foxcroft, D. R. (2009). The effect of alcohol advertising, marketing and portrayal on drinking behaviour in young people: Systematic review of prospective cohort studies. BMC Public Health, 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-9-51
Steinberg, L., Fletcher, A., & Darling, N. (1994). Parental monitoring and peer influences on adolescent substance use. In Pediatrics, 93, 1060–1064. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511527906.016.
Steinberg, Laurence, & Morris, A. S. (2001). Adolescent development. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 52, 83–110.
Stern, S., & Morr, L. (2013). Portrayals of teen smoking, drinking, and drug use in recent popular movies. Journal of Health Communication, 18(2), 179–191. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2012.688251.
Tanski, S. E., Dal Cin, S., Stoolmiller, M., & Sargent, J. D. (2010). Parental R-rated movie restriction and early-onset alcohol use. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, 71(3), 452–459. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsad.2010.71.452.
Tanski, S. E., Stoolmiller, M., Gerrard, M., & Sargent, J. D. (2012). Moderation of the association between media exposure and youth smoking onset: race/ethnicity, and parent smoking. Prevention Science, 13(1), 55–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-011-0244-3.
Toh, S. H., Howie, E. K., Coenen, P., & Straker, L. M. (2019). “From the moment i wake up i will use it⋯every day, very hour”: A qualitative study on the patterns of adolescents’ mobile touch screen device use from adolescent and parent perspectives. BMC Pediatrics. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-019-1399-5.
Wartella, E., Rideout, V., Montague, H., Beaudoin-Ryan, L., & Lauricella, A. (2016). Teens, Health and Technology: A National Survey. Media and Communication. https://doi.org/10.17645/mac.v4i3.515.
Wills, T. A., Sargent, J. D., Gibbons, F. X., Gerrard, M., & Stoolmiller, M. (2009). Movie exposure to alcohol cues and adolescent alcohol problems: a longitudinal analysis in a national sample. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 23(1), 23–35. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014137.
Wisniewski, P., Jia, H., Xu, H., Rosson, M. B., & Carroll, J. M. (2015). “preventative” vs. “reactive”: How parental mediation influences teens’ social media privacy behaviors. In CSCW 2015—Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing. https://doi.org/10.1145/2675133.2675293
Wood, M. D., Mitchell, R. E., Read, J. P., & Brand, N. H. (2004). Do parents still matter? parent and peer influences on alcohol involvement among recent high school graduates. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 18(1), 19–30. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-164X.18.1.19.
Wood, M. D., Read, J. P., Palfai, T. P., & Stevenson, J. F. (2001). Social influence processes and college student drinking: the mediational role of alcohol outcome expectancies. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 62(1), 32–43. https://doi.org/10.15288/jsa.2001.62.32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.M.J. conceived of the study, participated in its design and data collection, and drafted the manuscript; T.J. performed statistical analysis, participated in interpretation of the data, and drafted portions of the manuscript; M.C. participated in interpretation of the data and drafted portions of the manuscript; S.M.C. participated in the design and data collection and interpretation of the data; N.P.B. participated in the design and data collection and interpretation of the data; J.S. participated in data collection and interpretation of the data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (R01 AA016838, PI Jackson; K01 AA026335, PI: Janssen; T32 AA007459, PI Monti).
Data Sharing and Declaration
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The Brown University Institutional Review Board approved project procedures.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jackson, K.M., Janssen, T., Cox, M.J. et al. Mechanisms Underlying Associations between Media Alcohol Exposure, Parenting, and Early Adolescent Drinking: A Moderated Sequential Mediation Model. J Youth Adolescence 50, 1896–1910 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-020-01373-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-020-01373-0