Abstract
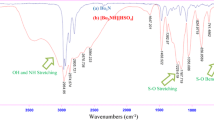
An efficient, one-pot quantitative procedure for the preparation of benzo[a]pyrano[2,3-c]phenazine derivatives from four-component condensation reaction of 2-hydroxynaphthalene-1,4-dione, benzene-1,2-diamine, aromatic aldehydes, and malononitrile in the presence of [(EtO)3Si(CH2)3N+H3][CH3COO−] as basic ionic liquid as catalyst in homogenous solution under solvent-free conditions at 90 °C is described. Simple procedure, high yields, short reaction times, and an environmentally benign method are advantages of this protocol. The [(EtO)3Si(CH2)3N+H3][CH3COO−] can be recovered and reused several times without loss of its activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
References
Calvo-Flores, F.G.: Sustainable chemistry metrics. Chemsuschem 2, 905–919 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.200900128
Wakai, C., Oleinikova, A., Weingärtner, H.: Reply to “Comment on ‘how polar are ionic liquids? determination of the static dielectric constant of an imidazolium-based ionic liquid by microwave spectroscopy.’” J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 5824 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0601973
Chen, Y., Han, X., Liu, Z., Li, Y., Sun, H., Wang, H., Wang, J.: Thermal decomposition and volatility of ionic liquids: factors, evaluation and strategies. J. Mol. Liq. 366, 120336 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.120336
Ghorbani, M., Simone, M.I.: Develo** new inexpensive room-temperature ionic liquids with high thermal stability and a greener synthetic profile. ACS Omega 5, 12637–12648 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b04091
Niedermaier, I., Kolbeck, C., Taccardi, N., Schulz, P.S., Li, J., Drewello, T., Wasserscheid, P., Steinrück, H.P., Maier, F.: Organic reactions in ionic liquids studied by in situ XPS. ChemPhysChem 13, 1725–1735 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201100965
Gao, Y., Arritt, S.W., Twamley, B., Shreeve, J.M.: Guanidinium-based ionic liquids. Inorg. Chem.. Chem. 44, 1704–1712 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/ic048513k
Kirchhecker, S., Esposito, D.: Amino acid based ionic liquids: a green and sustainable perspective. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2, 28–33 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2016.09.001
Yunus, N.M., Mutalib, M.I.A., Man, Z., Bustam, M.A., Murugesan, T.: Solubility of CO2 in pyridinium based ionic liquids. Chem. Eng. J. 189–190, 94–100 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.02.033
Chen, X., Liu, G., Yuan, S., Asumana, C., Wang, W., Yu, G.: Extractive desulfurization of fuel oils with thiazolium-based ionic liquids. Sep. Sci. Technol. 47, 819–826 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2011.637281
Fredlake, C.P., Crosthwaite, J.M., Hert, D.G., Aki, S.N.V.K., Brennecke, J.F.: Thermophysical properties of imidazolium-based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 49, 954–964 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/je034261a
Sanghi, S., Willett, E., Versek, C., Tuominen, M., Coughlin, E.B.: Physicochemical properties of 1,2,3-triazolium ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2, 848–853 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ra00286d
Greaves, T.L., Drummond, C.J.: ChemInform abstract: protic ionic liquids: properties and applications. ChemInform 39, 206–237 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.200818249
Bienaymé, H., Hulme, C., Oddon, G., Schmitt, P.: Maximizing synthetic efficiency: multi-component transformations lead the way. Chem. A Eur. J. 6, 3321–3329 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3765(20000915)6:18%3c3321::AID-CHEM3321%3e3.0.CO;2-A
Laursen, J.B., Nielsen, J.: Phenazine natural products: biosynthesis, synthetic analogues, and biological activity. Chem. Rev. 104, 1663–1685 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr020473j
Borrero, N.V., Bai, F., Perez, C., Duong, B.Q., Rocca, J.R., **, S., Huigens, R.W.: Phenazine antibiotic inspired discovery of potent bromophenazine antibacterial agents against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Org. Biomol. Chem.Biomol. Chem. 12, 881–886 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ob42416b
Hu, L., Chen, X., Han, L., Zhao, L., Miao, C., Huang, X., Chen, Y., Li, P., Li, Y.: Two new phenazine metabolites with antimicrobial activities from soil-derived Streptomyces species. J. Antibiot.Antibiot. 72, 574–577 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-019-0163-2
Verma, K., Tailor, Y.K., Khandelwal, S., Agarwal, M., Rushell, E., Kumari, Y., Awasthi, K., Kumar, M.: An efficient and environmentally sustainable domino protocol for the synthesis of structurally diverse spiroannulated pyrimidophenazines using erbium doped TiO2 nanoparticles as a recyclable and reusable heterogeneous acid catalyst. RSC Adv. 8, 30430–30440 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra04919j
Guttenberger, N., Blankenfeldt, W., Breinbauer, R.: Recent developments in the isolation, biological function, biosynthesis, and synthesis of phenazine natural products. Bioorg. Med. Chem.. Med. Chem. 25, 6149–6166 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.01.002
Low, Z.Y., Yip, A.J.W., Lal, S.K.: Repositioning ivermectin for covid-19 treatment: molecular mechanisms of action against SARS-CoV-2 replication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1868, 166294 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166294
Rhee, H.K., Yoo, J.H., Lee, E., Kwon, Y.J., Seo, H.R., Lee, Y.S., Choo, H.Y.P.: Synthesis and cytotoxicity of 2-phenylquinazolin-4(3H)-one derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46, 3900–3908 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.05.061
Le-Nhat-Thuy, G., Dang Thi, T.A., Nguyen Thi, Q.G., Hoang Thi, P., Nguyen, T.A., Nguyen, H.T., Nguyen Thi, T.H., Nguyen, H.S., Nguyen, T.: Van: synthesis and biological evaluation of novel benzo[a]pyridazino[3,4-c]phenazine derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.. Med. Chem. Lett. 43, 128054 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128054
Shirzaei, F., Shaterian, H.R.: [(EtO)3Si(CH2)3NH3+][CH3COO−] as a novel basic ionic liquid catalyzed green synthesis of new 2-(phenylsulfonyl)-1H-benzo[a]pyrano[2,3-c]phenazin-3-amine derivatives. J. Mol. Struct.Struct. 1256, 132558 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.132558
Shirzaei, F., Shaterian, H.R.: Basic ionic liquid, 2-hydroxyethylammonium formate, catalyzed one-pot synthesis of novel 2-(phenylsulfonyl)-1H-benzo[a]pyrano[2,3-c]phenazin-3-amine derivatives. Res. Chem. Intermed.Intermed. 48, 751–770 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-021-04627-z
Shaterian, H.R., Moradi, F., Mohammadnia, M.: Nano copper(II) oxide catalyzed four-component synthesis of functionalized benzo[a]pyrano[2,3-c]phenazine derivatives. Comptes Rendus Chim. 15, 1055–1059 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2012.09.012
Shaterian, H.R., Mohammadnia, M.: Mild basic ionic liquid catalyzed four component synthesis of functionalized benzo[a]pyrano[2,3-c]phenazine derivatives. J. Mol. Liq. 177, 162–166 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2012.11.006
Shaabani, A., Ghadari, R., Arabieh, M.: Synthesis of a new library of pyrano-phenazine derivatives via a novel three-component protocol. Helv. Chim. Acta. Chim. Acta 97, 228–236 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.201300006
Tabibian, M., Mohebat, R., Tabatabaee, M.: A novel one-pot and rapid synthesis of polyfunctionalized benzo[a]pyrimido[5′,4′:5,6]pyrido[2,3-c]phenazine derivatives under microwave irradiation. Turkish J. Chem. 42, 1008–1017 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-1710-13
Naeimi, H., Zarabi, M.F.: Multisulfonate hyperbranched polyglycerol functionalized graphene oxide as an efficient reusable catalyst for green synthesis of benzo[a]pyrano-[2,3-c]phenazines under solvent-free conditions. RSC Adv. 9, 7400–7410 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA10180A
Hasaninejad, A., Firoozi, S.: One-pot, sequential four-component synthesis of benzo[c]pyrano[3,2-a]phenazine, bis-benzo[c]pyrano[3,2-a]phenazine and oxospiro benzo[c]pyrano[3,2-a]phenazine derivatives using 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (DABCO) as an efficient and reusable solid bas. Mol. Divers. 17, 499–513 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-013-9446-x
Yazdani-elah-abadi, A., Razeghi, M., Shams, N.: Fulvic acid: an efficient and green catalyst for the one-pot four-component domino synthesis of benzo[a]phenazine annulated heterocycles in aqueous medium. Org. Prep. Proced. Int.Proced. Int. 52, 48–55 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/00304948.2019.1697608
Marsh, K.N., Boxall, J.A., Lichtenthaler, R.: Room temperature ionic liquids and their mixtures—a review. Fluid Phase Equilib.Equilib. 219, 93–98 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2004.02.003
Dashteh, M., Safaiee, M., Baghery, S., Zolfigol, M.A.: Application of cobalt phthalocyanine as a nanostructured catalyst in the synthesis of biological henna-based compounds. Appl. Organomet. Chem.Organomet. Chem. 33, 1–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4690
Safaei-Ghomi, J., Kareem Abbas, A., Shahpiri, M.: Synthesis of imidazoles promoted by H3PW12O40-amino-functionalized CdFe12O19@SiO2 nanocomposite. Nanocomposites 6, 149–157 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/20550324.2020.1858246
Ghorbani, A., Masoud, C., Lotfi, M.: Synthesis and characterization of spinel FeAl2O4 (hercynite) magnetic nanoparticles and their application in multicomponent reactions. Res. Chem. Intermed.Intermed. 4, 5705–5723 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-03930-0
Nikoorazm, M., Khanmoradi, M.: Application of Cu(II)-Guanine complexes anchored on SBA-15 and MCM-41 as efficient nanocatalysts for one-pot, four-component domino synthesis of phenazine derivatives and investigation of their antimicrobial behavior. Catal. Lett.. Lett. 150, 2823–2840 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03185-0
Funding
We are thankful to the University of Sistan and Baluchestan Research Council for the partial support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by FS, and HRS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shirzaei, F., Shaterian, H.R. [(EtO)3Si(CH2)3N+H3][CH3COO−] as Basic Ionic Liquid Catalyst Promoted Green Synthesis of Benzo[a]pyrano[2,3-c]phenazine Derivatives in Homogenous Solution. J Solution Chem 53, 328–340 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-023-01332-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-023-01332-w