Abstract
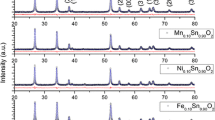
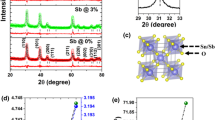
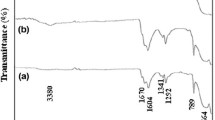
Co-Fe–Mn co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles have been effectively synthesised by sol–gel method. To explore the effect of co-do** in instigating room-temperature ferromagnetism in SnO2 nanocrystals, the structural, optical and magnetic behaviours of Sn0.85Co0.10Fe0.03Mn0.02O2 nanoparticles were examined. Also, the oxidation states of dopants were evaluated using XPS analysis. XRD data exhibited pure SnO2 phase, revealing the effectiveness of the method of synthesis in substituting the dopant ions into Sn sites. The average crystallite size of the synthesised sample was calculated to be 21 nm. SEM–EDX and HRTEM-SAED revealed the surface morphology, elemental composition, lattice plane and the polycrystalline nature of the nanoparticles. Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy data illustrated a decrease in bandgap compared to bulk SnO2 due to the effect of dopants. FTIR spectrum disclosed the prominent peaks corresponding to SnO2. The occurrence of room-temperature ferromagnetism in the prescribed sample has been validated from the magnetic hysteresis plotted using VSM data analysis. The analysis of all the abovementioned characterisations revealed the incorporation of dopants into SnO2 host material. The emergence of magnetism in the sample depends mainly on the distribution of vacancy defects and nano-size of the sample, in addition to the surface diffusion of magnetic dopant ions into the SnO2 lattice.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Matsumoto, Y., Murakami, M., Shono, T., Hasegawa, T., Fukumura, T., Kawasaki, M., Ahmet, P., Chikyow, T., Koshihara, S., Koinuma, H.: Room-temperature ferromagnetism in transparent transition metal-doped titanium dioxide. Science(80-.) 80(291), 854–856 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1056186
Rajan, R., Vizhi, R.E.: Investigation of room-temperature ferromagnetism on pristine and non-ferromagnetic dopant-substituted SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 30, 3199–3206 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4118-1
Dietl, T.: A ten-year perspective on dilute magnetic semiconductors and oxides. Nat. Mater. 9, 965–974 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2898
Coey, J.M.D., Venkatesan, M., Fitzgerald, C.B.: Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nat. Mater. 4, 173–179 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1310
Albanese, E., Leccese, M., Di Valentin, C., Pacchioni, G.: Magnetic properties of nitrogen-doped ZrO2: theoretical evidence of absence of room temperature ferromagnetism. Sci. Rep. 6, 31435 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31435
MacDonald, A.H., Schiffer, P., Samarth, N.: Ferromagnetic semiconductors: moving beyond (Ga, Mn)As. Nat. Mater. 4, 195–202 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1325
Lee, J., Subramaniam, N.G., Agnieszka Kowalik, I., Nisar, J., Lee, J., Kwon, Y., Lee, J., Kang, T., Peng, X., Arvanitis, D., Ahuja, R.: Towards a new class of heavy ion doped magnetic semiconductors for room temperature applications. Sci. Rep. 5, 17053 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17053
Dietl, T.: Functional ferromagnets 2, 4–6 (2003)
Kittilstved, K.R., Liu, W.K., Gamelin, D.R.: Electronic structure origins of polarity-dependent high-TC ferromagnetism in oxide-diluted magnetic semiconductors. Nat. Mater. 5, 291–297 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1616
Aragón, F.H., Cohen, R., Coaquira, J.A.H., Barros, G.V., Hidalgo, P., Nagamine, L.C.C.M., Gouvêa, D.: Effects of particle size on the structural and hyperfine properties of tin dioxide nanoparticles. Hyperfine Interact. 202, 73–79 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-011-0340-6
Dopants in nanocrystalline tin dioxide: Rumyantseva, M.N., Safonova, O. V., Boulova, M.N., Ryabova, L.I., Gas’kov, A.M. Russ. Chem. Bull. 52, 1217–1238 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024916020690
Punnoose, A., Seehra, M.S., Park, W.K., Moodera, J.S.: On the room temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped TiO2 films. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 7867–7869 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1556121
Park, J.H., Kim, M.G., Jang, H.M., Ryu, S., Kim, Y.M.: Co-metal clustering as the origin of ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1338 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1650915
Philip, J., Punnoose, A., Kim, B.I., Reddy, K.M., Layne, S., Holmes, J.O., Satpati, B., LeClair, P.R., Santos, T.S., Moodera, J.S.: Carrier-controlled ferromagnetism in transparent oxide semiconductors. Nat. Mater. 5, 298–304 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1613
Punnoose, A., Hays, J., Gopal, V., Shutthanandan, V.: Room-temperature ferromagnetism in chemically synthesized Sn1−xCoxO2 powders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 1559–1561 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1786633
Van Komen, C., Thurber, A., Reddy, K.M., Hays, J., Punnoose, A.: Structure–magnetic property relationship in transition metal (M=V, Cr, Mn, Fe Co, Ni) doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 07D141 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2836797
Rajan, R., Vizhi, R.E.: Effect of Co3+ substitution on the structural, optical, and room-temperature magnetic properties of SnO2 nanoparticulates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 12716–12724 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-05906-6
Chikhale, L.P., Patil, J.Y., Rajgure, A.V., Shaikh, F.I., Mulla, I.S., Suryavanshi, S.S.: Co-precipitation synthesis of nanocrystalline SnO2: effect of Fe do** on structural, morphological and ethanol vapor response properties. Measurement 57, 46–52 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEASUREMENT.2014.07.011
Muthukumaran, S., Gopalakrishnan, R.: Structural, optical, FTIR and photoluminescence properties of Zn0.96−xCo0.04CuxO (x=0.03, 0.04 and 0.05) nanopowders. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 407, 3448–3456 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSB.2012.04.057
Nakai, I., Sasano, M., Inui, K., Korekawa, T., Ishijima, H., Katoh, H., Li, Y.J., Kurisu, M.: Oxygen vacancy and magnetism of a room temperature ferromagnet Co-doped TiO2. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 63, 532–537 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.63.532
Kanamori, J.: Superexchange interaction and symmetry properties of electron orbitals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 10, 87–98 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3697(59)90061-7
Goodenough, J.B.: Theory of the role of covalence in the perovskite-type manganites [La, M (II)]MnO3. Phys. Rev. 100, 564–573 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.100.564
Zhu, S., Chen, C., Li, Z.: Magnetic enhancement and magnetic signal tunability of (Mn, Co) co-doped SnO2 dilute magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 471, 370–380 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.106
Lee, A.Y., Blakeslee, D.M., Powell, C.J., Rumble, J.R., Jr.: Development of the web-based NIST Xray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Database. Data Sci. J. 1, 1–12 (2002). https://doi.org/10.2481/dsj.1.1
Biesinger, M.C., Payne, B.P., Grosvenor, A.P., Lau, L.W.M., Gerson, A.R., Smart, R.S.C.: Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe. Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 2717–2730 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.051
Fu, Y., Sun, N., Feng, L., Wen, S., An, Y., Liu, J.: Local structure and magnetic properties of Fe-doped SnO 2 films. J. Alloys Compd. 698, 863–867 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.297
Bilovol, V., Ferrari, S., Saccone, F.D., Pampillo, L.G.: Effect of the dopant on the structural and hyperfine parameters of Sn 0.95 M 0.05 O 2 nanoparticles (M: V, Mn, Fe, Co). Mater. Res. Express. 6, 0850h6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab29cc
Uddin, M.T., Nicolas, Y., Olivier, C., Toupance, T., Servant, L., Müller, M.M., Kleebe, H.-J., Ziegler, J., Jaegermann, W.: Nanostructured SnO 2 –ZnO heterojunction photocatalysts showing enhanced photocatalytic activity for the degradation of organic dyes. Inorg. Chem. 51, 7764–7773 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ic300794j
Kuantama, E., Han, D.-W., Sung, Y.-M., Song, J.-E., Han, C.-H.: Structure and thermal properties of transparent conductive nanoporous F:SnO2 films. Thin Solid Films 517, 4211–4214 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2009.02.044
Ma, J., Liu, C., Chen, K.: Assembling non-ferromagnetic materials to ferromagnetic architectures using metal-semiconductor interfaces. Sci. Rep. 6, 34404 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34404
Vaseashta, A., Mihailescu, I.N.: Functionalized nanoscale materials, devices and systems. Springer (2008)
Gemming, S. (Sibylle), Schreiber, M., Suck, J.B.: Materials for tomorrow: theory, experiments, and modelling. 194 (2007)
Coey, J.M.D.: High-temperature ferromagnetism in dilute magnetic oxides. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 8–11 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1849054
Coey, J.M.D., Douvalis, A.P., Fitzgerald, C.B., Venkatesan, M.: Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped SnO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1332–1334 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1650041
Errico, L.A., Rentería, M., Weissmann, M.: Theoretical study of magnetism in transition-metal-doped TiO2 and TiO2−δ. Phys. Rev. B 72, 184425 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.184425
Vizhi, R.E., Rajan, R.: Structural, optical and room temperature magnetic properties of sol–gel synthesized (Co, Fe) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Cryst. Growth 584, 126565 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2022.126565
Banerjee, S., Tyagi, A.K.: Functional Materials: Preparation. Elsevier, Processing and Applications (2011)
Gaj, J., Kossut, J.: Introduction to the Physics of Diluted Magnetic Semiconductors. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg (2010)
Kharisov, B.I., Kharissova, O.V.: Radiation Synthesis of Materials and Compounds. CRC Press (2016)
Miglio, L., Montalenti, F.: Silicon-Germanium (SiGe) Nanostructures: Production, Properties, and Applications in Electronics. Woodhead Publishing, UK (2011)
Pohm, A.V., Comstock, C.S., Hurst, A.T.: Quadrupled nondestructive outputs from magnetoresistive memory cells using reversed word fields. J. Appl. Phys. 67, 4881–4883 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.344766
Johnson, M., Bennett, B.R., Yang, M.J., Miller, M.M., Shanabrook, B.V.: Hybrid ferromagnet-semiconductor gates for nonvolatile memory. In: Seventh Biennial IEEE International Nonvolatile Memory Technology Conference. Proceedings (Cat. No.98EX141). pp. 78–83. IEEE (1998)
Engel, B.N., Akerman, J., Butcher, B., Dave, R.W., DeHerrera, M., Durlam, M., Grynkewich, G., Janesky, J., Pietambaram, S.V., Rizzo, N.D., Slaughter, J.M., Smith, K., Sun, J.J., Tehrani, S.: A 4-Mb toggle MRAM based on a novel bit and switching method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 41, 132–136 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2004.840847
Datta, S., Das, B.: Electronic analog of the electro-optic modulator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 56, 665–667 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.102730
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the management of Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, for their constant support and the characterisation facilities provided. The authors also thank SAIF, IIT Madras, for providing VSM measurements; STIC, CUSAT, for carrying out HRTEM/SAED and Nanotechnology Research Centre (NRC), SRMIST, for providing XPS analysis of the synthesised nanoparticles.
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.R: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Resources, Investigation, Validation. R.E.V: Supervision, Writing - review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
The authors declare that this manuscript complies with scientific ethical standards. There are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship and are not listed. We further confirm that the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all of us. Furthermore, this article does not contain any studies involving human or animal participants.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajan, R., Vizhi, R.E. Enhanced Ferromagnetism in Nano-sized Sn0.85Co0.10Fe0.03Mn0.02O2 Dilute Magnetic Semiconductor Synthesised by Sol–Gel Method. J Supercond Nov Magn 37, 1089–1100 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-024-06689-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-024-06689-7