Abstract
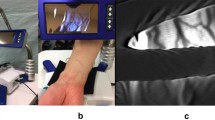
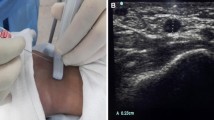
The purpose of this study was to assess the anatomy of the radial artery using ultrasound in anesthetized patients, and to correlate its anatomical data with patients’ characteristics. The success rate of radial artery cannulation using ultrasound was also evaluated to analyze the relationship between the anatomical data and the success rate. Study 1 One hundred ninety-five patients scheduled for general anesthesia were enrolled. Ultrasound measurements were obtained when the vital signs were stable after anesthesia induction. The wrist joint of patients were extended to 30°. The diameter and depth of the radial artery, and the angle between the radial artery and skin surface were measured using ultrasound. Anatomical data were correlated with patients’ characteristics. Study 2 Arterial cannulation was performed in 125 patients using long-axis in-plane technique to evaluate the success rate using ultrasound. Study 1 The diameter of the radial artery was mean value of 2.2 ± 0.4 mm and larger than 0.9 mm in all patients. It had significant correlation with body surface area (BSA) (Pearson correlation 0.292, P < 0.001). The incidence of abnormal angle between the radial artery and skin surface was significantly higher in elderly patients (≥65 years) than young patients (P = 0.017). Study 2 The first attempt success rate of arterial catheterization using ultrasound was 92.5 % using long-axis in-plane technique, regardless of patient’s characteristics. For small sized adult patients, a 22G angio-catheter should be used during radial artery cannulation, because the radial artery diameter significantly correlated with BSA in healthy anesthetized patients. In addition, ultrasound-guided catheterization is recommended in elderly patients because the incidence of abnormal angle between the radial artery and skin surface was high.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sandhu NS, Patel B. Use of ultrasonography as a rescue technique for failed radial artery cannulation. J Clin Anesth. 2006;18:138–41.
Levin PD, Sheinin O, Gozal Y. Use of ultrasound guidance in the insertion of radial artery catheters. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:481–4.
Hansen MA, Juhl-Olsen P, Thorn S, Frederiksen CA, Sloth E. Ultrasonography-guided radial artery catheterization is superior compared with the traditional palpation technique: a prospective, randomized, blinded, crossover study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2014;58:446–52.
Shiloh AL, Savel RH, Paulin LM, Eisen LA. Ultrasound-guided catheterization of the radial artery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Chest. 2011;139:524–9.
Ishii S, Shime N, Shibasaki M, Sawa T. Ultrasound-guided radial artery catheterization in infants and small children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2013;14:471–3.
Jani B, Rajkumar C. Ageing and vascular ageing. Postgrad Med J. 2006;82:357–62.
Mizukoshi K, Shibasaki M, Amaya F, Hirayama T, Shimizu F, Hosokawa K, et al. Ultrasound evidence of the optimal wrist position for radial artery cannulation. Can J Anaesth. 2009;56:427–31.
Ludman PF, Stephens NG, Harcombe A, et al. Radial versus femoral approach for diagnostic coronary angiography in stable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 1997;79:1239–41.
Benit E, Missault L, Eeman T, et al. Brachial, radial, or femoral approach for elective Palmaz-Schatz stent implantation: a randomizedcomparison. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1997;41:124–30.
Yoo BS, Yoon J, Ko JY, et al. Anatomical consideration of the radial artery for transradial coronary procedures: arterial diameter, branching anomaly and vessel tortuosity. Int J Cardiol. 2005;101:421–7.
Kotowycz MA, Johnston KW, Ivanov J, et al. Predictors of radial artery size in patients undergoing cardiac catheterization: insights from the Good Radial Artery Size Prediction (GRASP) study. Can J Cardiol. 2014;30:211–6.
Yokoyama N, Takeshita S, Ochiai M, et al. Anatomic variations of the radial artery in patients undergoing transradial coronary intervention. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2000;49:357–62.
Berk D, Gurkan Y, Kus A, Ulugol H, Solak M, Toker K. Ultrasound-guided radial arterial cannulation: long axis/in-plane versus short axis/out-of-plane approaches? J Clin Monit Comput. 2013;27:319–24.
Shiver S, Blaivas M, Lyon M. A prospective comparison of ultrasound-guided and blindly placed radial arterial catheters. Acad Emerg Med. 2006;3:1275–9.
Zochios VA, Wilkinson J, Dasgupta K. The role of ultrasound as an adjunct to arterial catheterization in critically ill surgical and intensive care unit patients. J Vasc Access. 2014;15:1–4.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D., Kim, J.Y., Kim, H.S. et al. Ultrasound evaluation of the radial artery for arterial catheterization in healthy anesthetized patients. J Clin Monit Comput 30, 215–219 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-015-9704-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-015-9704-9