Abstract
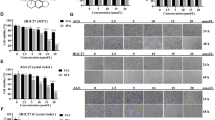
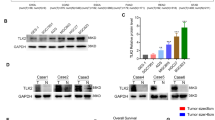
Energy metabolism has always been a hot topic in cancer progression and targeted therapy, and exploring the role of genes in energy metabolic pathways in cancer cells has become key to address this issue. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α kinase 2 (EIF2AK2) plays regulatory roles in cancer and disorders of energy metabolism. Indeed, the role of EIF2AK2 in energy metabolism has been underestimated. The aim of this study is to reveal the expression specificity of EIF2AK2 in gastric cancer (GC) progression and metastasis, and to demonstrate the role of EIF2AK2 in energy metabolism, cytoskeleton, proliferation, death and metastasis pathways in GC cells. Mechanistically, EIF2AK2 overexpression promoted cytoskeleton remodeling and ATP production, mediated cell proliferation and metastasis, upregulated OAS1 expression, decreases p-AMPK expression and inhibited apoptosis in GC cells. Conversely, knockdown of EIF2AK2 resulted in the opposite effect. However, overexpression of OAS1 mediated the upregulation of mitochondrial membrane potential and promoted ATP production and NAD+/NADH ratio, but knockdown of OAS1 inhibited the above effects. In addition, knockdown of OAS1 had no effect on EIF2AK2 expression, but inhibited AMPK and upregulated p-AMPK expression. In conclusion, our study identified EIF2AK2 and OAS1 as previously undescribed regulators of energy metabolism in GC cells. We hypothesized that EIF2AK2-OAS1 axis may regulate energy metabolism and inhibit cellular malignant behavior in cancer cells by affecting ATP production to induce AMPK phosphorylation, suggesting EIF2AK2 as a potential therapeutic target for cancer cell progression.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Ahmed B, Qadir MI, Ghafoor S (2020) Malignant melanoma: skin Cancer-diagnosis, Prevention, and treatment. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 30:291–297. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2020028454
Aminzadeh-Gohari S, Weber DD, Vidali S et al (2020) From old to new - repurposing drugs to target mitochondrial energy metabolism in cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol 98:211–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.05.025
Bianchi L, Damiani I, Castiglioni S et al (2023) Smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch Induced by traditional cigarette smoke condensate: a holistic overview. Int J Mol Sci 24:6431. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076431
Borcherding N, Brestoff JR (2023) The power and potential of mitochondria transfer. Nature 623:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06537-z
Chang SC, Zhang BX, Su EC et al (2021) Hiltonol Cocktail kills Lung Cancer cells by activating Cancer-suppressors, PKR/OAS, and restraining the Tumor Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci 22:1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041626
Darini C, Ghaddar N, Chabot C et al (2019) An integrated stress response via PKR suppresses HER2 + cancers and improves trastuzumab therapy. Nat Commun 10:2139. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10138-8
DeBerardinis RJ, Chandel NS (2016) Fundamentals of cancer metabolism. Sci Adv 2:e1600200. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1600200
Du HX, Wang H, Ma XP et al (2023) Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α kinase 2 in pancreatic cancer: an approach towards managing clinical prognosis and molecular immunological characterization. Oncol Lett 26:478. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2023.14066
El-Kott AF, ElBealy ER, Alshehri AS et al (2021) Salidroside induces cell apoptosis and inhibits the invasiveness of HT29 colorectal cells by regulating protein kinase R, NF-κB and STAT3. Cancer biomarkers: section a of Disease markers. 31:13–25. https://doi.org/10.3233/cbm-203257
Garcia-Ortega MB, Lopez GJ, Jimenez G et al (2017) Clinical and therapeutic potential of protein kinase PKR in cancer and metabolism. Expert Rev Mol Med 19:e9. https://doi.org/10.1017/erm.2017.11
Guo C, Hao C, Shao R et al (2015) RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) depletes nutrients, inducing phosphorylation of AMP-activated kinase in lung cancer. Oncotarget 6:11114–11124. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3573
Hu J, Pei W, Jiang M et al (2022) DFNA5 regulates immune cells infiltration and exhaustion. Cancer Cell Int 22:107. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-022-02487-0
Islam RA, Hossain S, Chowdhury EH (2017) Potential therapeutic targets in energy metabolism pathways of breast Cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 17:707–721. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568009617666170330150458
Kaipparettu BA, Ma Y, Wong LJ (2010) Functional effects of cancer mitochondria on energy metabolism and tumorigenesis: utility of transmitochondrial cybrids. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1201:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05621.x
Ke R, Xu Q, Li C et al (2018) Mechanisms of AMPK in the maintenance of ATP balance during energy metabolism. Cell Biol Int 42:384–392. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.10915
Kim Y, Park J, Kim S et al (2018) PKR Senses Nuclear and mitochondrial signals by interacting with endogenous double-stranded RNAs. Mol Cell 71:1051–1063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.07.029
Li W, Bao G, Chen W et al (2018) Connexin 43 Hemichannel as a novel mediator of sterile and infectious inflammatory diseases. Sci Rep 8:166. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18452-1
Li C, Wang X, Chen T et al (2022) Huaier induces Immunogenic Cell Death Via CircCLASP1/PKR/eIF2α signaling pathway in Triple negative breast Cancer. Front cell Dev Biology 10:913824. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.913824
Liang X, Peng Z, Lin Z et al (2023) Identification of prognostic genes for breast cancer related to systemic lupus erythematosus by integrated analysis and machine learning. Immunobiology 228:152730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2023.152730
Lin SC, Hardie DG (2018) AMPK: sensing glucose as well as Cellular Energy Status. Cell Metabol 27:299–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.10.009
Liu Y, Tang R, Meng QC et al (2024) NUSAP1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression by drives the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and reduces AMPK phosphorylation. BMC Cancer 24:87. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-024-11842-5
Liu S, Jiao B, Zhao H et al (2024a) LncRNAs-circRNAs as rising epigenetic binary superstars in regulating lipid metabolic reprogramming of cancers. Advanced science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg. Germany) 11:e2303570. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202303570
Lu B, Nakamura T, Inouye K et al (2012) Novel role of PKR in inflammasome activation and HMGB1 release. Nature 488:670–674. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11290
Mao D, Reuter CM, Ruzhnikov MRZ et al (2020) De novo EIF2AK1 and EIF2AK2 variants are Associated with Developmental Delay, Leukoencephalopathy, and neurologic decompensation. Am J Hum Genet 106:570–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.02.016
Matheson CJ, Casalvieri KA, Backos DS et al (2020) Substituted oxindol-3-ylidenes as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 197:112316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112316
Padariya M, Sznarkowska A, Kote S et al (2021) Functional interfaces, Biological pathways, and regulations of Interferon-related DNA damage resistance signature (IRDS) genes. Biomolecules 11:622. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050622
Pang T, Tang Q, Wei J et al (2023) Construction of a novel immune-related prognostic-predicting model of gastric cancer. Gene 852:147032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2022.147032
Reyes-Farias M, Carrasco-Pozo C (2019) The Anti-cancer Effect of Quercetin: Molecular implications in Cancer Metabolism. Int J Mol Sci 20:109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133177
Sakamuru S, Attene-Ramos MS, **a M (2016) Mitochondrial membrane potential assay. Methods in molecular biology. (Clifton NJ) 1473:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6346-1_2
Sui Y, Li S, Fu XQ et al (2023) Bioinformatics analyses of combined databases identify shared differentially expressed genes in cancer and autoimmune disease. J Translational Med 21:109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-023-03943-9
Topisirovic I, Sonenberg N (2011) mRNA translation and energy metabolism in cancer: the role of the MAPK and mTORC1 pathways. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 76:355–367. https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.2011.76.010785
Wang G, Wang JJ, Xu XN et al (2022) Targeting cellular energy metabolism- mediated ferroptosis by small molecule compounds for colorectal cancer therapy. J Drug Target 30:819–832. https://doi.org/10.1080/1061186x.2022.2071909
You L, Wang Z, Li H et al (2015) The role of STAT3 in autophagy. Autophagy 11:729–739. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1017192
Zhao W, Quansah E, Yuan M et al (2019) Region-specific gene expression in the epididymis of Yak. Theriogenology 139:132–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2019.08.006
Zhou Y, **ao Y, Liu H et al (2024) Elevation of H3K27me3 level contributes to the radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inhibiting OAS1 expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 326:C60–c73. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00358.2023
Funding
This study was supported by the Ordos Science and Technology Cooperation Fund, Project of Hebei Medical Science Research (No. 20221526).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by [Yafang Lai], [**aofei, Wang], [**grong Ma], [Chaoqun Du], [Yuyu Wang], [Yaxin Wang], [Mingwei Zhao] and [Wenzhao Yuan]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [Yafang Lai], [**aofei, Wang], [**grong Ma] and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of North China University of Science and Technology Affiliated Hospital (No: 2020405).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, Y., Wang, X., Ma, J. et al. Knockdown of EIF2AK2-OAS1 axis reduces ATP production inducing AMPK phosphorylation to inhibit the malignant behavior of gastric cancer cells. J Bioenerg Biomembr 56, 433–449 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-024-10023-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-024-10023-0