Abstract
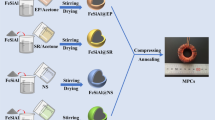
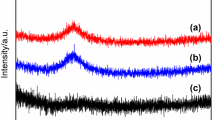
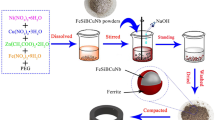
In order to develop FeSiAl soft magnetic powder cores (SMPCs) with excellent soft magnetic properties, FeSiAl powder passivated by hexafluorozirconic acid (H2ZrF6) was sucessfully prepared and the effect of different concentrations of H2ZrF6 on the effective permeability (μe) and core loss (Pcv) of FeSiAl SMPCs were systematically studied. H2ZrF6 (0.1 wt% of FeSiAl powder) passivation successfully optimized the soft magnetic properties, when the μe reached 94, the Pcv was only 180 mW/cm3 at 0.05 T and 100 kHz. SEM, XRD, FTIR, XPS, and TEM were used to investigate the microstructure and growth mechanism of the coating layer. The FeSiAl powder was passivated by H2ZrF6 to form a composite coating layer with dominating Fe2O3, Al2O3, SiO2, ZrF4 and a small amount of AlF3, ZrO2, while the AlF3 and ZrO2 content increased significantly after annealing. In addition, this study effectively improved the high frequency characteristics of FeSiAl SMPCs and analyzed the generation of coating layer, providing a feasible way for the insulation treatment of soft magnetic powder cores.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
E.A. Périgo, B. Weidenfeller, P. Kollár et al., Past, present, and future of soft magnetic composites. Appl. Phys. Rev. 5, 031301 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5027045
B. Sai Ram, A.K. Paul, S.V. Kulkarni, Soft magnetic materials and their applications in transformers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 537, 168210 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.168210
W.C. Li, H.W. Cai, Y. Kang et al., High permeability and low loss bioinspired soft magnetic composites with nacre-like structure for high frequency applications. Acta Mater. 167, 267–274 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2019.01.035
O. Gutfleisch, M.A. Willard, E. Brück et al., Magnetic materials and devices for the 21st century: stronger, lighter, and more energy efficient. Adv. Mater. 23, 821–842 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201002180
H. Shokrollahi, K. Janghorban, Soft magnetic composite materials (SMCs). J. Mater. Process. Technol. 189, 1–12 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.02.034
J.M. Silveyra, E. Ferrara, D.L. Huber et al., Soft magnetic materials for a sustainable and electrified world. Science 362, aa0195 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao0195
I. Hemmati, H.R. Madaah Hosseini, A. Kianvash, The correlations between processing parameters and magnetic properties of an iron–resin soft magnetic composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 305, 147–151 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.12.004
M. Strečková, J. Füzer, L. Kobera et al., A comprehensive study of soft magnetic materials based on FeSi spheres and polymeric resin modified by silica nanorods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 147, 649–660 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.06.004
Y.X. Pang, S.N.B. Hodgson, B. Weglinski et al., Investigations into sol-gel silica and silica hybrid coatings for dielectromagnetic soft magnetic composite applications. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 5926–5936 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0360-9
H.Y. Yu, X.X. Lai, X.C. Zhong et al., Optimization of sol-gel prepared SiO2 coating and FeSiCr@SiO2 soft magnetic composites based on critical ammonia concentration. Mater. Chem. Phys. 303, 127765 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127765
K.J. Geng, Y.Y. **e, L. Yan et al., Fe-Si/ZrO2 composites with core-shell structure and excellent magnetic properties prepared by mechanical milling and spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 718, 53–62 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.114
K.J. Geng, Y.Y. **e, L.L. Xu et al., Structure and magnetic properties of ZrO2-coated Fe powders and Fe/ZrO2 soft magnetic composites. Adv. Powder Technol. 28, 2015–2022 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.04.029
R.R. Bai, Z.H. Zhu, H. Zhao et al., The percolation effect and optimization of soft magnetic properties of FeSiAl magnetic powder cores. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 433, 285–291 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.03.016
S. Wu, A.Z. Sun, W.H. Xu et al., Iron-based soft magnetic composites with Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles coating obtained by sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3899–3905 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.06.042
J. Li, X.L. Peng, Y.T. Yang et al., Preparation and characterization of MnZn/FeSiAl soft magnetic composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 132–136 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.11.068
H.J. Liu, H.L. Su, W.B. Geng et al., Effect of particle size distribution on the magnetic properties of Fe-Si-Al powder core. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 29, 463–468 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3282-4
D. Liu, C. Wu, M. Yan et al., Correlating the microstructure, growth mechanism and magnetic properties of FeSiAl soft magnetic composites fabricated via HNO3 oxidation. Acta Mater. 146, 294–303 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.01.001
J.S. Pinheiro, G. Regio, H.R.P. Cardoso et al., Influence of concentration and pH of hexafluorozirconic acid on corrosion resistance of anodized AA7075-T6. Mater. Res. 22, e20190048 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2019-0048
O. Lunder, C. Simensen, Y. Yu et al., Formation and characterisation of Ti–Zr based conversion layers on AA6060 aluminium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 184, 278–290 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2003.11.003
V.B. Moreira, A. Meneguzzi, E. Jiménez-Piqué et al., Aluminum protection by using green zirconium oxide layer and organic coating: an efficient and adherent dual system. Sustainability 13, 9688 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179688
P. Kollár, Z. Birčáková, J. Füzer et al., Power loss separation in Fe-based composite materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 327, 146–150 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.09.055
A.H. Taghvaei, H. Shokrollahi, K. Janghorban et al., Eddy current and total power loss separation in the iron-phosphate-polyepoxy soft magnetic composites. Mater. Des. 30, 3989–3995 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.05.026
H. Shokrollahi, K. Janghorban, Effect of warm compaction on the magnetic and electrical properties of Fe-based soft magnetic composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 313, 182–186 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.12.022
D. Liu, C. Wu, M. Yan, Investigation on sol–gel Al2O3 and hybrid phosphate-alumina insulation coatings for FeSiAl soft magnetic composites. J. Mater. Sci. 50, 6559–6566 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9189-4
H.B. Sun, G.H. Zhou, Z.L. Guo et al., Efficient synthesis of TiO2-coated layer for Fe-based soft magnetic composites and their regulation mechanism analysis on magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. 33, 13956–13967 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08326-2
J.L. Ni, S.J. Zhu, S.J. Feng et al., Investigation on magnetic properties of FeSiAl/SrFe12O19 composites. J. Mater. Sci. 32, 16956–16960 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06259-w
M. Yan, Q.M. Chen, D. Liu et al., Sodium nitrate passivation as a novel insulation technology for soft magnetic composites. Engineering 20, 134–142 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2022.01.016
C. Wu, X.W. Gao, G.L. Zhao et al., Two growth mechanisms in one-step fabrication of the oxide matrix for FeSiAl soft magnetic composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 452, 114–119 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.12.032
S.L. **, X.J. Wang, K.C. Tome et al., Hydrogen release: In-situ calorimetry studies of NaBH4+2MgH2 doped by ZrF4. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 46, 922–929 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.09.237
Z.Y. Wu, L. Kang, X.W. Liao et al., Realizing high-resistivity and low-loss Fe–Si–Al based soft magnetic powder cores through interfacial chemistry regulation. Ceram. Int. 49, 19870–19878 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.03.106
M.K. Zakaryan, S.L. Kharatyan, A. Aprahamian et al., Combustion in the ZrF4-Mg-Si and ZrF4-Al-Si systems for preparation of zirconium silicides. Combust. Flame 232, 111514 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2021.111514
B.X. Chen, J.P. Peng, Y.W. Wang et al., Penetration behavior of electrolyte into graphite cathode in NaF−KF−LiF−AlF3 system with low cryolite ratios. Trans. Nonferr. Metal Soc. 32, 2727–2735 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1003-6326(22)65979-x
Y. Wang, The uniform Si-O coating on cotton fibers by an atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 50, 1739–1746 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2010.549051
J. Sung Lee, H. Soo Kim, J. Su Lee et al., Synthesis of α-Al2O3 at mild temperatures by controlling aluminum precursor, pH, and ethylenediamine chelating additive. Ceram. Int. 38, 6685–6691 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.05.057
M. Ramachandran, R. Subadevi, W.R. Liu et al., Facile synthesis and characterization of ZrO2 nanoparticles via modified co-precipitation method. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 18, 368–373 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.14562
M. Gotić, G. Dražić, S. Musić, Hydrothermal synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanorings with the help of divalent metal cations, Mn2+, Cu2+, Zn2+ and Ni2+. J. Mol. Struct. 993, 167–176 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2010.12.063
C.V.A. Duke, J.M. Miller, J.H. Clark et al., 19F MAS NMR and FTIR analysis of the adsorption of alkall metal fluorides onto alumina. J. Mol. Catal. 62, 233–242 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-5102(90)85216-5
X. Zuo, W.F. Li, S.L. Mu et al., Investigation of composition and structure for a novel Ti–Zr chemical conversion coating on 6063 aluminum alloy. Prog. Org. Coat. 87, 61–68 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2015.05.008
K.J. Ewing, B.M. Wright, J. Jaganathan et al., Distribution of oxide in a bed of thermally decomposed ZrF4 - H2O and its effect on ZrF4 sublimation. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75, 1918–1923 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1992.tb07217.x
Z.G. Luo, X.A. Fan, W.T. Hu et al., Properties of Fe2SiO4/SiO2 coated Fe-Si soft magnetic composites prepared by sintering Fe-6.5wt%Si/Fe3O4 composite particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 499, 166278 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166278
T. Fujii, F.M.F. de Groot, G.A. Sawatzky et al., In situ XPS analysis of various iron oxide films grown by NO2-assisted molecular-beam epitaxy. Phys. Rev. B 59, 3195–3202 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.59.3195
Y.X. Liu, J.W. Li, Y. Sun et al., Effect of annealing temperature on magnetic properties and corrosion resistance of Fe75.8Si12B8Nb2.6Cu0.6P1 alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 15, 3880–3894 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.10.050
L.K. Wu, J.J. **a, H.Z. Cao et al., Improving the high-temperature oxidation resistance of TiAl alloy by anodizing in methanol/NaF solution. Oxid. Met. 90, 617–631 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-018-9858-1
A. Sarfraz, R. Posner, M.M. Lange et al., Role of intermetallics and copper in the deposition of ZrO2 conversion coatings on AA6014. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161, C509–C516 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0121412jes
V. Cristaudo, K. Baert, P. Laha et al., A combined XPS/ToF-SIMS approach for the 3D compositional characterization of Zr-based conversion of galvanized steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 562, 150166 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150166
B.V. Crist, XPS in industry-Problems with binding energies in journals and binding energy databases. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 231, 75–87 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elspec.2018.02.005
L. Zhang, B.M. Wang, D.Y. Ying et al., Effect of the impurity ions on the crystallization of urea phosphate. Int. J. Chem. Reactor Eng. 17, 20180275 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1515/ijcre-2018-0275
B. Sarangi, A. Sarangi, H.S. Ray, Kinetics of aluminothermic reduction of MnO2 and Fe2O3: a thermoanalytical investigation. ISIJ Int. 36, 1135–1141 (1996). https://doi.org/10.2355/isi**ternational.36.1135
A.M. Cano, A.E. Marquardt, J.W. DuMont et al., Effect of HF pressure on thermal Al2O3 atomic layer etch rates and Al2O3 fluorination. J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 10346–10355 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b00124
A.M. Cano, J.L. Partridge, S.M. George, Thermal atomic layer etching of Al2O3 using sequential HF and BCl3 exposures: evidence for combined ligand-exchange and conversion mechanisms. Chem. Mater. 34, 6440–6449 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.2c01120
Gl. Zhao, C. Wu, M. Yan, Enhanced magnetic properties of Fe soft magnetic composites by surface oxidation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 399, 51–57 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.09.054
D. Gräf, M. Grundner, R. Schulz, Reaction of water with hydrofluoric acid treated silicon(111) and (100) surfaces. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 7, 808–813 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1116/1.575845
J.H. Nordlien, J.C. Walmsley, H. Osterberg et al., Formation of a zirconium-titanium based conversion layer on AA 6060 aluminium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 153, 72–78 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0257-8972(01)01663-2
W.C. Li, Z.J. Wang, Y. Ying et al., In-situ formation of Fe3O4 and ZrO2 coated Fe-based soft magnetic composites by hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 45, 3864–3870 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.11.058
Funding
This work was supported by Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (Grant No. 2021294), the S&T Innovation 2025 Major Special Program (Grant No. 2021Z038), K.C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University, and the “Pioneer and Leading Goose” R&D Program of Zhejiang (Grant No. 2023C01138).