Abstract
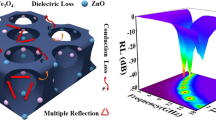
The three-dimensional (3D) porous carbon materials are helpful for forming thin, light-weight, wide effective absorption bandwidth and strong absorption intensity absorbers. However, previous methods were not environmentally friendly enough. Thus, in this work, the Fe/Fe3C@porous carbon was synthesized from soluble starch and Fe(NO3)3·9H2O via chemical bowling and subsequent carbonization at 700 °C with different ratios. When the ratio of starch to Fe(NO3)3·9H2O is 1:1.5, the porous carbon exhibits a strong absorption ability with minimum reflection loss (RLmin) value of −16.64 dB at 16.78 GHz, when the thickness is 1.75 mm and the proportion of paraffin wax is 30 wt%. The synergy of well impedance matching, sufficient loss performance, and interface polarization makes 3D porous carbon materials an excellent wave absorber. This work provides a good inspiration for studying outstanding performance microwave absorption materials.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
D.D. Zhi, T. Li, J.Z. Li, H.S. Ren, F.B. Meng, A review of three-dimensional graphene-based aerogels: synthesis, structure and application for microwave absorption. Compos. Part B-Eng. 211, 108642 (2021)
Y.L. Lian, B.H. Han, D.W. Liu, Y.H. Wang, H.H. Zhao, P. Xu, X.J. Han, Y.C. Du, Solvent-free synthesis of ultrafine tungsten carbide nanoparticles-decorated carbon nanosheets for microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 12, 153 (2020)
H.Q. Zhao, Y. Cheng, W. Liu, L.J. Yang, B.S. Zhang, L.Y. Paul Wang, G.B. Ji, Z.C.J. Xu, Biomass-derived porous carbon-based nanostructures for microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 11, 24 (2019)
M.T. Qiao, X.F. Lei, Y. Ma, L.D. Tian, X.W. He, K.H. Su, Q.Y. Zhang, Application of yolk-shell Fe3O4@N-doped carbon nanochains as highly effective microwave-absorption material. Nano Res. 11, 1500–1519 (2018)
Y. Wang, Y.C. Du, P. Xu, R. Qiang, X.J. Han, Recent advances in conjugated polymer-based microwave absorbing materials. Polymers. 9, 29 (2017)
G.H. He, Y.P. Duan, H.F. Pang, Microwave absorption of crystalline Fe/MnO@C nanocapsules embedded in amorphous carbon. Nano-Micro Lett. 12, 57 (2020)
H.L. Yang, X. Zhang, Z.Q. **ong, Z.J. Shen, C.B. Liu, Cu2O@nanoporous carbon composites derived from Cu-based MOFs with ultrabroad-bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorbing performance. Ceram. Int. 47, 2155–2164 (2021)
K.L. Zhang, J.Y. Zhang, Z.L. Hou, S. Bi, Q.L. Zhao, Multifunctional broadband microwave absorption of flexible graphene composites. Carbon. 141, 608–617 (2019)
K.R. Paton, A.H. Windle, Efficient microwave energy absorption by carbon nanotubes. Carbon. 46, 1935–1941 (2008)
D.D. Min, Enhanced microwave absorption performance of double-layer absorbers containing BaFe ferrite and graphite nanosheet composites. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 819–825 (2020)
G.W. Dheeraj, V. Ajitanshu, Microwave absorbing properties of carbon fiber based materials: a review and prospective. J. Alloys Compd. 881, 160572 (2021)
Q. Shi, Y. Zhao, M.Y. Li, B.G. Li, Z.T. Hu, 3D lamellar skeletal network of porous carbon derived from hull of water chestnut with excellent microwave absorption properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 641, 449–458 (2023)
C. Yao, Z.H. Wu, J.Y. Liu, X.Y. Guo, W. Zhang, W. Huang, H.F. Zhou, Construction of lychee-like MoS2 microspheres on rice husk-derived porous carbon for enhanced dielectric loss and efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. : Mater. Electron. 34, 1213 (2023)
Z.J. Shen, H.L. Yang, Z.Q. **ong, Y. **e, C.B. Liu, Hollow core-shell CoNi@C and CoNi@NC composites as high-performance microwave absorbers. J. Alloys Compd. 871, 159574 (2021)
B.L. Wang, Q. Wu, Y.G. Fu, T. Liu, A review on carbon/magnetic metal composites for microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 86, 91–109 (2021)
L.T. Weng, X. Lei, Z.Q. Zhang, J.P. Liu, P.F. Li, J.L. Wang, High-performance electromagnetic wave absorption of porous honeycomb-like FeNi/C composites at 2–18 GHz. J. Mater. Sci. : Mater. Electron. 34, 756 (2023)
J.B. Su, R. Yang, P.K. Zhang, B.L. Wang, H. Zhao, W.H. Zhang, W.K. Wang, C.B. Wang, Fe/Fe3O4/biomass carbon derived from agaric to achieve high-performance microwave absorption. Diam. Related Mater. 129, 109386 (2022)
E.C.L. Pereira, M.E. Fernandes, J. Santos, L.F. Calheiros, A.A. Silva, B.G. Soares, Broadband microwave absorbing materials for green electronics based on poly (lactic acid)/ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer blends loaded with carbon nanotube. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 139, e52510 (2022)
H.L. Yang, Z.J. Shen, H.L. Peng, Z.Q. **ong, C.B. Liu, 1D-3D mixed-dimensional MnO2@nanoporous carbon composites derived from Mn-metal organic framework with full-band ultra-strong microwave absorption response. Chem. Eng. J. 417, 128087 (2021)
R.M. Cywar, N.A. Rorrer, C.B. Hoyt, G.T. Beckham, E.Y.X. Chen, Bio-based polymers with performance-advantaged properties. Nat. Rev. Mater. 7, 83–103 (2022)
J.B. Su, L.J. He, W.C. Zhou, C.B. Wang, J.F. Huang, K. Kajiyoshi, X.L. Zhao, P.K. Zhang, Achieving excellent wide-range efficient microwave absorption property by synthesis of Fe-doped CuAlO powders via a facile sol–gel route. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 9328–9334 (2020)
M.L. Ma, Y.X. Bi, Z.G. Jiao, J.W. Yue, Z.J. Liao, Y. Wang, Y. Ma, W.B. Huang, Facile fabrication of metal-organic framework derived Fe/Fe3O4/FeN/N-doped carbon composites coated with PPy for superior microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 608, 525–535 (2022)
J.C. Sun, Z.D. He, W.J. Dong, W.H. Wu, G.X. Tong, Broadband and strong microwave absorption of Fe/Fe3C/C core-shell spherical chains enhanced by dual dielectric relaxation and dual magnetic resonances. J. Alloys Compd. 782, 193–202 (2019)
G.H. Fan, Y.L. Jiang, J.H. **n, Z.D. Zhang, X.Y. Fu, P.T. **e, C.B. Cheng, Y. Liu, Y.P. Qu, K. Sun, R.H. Fan, Facile synthesis of Fe@Fe3C/C nanocomposites derived from bulrush for excellent electromagnetic wave-absorbing properties. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 18765–18774 (2019)
C.L. Hu, H.P. Liu, Y.H. Zhang, M. Zhang, J.Y. Yu, X.G. Liu, X.F. Zhang, Tuning microwave absorption properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes by surface functional groups. J. Mater. Sci. 54, 2417–2426 (2019)
V. Datsyuk, M. Kalyva, K. Papagelis, J. Parthenios, D. Tasis, A. Siokou, I. Kallitsis, C. Galiotis, Chemical oxidation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Carbon. 40, 833–840 (2008)
B. Ilkiv, S. Petrovska, R. Sergiienko, O. Foya, O. Ilkiv, E. Shibata, T. Nakamura, Y. Zaulychnyy, Electronic structure of hollow graphitic carbon nanoparticles fabricated from acetylene carbon black. Fuller. Nanotubes Carbon Nanostruct. 23, 449–454 (2015)
G.J. Gou, F.B. Meng, H.G. Wang, M. Jiang, W. Wei, Z.W. Zhou, Wheat straw-derived magnetic carbon foams: In-situ preparation and tunable high-performance microwave absorption. Nano Res. 12, 1423–1429 (2019)
Z.J. Shen, H.L. Yang, C.B. Liu, E.W. Guo, S.Y. Huang, Z.Q. **ong, Polymetallic MOF-derived corn-like composites for magnetic-dielectric balance to facilitate broadband electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon. 185, 464–476 (2021)
H.L. Peng, Z.Q. **ong, Z.H. Gan, C.B. Liu, Y. **e, Microcapsule MOFs@MOFs derived porous nut-bread composites with broadband microwave absorption. Compos. Part B-Eng. 224, 109170 (2021)
Z.J. Shen, C.B. Liu, H.L. Yang, Y. **e, Q.W. Zeng, R.C. Che, Fabrication of hollow cube dual-semiconductor Ln2O3/MnO/C nanocomposites with excellent microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 28689–28702 (2021)
X.C. Di, Y. Wang, Y.Q. Fu, X.M. Wu, P. Wang, Wheat flour-derived nanoporous carbon@ZnFe2O4 hierarchical composite as an outstanding microwave absorber. Carbon 173, 174–184 (2021)
X. He, H.L. Peng, Z.Q. **ong, X.L. Nie, D. Wang, G.S. Wang, C.B. Liu, A sustainable and low-cost route to prepare magnetic particle-embedded ultra-thin carbon nanosheets with broadband microwave absorption from biowastes. Carbon. 198, 195–206 (2022)
Y.Q. Fan, Y.H. Li, Y.L. Yao, Y. Sun, B.H. Tong, J. Zhan, Hierarchically porous carbon sheets/Co nanofibers derived from corncobs for enhanced microwave absorbing properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 534, 147510 (2020)
X.H. Liang, Z.M. Man, B. Quan, J. Zheng, W.H. Gu, Z. Zhang, G.B. Ji, Environment-stable CoxNiy encapsulation in stacked porous carbon nanosheets for enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 12, 102–113 (2020)
X. He, Z.Q. **ong, C.W. Lei, Z.J. Shen, A.Q. Ni, Y. **e, C.B. Liu, Excellent microwave absorption performance of LaFeO3/Fe3O4/C perovskite composites with optimized structure and impedance matching. Carbon 213, 118200 (2023)
Z.Z. Guo, P.G. Ren, F.D. Zhang, H.J. Duan, Z.Y. Chen, Y.L. **, F. Ren, Z.M. Li, Magnetic coupling N self-doped porous carbon derived from biomass with broad absorption bandwidth and high-efficiency microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 610, 1077–1087 (2022)
W.H. Gu, X.Q. Cui, J. Zheng, J.W. Yu, Y. Zhao, G.B. Ji, Heterostructure design of Fe3N alloy/porous carbon nanosheet composites for efficient microwave attenuation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 67, 265–272 (2021)
X.A. Li, X.Y. Qu, Z. Xu, W.Q. Dong, F.Y. Wang, W.C. Guo, H.Y. Wang, Y.C. Du, Fabrication of three-dimensional flower-like heterogeneous Fe3O4/Fe particles with tunable chemical composition and microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 19267–19276 (2019)
Y. Wang, X.C. Di, X.M. Wu, X.H. Li, MOF-derived nanoporous carbon/Co/Co3O4/CNTs/RGO composite with hierarchical structure as a high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Alloys Compd. 846, 156215 (2020)
R.X. Xu, D.W. Xu, Z. Zeng, D. Liu, CoFe2O4/porous carbon nanosheet composites for broadband microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 427, 130796 (2022)
K. Jia, R. Zhao, J.C. Zhong, X.B. Liu, Preparation and microwave absorption properties of loose nanoscale Fe3O4 spheres. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2167–2171 (2010)
S. Dong, P.T. Hu, X.T. Li, C.Q. Hong, X.H. Zhang, J.C. Han, NiCo2S4 nanosheets on 3D wood-derived carbon for microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 398, 125588 (2020)
C.W. Zhang, Y. Peng, Y. Song, J.J. Li, F.X. Yin, Y. Yuan, Periodic three-dimensional nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon spheres embedded with Co/Co3O4 nanoparticles toward microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 24102–24111 (2020)
C.B. Liu, L. Li, X. Zhang, W.Y. Chen, Z.J. Zhang, Y.C. Qin, D.Z. Chen, Synthesis, characterization of chiral poly (ferrocenyl-schiff base) iron(II) complexes/RGO composites with enhanced microwave absorption properties. Polymer. 150, 301–310 (2018)
G.J. Gou, Y. Liu, Q. Wan, W.L. Hua, X.L. **e, B. Zhu, Z. Tao, Controllable synthesis of nitrogen-doped porous Fe3C@C nanocomposites for efficient microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 955, 170184 (2023)
Z.J. Shen, H.L. Peng, Z.Q. **ong, H.L. Yang, Z.H. Huang, S.Y. Huang, C.B. Liu, Facile fabrication of Nd2O2S/C nanocomposite with enhanced microwave absorption induced by defects. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 105, 2082–2093 (2021)
H.L. Peng, X. Zhang, H.L. Yang, Z.Q. **ong, C.B. Liu, Y. **e, Fabrication of core-shell nanoporous carbon@chiral polyschiff base iron(II) composites for high-performance electromagnetic wave attenuationin the low-frequency. J. Alloys Compd. 850, 156816 (2021)
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant No. 2021YFG0222), the Opening Project of Oil & Gas Field Applied Chemistry Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Grant No. YQKF202104), the Natural Science Foundation of Southwest University of Science and Technology (Grant No. 20ZX7140), and the Key Research and Development Project of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2023YFG0228).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WH contributed to experiment design, experiment, figures construction, manuscript writing, experimental technical guidance, checked and revised the manuscript; CH contributed to experiment and analyzed experimental results; XX contributed to checked and revised the manuscript; GG contributed to experiment design, checked and revised the manuscript, experimental technical guidance, and analyzed experimental results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, W., Hu, C., **e, X. et al. Facile fabrication of Fe/Fe3C@starch-derived hierarchical porous carbon for microwave absorption. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 131 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11830-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11830-8



