Abstract
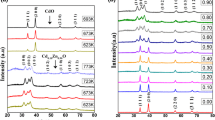
Un-doped, Zn-doped, and Al–Zn co-doped CdO thin films were deposited onto glass substrates at 350 °C by spray pyrolysis. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was conducted to investigate the structural properties of the films. The XRD patterns confirmed that all the films crystallize in a cubic structure and that the addition of Zn and Al did not alter the CdO crystal structure. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis further confirmed the successful incorporation of Zn and Al into the CdO films. Theoretical calculations based on first-principles were performed, and crystallographic information files (CIF) were obtained for optimized theoretical supercells in space group Pm3-m. The CIF files were used as input for experimental XRD spectra Rietveld refinement, to determine the Wyckoff positions of the dopants and their occupation rates. The optical properties of the films were characterized using transmittance measurements in the wavelength range of 300–1700 nm. The optical data indicated an increase in the average transmittance from 60 to 70% within the wavelength range of 600–1700 nm upon Al–Zn co-do**. The estimated direct optical band gap of the un-doped, doped, and co-doped CdO thin films is varied between 2.41 and 2.50 eV. All the samples exhibited n-type conductivity with low electrical resistivity of about 1.32 × 10–4 Ω⋅cm. Co-doped CdO thin films with 1% Al and 3% Zn exhibited higher carrier concentration (4.39 × 10+20 cm−3) than the other samples.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
L.L. Pan, G.Y. Li, J.S. Lian, Structural, optical and electrical properties of cerium and gadolinium doped CdO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 274, 365 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.03.066
G. Murtaza, B. Amin, S. Arif, M. Maqbool, I. Ahmad, A. Afaq, S. Nazir, M. Imran, M. Haneef, Structural, electronic and optical properties of CaxCd1−xO and its conversion from semimetal to wide bandgap semiconductor. Comput. Mater. Sci. 58, 71 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2012.01.020
A.H. Yahi, A. Bouzidi, R. Miloua, M. Medles, J.-F. Blach, The relationship between processing and structural, optical, electrical properties of spray pyrolysed SnO2 thin films prepared for different deposition times. Optik 196, 163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163198
A. Nakrela, N. Benramdane, A. Bouzidi, Z. Kebbab, M. Medles, C. Mathieu, Site location of Al-dopant in ZnO lattice by exploiting the structural and optical characterisation of ZnO: Al thin films. Results Phys. 6, 133 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2016.01.010
S. Ray, R. Banerjee, N. Basu, A.K. Batabyal, A.K. Barua, Properties of tin doped indium oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 3497 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.332415
A.J. Varkey, A.F. Fort, Transparent conducting cadmium oxide thin films prepared by a solution growth technique. Thin Solid Films 239, 211 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6090(94)90853-2
H. Güney, D. İskenderoğlu, The effect of Zn do** on CdO thin films grown by SILAR method at room temperature. Physica B 552, 119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.09.045
A.A. Dakhel, Bandgap narrowing in CdO doped with europium. Opt. Mater. 31, 691 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2008.08.001
M. Anitha, K. Saravanakumar, N. Anitha, L. Amalraj, Influence of a novel co-do** (Zn+ F) on the physical properties of nano structured (1 1 1) oriented CdO thin films applicable for window layer of solar cell. Appl. Surf. Sci. 443, 55 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.231
A.A. Dakhel, Effect of thallium do** on the electrical and optical properties of CdO thin films. Physica Status Solidi (a) 205, 2704 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.200723472
P. Velusamy, R.R. Babu, K. Ramamurthi, M.S. Dahlem, E. Elangovan, Highly transparent conducting cerium incorporated CdO thin films deposited by a spray pyrolytic technique. RSC Adv. 5, 102741 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra15262c
M.A. Mahdi, S.R. Yousefi, L.S. Jasim, M. Salavati-Niasari, Green synthesis of DyBa2Fe3O7. 988/DyFeO3 nanocomposites using almond extract with dual eco-friendly applications: photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 47, 14319 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.02.175
S.R. Yousefi, M. Ghanbari, O. Amiri, Z. Marzhoseyni, P. Mehdizadeh, M. Hajizadeh-Oghaz, M. Salavati-Niasari, Dy2BaCuO5/Ba4DyCu3O9.09 S-scheme heterojunction nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activities. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 104, 2952 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.17696
S.R. Yousefi, H.A. Alshamsi, O. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, Synthesis, characterization and application of Co/Co3O4 nanocomposites as an effective photocatalyst for discoloration of organic dye contaminants in wastewater and antibacterial properties. J. Mol. Liq. 337, 116405 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116405
S.R. Yousefi, A. Sobhani, H.A. Alshamsi, M. Salavati-Niasari, Green sonochemical synthesis of BaDy2 NiO5/Dy2 O3 and BaDy2 NiO5/NiO nanocomposites in the presence of core almond as a cap** agent and their application as photocatalysts for the removal of organic dyes in water. RSC Adv. 11, 11500 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA10288A
S.R. Yousefi, M. Masjedi-Arani, M.S. Morassaei, M. Salavati-Niasari, H. Moayedi, Hydrothermal synthesis of DyMn2O5/Ba3Mn2O8 nanocomposite as a potential hydrogen storage material. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44, 24005 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.07.113
S.R. Yousefi, O. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, Control sonochemical parameter to prepare pure Zn0.35Fe2.65O4 nanostructures and study their photocatalytic activity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 58, 104619 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104619
S.R. Yousefi, A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, A new nanocomposite superionic system (CdHgI4/HgI2): synthesis, characterization and experimental investigation. Adv. Powder Technol. 28, 1258 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.02.013
S.R. Yousefi, D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, M. Hassanpour, Photo-degradation of organic dyes: simple chemical synthesis of Ni (OH)2 nanoparticles, Ni/Ni (OH)2 and Ni/NiO magnetic nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 1244 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3882-6
S.R. Yousefi, D. Ghanbari, and M. Salavati-Niasari. (2016) Hydrothermal synthesis of nickel hydroxide nanostructures and flame retardant poly vinyl alcohol and cellulose acetate nanocomposites. Doi:https://doi.org/10.7508/jns.2016.01.00*
M. Yan, M. Lane, C.R. Kannewurf, R.P.H. Chang, Highly conductive epitaxial CdO thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 2342 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1365410
A.A. Dakhel, F.Z. Henari, Optical characterization of thermally evaporated thin CdO films. Cryst. Res. Technol.: J. Exp. Ind. Crystallogr. 38, 979 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200310124
T.K. Subramanyam, S. Uthanna, B.S. Naidu, Preparation and characterization of CdO films deposited by dc magnetron reactive sputtering. Mater. Lett. 35, 214 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(97)00246-2
D.M. Carballeda-Galicia, R. Castanedo-Perez, O. Jimenez-Sandoval, S. Jimenez-Sandoval, G. Torres-Delgado, C.I. Zuniga-Romero, High transmittance CdO thin films obtained by the sol–gel method. Thin Solid Films 371, 105 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(00)00987-1
S. **, Y. Yang, J.E. Medvedeva, J.R. Ireland, A.W. Metz, J. Ni, C.R. Kannewurf, A.J. Freeman, T.J. Marks, Dopant ion size and electronic structure effects on transparent conducting oxides. Sc-doped CdO thin films grown by MOCVD. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 13787 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0467925
A.M. Bazargan, S.M.A. Fateminia, M.E. Ganji, M.A. Bahrevar, Electrospinning preparation and characterization of cadmium oxide nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 155, 523 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.08.004
K. Salim, M. Medles, A. Nakrela, R. Miloua, A. Bouzidi, R. Desfeux, Enhancement of optical and electrical properties of spray pyrolysed ZnO thin films obtained from nitrate chemical by Al–Sn co-do**. Optik 210, 164504 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164504
K. Usharani, A.R. Balu, Structural, optical, and electrical properties of Zn-doped CdO thin films fabricated by a simplified spray pyrolysis technique. Acta Metall. Sin. (English Letters) 28, 64 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-014-0168-6
M.K.R. Khan, M.A. Rahman, M. Shahjahan, M.M. Rahman, M.A. Hakim, D.K. Saha, J.U. Khan, Effect of Al-do** on optical and electrical properties of spray pyrolytic nano-crystalline CdO thin films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 10, 790 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2009.09.016
E.A. Syukkalova, A.V. Sadetskaya, N.D. Demidova, N.P. Bobrysheva, M.G. Osmolowsky, M.A. Voznesenskiy, O.M. Osmolovskaya, The effect of reaction medium and hydrothermal synthesis conditions on morphological parameters and thermal behavior of calcium phosphate nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 47, 2809 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.135
B. Małecka, Thermal decomposition of Cd (CH3COO)2·2H2O studied by a coupled TG-DTA-MS method. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 78, 535 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/b:jtan.0000046117.25037.5a
P. Melnikov, V.A. Nascimento, I.V. Arkhangelsky, L.Z. Zanoni Consolo, Thermal decomposition mechanism of aluminum nitrate octahydrate and characterization of intermediate products by the technique of computerized modeling. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 111, 543 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-012-2566-1
C.S. Prajapati, P.P. Sahay, Growth, structure and optical characterization of Al-doped ZnO nanoparticle thin films. Cryst. Res. Technol. 46, 1086 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.201100192
S.J. Helen, S. Devadason, T. Mahalingam, Improved physical properties of spray pyrolysed Al: CdO nanocrystalline thin films. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 4426 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4313-z
A. Kozak, K. Wieczorek-Ciurowa, A. Kozak, The thermal transformations in Zn (NO3)2–H2O (1:6) system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 74, 497 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/b:jtan.0000005186.15474.be
P. Atkins, J. De Paula, Physical chemistry for the life sciences (Oxford University Press, 2011)
R. Chang, Physical chemistry for the biosciences (University Science Books, 2005)
M.A.V.R. Da Silva, L.M.N.B.F. Santos, Standard molar enthalpies of formation of Ni (CH3COO)2, Ni (CH3COO)2·4.00 H2O, Cd (CH3COO)2, and Cd (CH3COO)2·2.00 H2O in the crystalline state. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 32, 1327 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcht.2000.0681
K. Annamalai, K.P. Ishwar, A.J. Milind, Advanced thermodynamics engineering (CRC Press, 2011)
C.L. Yaws, Chemical properties handbook (McGraw-Hill Education, 1999)
DIFFRAC.TOPAS
P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, G.K. Madsen, D. Kvasnicka, and J. Luitz. "wien2k." An augmented plane wave+ local orbitals program for calculating crystal properties 60 1 (2001).
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865
V.K. Gupta, A. Fakhri, S. Tahami, S. Agarwal, Zn doped CdO nanoparticles: structural, morphological, optical, photocatalytic and anti-bacterial properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 504, 164 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.05.026
P. Velusamy, R.R. Babu, K. Ramamurthi, E. Elangovan, J. Viegas, M. Sridharan, Gas sensing and opto-electronic properties of spray deposited cobalt doped CdO thin films. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 255, 871 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.147
A. Rahman, M. Aadil, S. Zulfiqar, I.A. Alsafari, M. Shahid, P.O. Agboola, M.F. Warsi, M.E.F. Abdel-Haliem, Fabrication of binary metal substituted CdO with superior aptitude for dye degradation and antibacterial activity. Ceram. Int. 47, 8082 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.11.163
P. Scherrer, Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen 26, 98 (1918)
J.I. Langford, A.J.C. Wilson, Scherrer after sixty years: a survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 11, 102 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889878012844
V. Uvarov, I. Popov, Metrological characterization of X-ray diffraction methods for determination of crystallite size in nano-scale materials. Mater. Charact. 85, 111 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2013.09.002
H. Güney, The structural, morphological, optical and electrical properties of Pb doped CdO thin films grown by spray method. Vacuum 159, 261 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.10.053
N. Manjula, A.R. Balu, Double do** (Mn+Cl) effects on the structural, morphological, photoluminescence, optoelectronic properties and antibacterial activity of CdO thin films. Optik 130, 464 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.10.074
K. Sankarasubramanian, P. Soundarrajan, T. Logu, S. Kiruthika, K. Sethuraman, R.R. Babu, K. Ramamurthi, Influence of Mn do** on structural, optical and electrical properties of CdO thin films prepared by cost effective spray pyrolysis method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 26, 346 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.05.005
D.R. Lide, CRC handbook of chemistry and physics (CRC Press, 2004)
R. Sivasamy, P. Venugopal, E. Mosquera, Synthesis of Gd2O3/CdO composite by sol–gel method: structural, morphological, optical, electrochemical and magnetic studies. Vacuum 175, 109255 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109255
K. Momma, F. Izumi, VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 44, 1272 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889811038970
C. Freysoldt, B. Grabowski, T. Hickel, J. Neugebauer, First-principles calculations for point defects in solids. Rev. Mod. Phys. 86, 253 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.86.253
A. Le Bail, H. Duroy, J.L. Fourquet, Ab-initio structure determination of LiSbWO6 by X-ray powder diffraction. Mater. Res. Bull. 23, 447 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5408(88)90019-0
A.A. Coelho, Whole-profile structure solution from powder diffraction data using simulated annealing. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 33, 899 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1107/S002188980000248X
W.A. Dollase, Correction of intensities for preferred orientation in powder diffractometry: application of the March model. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 19, 267 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0021889886089458
D.C. Palmer. "CrystalMaker, CrystalMaker Software Ltd., Begbroke, Oxfordshire, England, (2014). http://crystalmaker.com/about/index.html
S. Narasimhan, S. De Gironcoli, Ab initio calculation of the thermal properties of Cu performance of the LDA and GGA. Phys. Rev. B 65, 064302 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.65.064302
M. Anitha, N. Anitha, K. Saravanakumar, I. Kulandaisamy, L. Amalraj, Effect of Zn do** on structural, morphological, optical and electrical properties of nebulized spray deposited CdO thin films. Appl. Phys. A 124, 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1993-7
H. Kim, C.M. Gilmore, J.S. Horwitz, A. Piqué, H. Murata, Transparent conducting aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films for organic light-emitting devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 259 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.125740
R. Kumaravel, K. Ramamurthi, V. Krishnakumar, Effect of indium do** in CdO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71, 1545 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2010.07.021
R. Miloua, Z. Kebbab, F. Chiker, K. Sahraoui, M. Khadraoui, N. Benramdane, Determination of layer thickness and optical constants of thin films by using a modified pattern search method. Opt. Lett. 37, 449 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.37.000449
M.N. Amroun, M. Khadraoui, Effect of substrate temperature on the properties of SnS2 thin films. Optik 184, 16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.03.011
S.H. Mohamed, N.M.A. Hadia, A.K. Diab, A.M. Abdel Hakeem, Synthesis, photoluminescence and optical constants evaluations of ultralong CdO nanowires prepared by vapor transport method. J. Alloys Compd. 609, 68 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.04.065
T. Moss, The interpretation of the properties of indium antimonide. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 67, 775 (1954). https://doi.org/10.1088/0370-1301/67/10/306
E. Burstein, Anomalous optical absorption limit in InSb. Phys. Rev. 93, 632 (1954). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.93.632
A. Zaoui, M. Zaoui, S. Kacimi, A. Boukortt, B. Bouhafs, Stability and electronic properties of ZnxCd1−xO alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 120, 98 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.10.027
M.N. Amroun, M. Khadraoui, R. Miloua, Z. Kebbab, K. Sahraoui, Investigation on the structural, optical and electrical properties of mixed SnS2–CdS thin films. Optik 131, 152 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.11.005
K. Usharani, A.R. Balu, Properties of spray deposited Zn, Mg incorporated CdO thin films. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 2071 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-015-3993-0
A.A. Ziabari, F.E. Ghodsi, G. Kiriakidis, Correlation between morphology and electro-optical properties of nanostructured CdO thin films: influence of Al do**. Surf. Coat. Technol. 213, 15 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.10.003
A.A. Ziabari, Exploring low, moderate and heavy Al do** impacts on microstructure and optical attributes of nanostructured cadmium oxide thin films. Superlattices Microstruct. 72, 172 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2014.04.005
A. Bagheri Khatibani, Z.A. Hallaj, S.M. Rozati, Some physical properties of CdO: F thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 130, 254 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2015-15254-6
D.M. Latif, I.H. Shallal, A.A. Shuihab, Synthesis and study of some physical properties of cadmium oxide CdO thin films. Energy Procedia 157, 611 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.11.226
R. Kumaravel, S. Menaka, S.R.M. Snega, K. Ramamurthi, K. Jeganathan, Electrical, optical and structural properties of aluminum doped cadmium oxide thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 122, 444 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.03.022
S. Vinoth, R.R. Isaac, P. Mohanraj, V. Ganesh, H. Algarni, S. AlFaify, Enhancement in optoelectronic properties of lanthanum co-doped CdO: Zn thin films for TCO applications. Superlattices Microstruct. 162, 107097 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2021.107097
B.J. Zheng, J.S. Lian, L. Zhao, Q. Jiang, Optical and electrical properties of Sn-doped CdO thin films obtained by pulse laser deposition. Vacuum 85, 861 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2011.01.002
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of this work from the General Direction of Scientific Research and Technology (DGRSDT/MESRS) of Algeria, under PRFU Project No: A10N01UN220120200008. The Chevreul Institute is thanked for its help in the development of this work through the ARCHI-CM project supported by the “Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur de la Recherche et de l’Innovation”, the region “Hauts-de-France”, the ERDF program of the European Union and the “Métropole Européenne de Lille”. Chevreul Institute (FR 2638), Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur, de la Recherche et de l’Innovation, Hauts-de-France Region, Fonds Européen de Développement Régional (FEDER) and Major Domain of Interest (DIM) “Eco-Energy Efficiency” of Artois University are acknowledged for supporting and funding partially this work.
Funding
No fund has been received for this research study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. WA: experimental work, investigation, writing original draft. MM and RM: theoretical work. MM: formal analysis, data curation, review. MM, MK, AN, AB, AD, MH, FB, and RD: characterization, investigation, methodology. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Azzaoui, W., Medles, M., Miloua, R. et al. Rietveld refinement combined with first-principles study of Zn and Al–Zn doped CdO thin films and their structural, optical and electrical characterisations. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1010 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10384-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10384-z