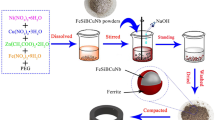
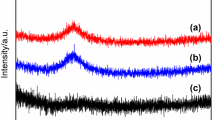
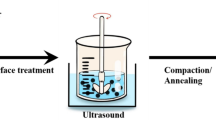
Abstract
To study the magnetic loss of electronic devices in high-frequency applications, Fe–Si–B magnetic powder cores coated with Al2O3 or phosphoric acid–alumina composite coating were prepared. In this paper, the effects of nano-Al2O3 powders and phosphoric acid with different contents on magnetic properties such as magnetic loss and permeability of magnetic materials were investigated. In addition, three kinds of amorphous Fe–Si–B powders (D50 = 21.78 μm, 11.59 μm, 5.554 μm) were mixed to find the best particle size ratio. The results show that the coating of mixture of 0.8 wt% phosphoric acid and 0.2 wt% Al2O3 achieves excellent magnetic properties (μ′ = 22.34; Pcv = 205.4 mW/cm3 measured at 1000 kHz, 20 mT) with a particle size ratio of 2:6:2.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
L. Zhang, D. Li, Z. Lu, C. Lu, T. Liu, F. Guo et al., Novel Fe-based amorphous magnetic powder cores with ultra-low core losses. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 53(5), 1290–1293 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08607-8
C. Chang, Y. Dong, M. Liu, H. Guo, Q. **ao, Y. Zhang, Low core loss combined with high permeability for Fe-based amorphous powder cores produced by gas atomization powders. J. Alloys Compd. 766, 959–963 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.055
Y. Han, F.L. Kong, F.F. Han, A. Inoue, S.L. Zhu, E. Shalaan et al., New Fe-based soft magnetic amorphous alloys with high saturation magnetization and good corrosion resistance for dust core application. Intermetallics 76, 18–25 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2016.05.011
X. Li, G. Lu, Z. Zhang, D. Ju, A. Makino, Bulk amorphous powder cores with low core loss by spark-plasma sintering Fe76Si9.6B8.4P6 amorphous powder with small amounts of SiO2. J. Alloys Compd. 647, 917–920 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.05.139
Y. Zhang, Y. Dong, L. Liu, L. Chang, B. Zhou, Q. Chi et al., High filling alumina/epoxy nanocomposite as coating layer for Fe-based amorphous powder cores with enhanced magnetic performance. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30(16), 14869–14877 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01858-0
M. Strečková, J. Füzer, L. Kobera, J. Brus, M. Fáberová, R. Bureš et al., A comprehensive study of soft magnetic materials based on FeSi spheres and polymeric resin modified by silica nanorods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 147(3), 649–660 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2014.06.004
S. Choi, S. Lee, C.Y. Bon, K. Lee, S.J. Choi, S.-I. Yoo, Novel fabrication method for a high-performance soft-magnetic composite composed of alumina-coated Fe-based metal powder. J. Electron. Mater. 50(2), 664–674 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08607-8
K.-Y. Huang, Y.-Q. Dong, M. Liu, J.-H. Ren, S.-H. Lu, Z.-K. Zhao et al., Controllable SiO2 coating layer of FeSiBPNb amorphous powder cores with excellent soft magnetic properties. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25(6), 624–629 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0093-4
K. Geng, Y. **e, L. Yan, B. Yan, Fe–Si/ZrO2 composites with core-shell structure and excellent magnetic properties prepared by mechanical milling and spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 718, 53–62 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.114
H.-I. Hsiang, L.-F. Fan, J.-J. Hung, Phosphoric acid addition effect on the microstructure and magnetic properties of iron-based soft magnetic composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 447, 1–8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.08.096
J. Chang, T. Zhan, X. Peng, J. Li, Y. Yang, J. Xu et al., Improved permeability and core loss of amorphous FeSiB/Ni–Zn ferrite soft magnetic composites prepared in an external magnetic field. J. Alloys Compd. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161335
L. **aolong, D. Yaqiang, L. Min, C. Chuntao, W. **n-Min, New Fe-based amorphous soft magnetic composites with significant enhancement of magnetic properties by compositing with nano-(NiZn)Fe2O4. J. Alloys Compd. 696, 1323–1328 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.241
R. Nowosielski, J.J. Wysłocki, I. Wnuk, P. Gramatyka, Nanocrystalline soft magnetic composite cores. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 175(1–3), 324–329 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.04.017
D. Chen, K. Li, H. Yu, J. Zuo, X. Chen, B. Guo et al., Effects of secondary particle size distribution on the magnetic properties of carbonyl iron powder cores. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.166062
A.H. Taghvaei, H. Shokrollahi, M. Ghaffari, K. Janghorban, Influence of particle size and compaction pressure on the magnetic properties of iron-phenolic soft magnetic composites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 71(1), 7–11 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2009.08.008
H.J. Woo, J.H. Ahn, C.P. Kim, D.H. Choi, S. Kim, B.W. Lee, Effect of the particle size classification of FeSiCrB amorphous soft magnetic composites to improve magnetic properties of power inductors. J. Noncryst. Solids (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2021.121309
J. Zhou, Y.F. Cui, H.S. Liu, W. Wang, K. Peng, Y.D. **ao, Magnetic properties of Fe78.4Si9.5B9Cu0.6Nb2.5 nanocrystalline alloy powder cores. J. Mater. Sci. 46(23), 7567–7572 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5731-1
H. Liang, L. Zhang, H. Wu, Exploration of twin-modified grain boundary engineering in metallic copper predominated electromagnetic wave absorber. Small 18(38), e2203620 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202203620
H. Liang, H. **ng, M. Qin, H. Wu, Bamboo-like short carbon fibers@Fe3O4@phenolic resin and honeycomb-like short carbon fibers@Fe3O4@FeO composites as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Composites A (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.105959
D. Grybos, J.S. Leszczynski, M. Kwiecień, C. Swieboda, P. Lasak, W. Pluta et al., Properties of Fe-based nanocrystalline magnetic powder cores (MPC) and structure of particle size distribution (PSD). J. Electr. Eng. 69(2), 163–169 (2018). (Https://doi.org/10.2478/jee-2018-0020)
Y. Shi, Y. Zhang, Simulation of random packing of spherical particles with different size distributions. Appl. Phys. A 92(3), 621–626 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-008-4547-6
H.I. Hsiang, K.H. Chuang, W.H. Lee, FeSiCr alloy powder to carbonyl iron powder mixing ratio effects on the magnetic properties of the iron-based alloy powder cores prepared using screen printing. Materials (Basel) (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14041034
Y. Chen, L. Zhang, H. Sun, F. Chen, P. Zhang, X. Qu et al., Enhanced magnetic properties of iron-based soft magnetic composites with phosphate–polyimide insulating layer. J. Alloys Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152205
A.H. Taghvaei, H. Shokrollahi, K. Janghorban, H. Abiri, Eddy current and total power loss separation in the iron–phosphate–polyepoxy soft magnetic composites. Mater. Des. 30(10), 3989–3995 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.05.026
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFB3502400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51872004), the Key Research and Development Plan of Anhui Province (Nos. 201904a05020038, 202003a05020051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Visualization. CZ: Methodology, Validation. XL: Funding acquisition. XK: Resources, Writing—review and editing, Supervision. SF: Formal analysis, Investigation. QL: Project administration. WS: Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Zhang, C., Liu, X. et al. Study on the magnetic property of Fe–Si–B amorphous magnetic powder core coated with Al2O3/phosphoric acid–Al2O3 double layer. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 292 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09755-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09755-9