Abstract
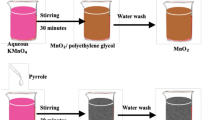
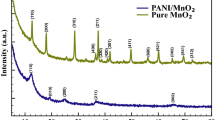
Simple redox reactions at ambient conditions have prepared manganese dioxide (MnO2) and MnO2/conducting polymer nanocomposites. Kee** the aqueous KMnO4 solution as a manganese source, MnO2, MnO2/polyaniline, and MnO2/polypyrrole nanocomposites are synthesized using ethylene glycol, aniline, and pyrrole as reducing agents, respectively. The powder X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that the prepared MnO2 and MnO2-based nanocomposites are amorphous. Fourier transform infrared spectral measurements further confirm the presence of functional groups. The change in the morphology of all samples was observed through scanning electron microscopy. The AC electrical conductivity and dielectric measurements are taken in the applied frequency range of 10 Hz–100 MHz. With the help of these experimental parameters, the electrical properties of MnO2, MnO2/polyaniline, and MnO2/polypyrrole nanocomposites are analyzed. Out of all prepared nanocomposites, the results signpost better conductivity for Ppy-MnO2 nanocomposite, and its conductivity enhances with the rise in applied frequency. Based on the observations, manganese-based conducting polymer composites can be used to develop electronic device-level applications. Also, the preparation method adopted in this study is simple, and these materials can produce on a large scale.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
D.R. Rolison, R.W. Long, J.C. Lytle, A.E. Fischer, C.P. Rhodes, T.M. McEvoy, M.E. Bourga, A.M. Lubers, Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 226–252 (2009)
L.L. Zhang, X.S. Zhao, Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 2520–2531 (2009)
C. Li, H. Bai, G. Shi, Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 2397–2409 (2009)
P. Ragupathy, D.H. Park, G. Campet, H.N. Vasan, S.J. Hwang, J.H. Choy, N. Munichandraiah, J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 6303–6309 (2009)
S. Devaraj, N. Munichandraiah, J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 4406–4417 (2008)
P. Ragupathy, H.N. Vasan, N. Munichandraiah, J Electrochem. Soc. 155, A34–A40 (2008)
Y.A. Kulakarni, M.R. Jagadeesh, S. Jambaladinni, H.M. Suresh Kumar, M.S. Vasanthkumar, S. Shivakumara, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 3352–3360 (2021)
Y.A. Kulakarni, M.R. Jagadeesh, S. Jambaladinni, H.M. Suresh Kumar, M.S. Vasanthkumar, S. Shivakumara, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 31, 7226–7231 (2020)
R.E. John, A. Chandran, M. Samuel, M. Thomas, K.C. George, Physica E 116, 113720 (2020)
S. Shivakumara, N. Munichandraiah, J. Alloys Compd. 787, 1044–1050 (2019)
S. Palsaniya, H.B. Nemade, A.K. Dasmahapatra, Carbon 150, 179–190 (2019)
H. Khan, K. Malook, M. Shah, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 29, 1990–1998 (2018)
V.C. Lokhande, A.C. Lokhande, C.D. Lokhande, J.H. Kim, T. Ji, J. Alloys Compd. 682, 381–402 (2016)
N.B. Rithin Kumar, V. Crasta, B.M. Praveen, M. Kumar, Nanotechnol. Rev. 4, 457–467 (2015)
E. Veena Gopalan, K.A. Malini, S. Saravanan, D. Sakthi Kumar, Y. Yoshidaand, M.R. Anantharaman, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41, 185005 (2008)
S. Capaccioli, M. Lucchesi, P.A. Rolla, G. Ruggeri, J. Phys. : Condens. Matter 10, 5595–5617 (1998)
A. Vijayamari, K. Sadayandi, S. Sagadevan, P. Singh, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 2739–2746 (2017)
N. Sohal, B. Maity, N.P. Shetti, S. Basu, ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4, 2285–2302 (2021)
N. Sohal, B. Maity, S. Basu, ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 4, 5158–5168 (2021)
M. Huang, F. Li, F. Dong, Y.X. Zhang, L.L. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 21380–21423 (2015)
P. Sen, A. De, A.D. Chowdhury, S.K. Bandyopadhyay, N. Agnihotri, M. Mukherjee, Electrochim. Acta 108, 265–273 (2013)
C.X. Guo, M. Wang, T. Chen, X.W. Lou, C.M. Li, Adv. Energy Mater. 1, 736–741 (2011)
Acknowledgements
Taif university Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/44), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia. The authors thank the Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology, Davanagere, for providing a laboratory facility.
Funding
This research has been funded by Taif university Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/44), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The conceptualization and Methodology of this research work were done by the authors YAK and MRJ. Material preparation and Material Characterization were done by ASAA and BMP and YAK performed collection and analysis, The first draft of the manuscript was written by MRJ. Manuscript revision and editing AA, AA. The final draft was supervised and reviewed by BMP and ASAA. Finally, all authors read and approved the final manuscript. Revision and Editing of the manuscript DGPK, MSV, SS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
“The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.”
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kulakarni, Y.A., Jagadeesh, M.R., Almalki, A.S.A. et al. AC conductivity and dielectric investigations of amorphous manganese oxide and amorphous manganese oxide/conducting polymer nanocomposites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 176 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09626-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09626-3