Abstract
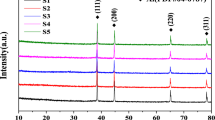
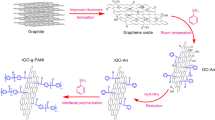
A novel Al@reduced graphene oxide (Al@RGO) composite was designed and synthesized by a one-step hydrothermal method. We investigated the effect of the graphene on the microwave absorbing properties and infrared emissivity of composites. The crystal structure, microscopic morphology, infrared emissivity and electromagnetic parameters of the prepared samples were characterized by XRD, FESEM, TEM, XPS, dual band infrared emissometer and vector network analyzer. TEM and SEM show that the thin Al sheet is uniformly wrapped by RGO with a crumpled surface. Functionalized RGO and surface cation-modified Al sheets are tightly compounded through an electrostatic interaction. The oxygen content and defect from RGO as polarization center endows the material with enhanced molecular polarization and dipole polarization effect. The Al sheet is well coated with RGO, enhancing interface polarization and impedance matching. The minimum reflection loss (RL) of optimized Al@RGO composites is − 46.11 dB at 13.68 GHz under the coating thickness of only 2 mm. The bandwidth below − 10 dB can reach 4.88 GHz (11.52–16.4 GHz). Al sheet is a suitable base material for both microwave absorption and infrared stealth. The Al@RGO composites exhibit excellent infrared stealth ability, and their lowest infrared emissivity is 0.62. Thus, Al@RGO composites show potential application for both electromagnetic wave absorption and infrared stealth.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.J. Wu, D. Lan, B. Li, L.M. Zhang, Y. Fu, Y. Zhang, H. **ng, High-entropy alloy@air@Ni–NiO core-shell microspheres for electromagnetic absorption applications. Compos. Part B—Eng. 179, 107524 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107524
A.P. Alegaonkar, P.S. Alegaonkar, Nano-carbon/polymer composites for electromagnetic shielding, structural mechanical and field emission applications. Thermoset Compos.: Prep. Prop. Appl. 38, 128 (2018). https://doi.org/10.21741/9781945291876
A.P. Alegaonkar, P.S. Alegaonkar, Nanocarbons: Preparation, Assessments, and Applications in Structural Engineering, Spintronics, Gas Sensing, EMI Shielding, and Cloaking in X-band. Nanocarbon and Its Composites. Woodhead Publishing, Cambride, 2019, 171–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102509-3.00007-9
H.S. Liang, J.L. Liu, Y. Zhang, L. Luo, H.J. Wu, Ultra-thin broccoli-like SCFs@TiO2 one-dimensional electromagnetic wave absorbing material. Compos. Part B—Eng. 179, 107507 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107507
S. Acharya, C.S. Gopinath, P. Alegaonkar et al., Enhanced microwave absorption property of reduced graphene oxide (RGO)–strontium hexaferrite (SF)/poly (vinylidene) fluoride (PVDF). Diam. Relat. Mater. 89, 28–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2018.07.024
R.W. Shu, H.L. **ng, X.L. Ji, D.X. Tan, Y. Gan, Preparation, microwave absorption and infrared emissivity of Ni-doped ZnO/Al powders by coprecipitation method in the GHz range. Nano 11, 1650047 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793292016500478
S. Acharya, J. Ray, T.U. Patro et al., Microwave absorption properties of reduced graphene oxide strontium hexaferrite/poly (methyl methacrylate) composites. Nanotechnology 29, 115605 (2018)
S. Acharya, P. Alegaonkar, S. Datar, Effect of formation of heterostructure of SrAl4Fe8O19/RGO/PVDF on the microwave absorption properties of the composite. Chem. Eng. J. 374, 144–154 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.078
Z.Y. Shen, H.L. **ng, H. Wang, H.X. Jia, Y. Liu, A.J. Chen, P.Y. Yang, Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic absorption properties of co-doped CeO2/RGO nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 753, 28–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.04.195
Y.L. Zhang, X.X. Wang, M.S. Cao, N.A.N.O. Res, Confinedly implanted NiFe2O4-rGO: cluster tailoring and highly tunable electromagnetic properties for selective-frequency microwave absorption. Nano Res. 3, 1426–1436 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1758-1
Y.P. Wang, Z. Peng, W. Jiang, Controlled synthesis of Fe3O4@SnO2/RGO nanocomposite for microwave absorption enhancement. Ceram. Int. 42, 10682–10689 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.03.180
L. Yuan, X.L. Weng, W.F. Du, J.L. **e, L.J. Deng, Optical and magnetic properties of Al/Fe3O4 core–shell low infrared emissivity pigments. J. Alloys Compd. 583, 492–497 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.08.133
L. Yuan, J. Hu, X.L. Weng, Q.Y. Zhang, L.J. deng, Galvanic displacement synthesis of Al/Ni core–shell pigments and their low infrared emissivity application. J. Alloys Compd. 670, 275–280 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.02.028
M.Y. Shi, C. Xu, Z.H. Yang, J. Liang, L. Wang, S.J. Tan, G.Y. Xu, Achieving good infrared-radar compatible stealth property on metamaterial-based absorber by controlling the floating rate of Al type infrared coating. J. Alloys Compd. 764, 314–322 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.093
Y.F. Liu, J.L. **e, M. Luo, B. Peng, L.J. Deng, Synthesis and characterization of magnetic Al/NiO composite pigments with low infrared emissivity. Mater. Sci. Forum. 898, 1561–1568 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.898.1561
K.Z. Wang, C.X. Wang, Y.J. Yin, K.L. Chen, Modification of Al pigment with graphene for infrared/visual stealth compatible fabric coating. J. Alloys Compd. 690, 741–748 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.171
X.X. Yan, G.Y. Xu, Corrosion and mechanical properties of polyurethane/Al composite coatings with low infrared emissivity. J. Alloys Compd. 491, 649–653 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.11.030
X.G. Huang, W.F. Rao, Y.Y. Chen, W.H. Ding, H.L. Zhu, M.X. YU, J. Chen, Q.T. Zhang, Infrared emitting properties and environmental stability performance of aluminum/polymer composite coating. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 5543–5548 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4458-9
D.C. Marcano, D.V. Kosynkin, J.M. Berlin, A. Sinitskii, Z.Z. Sun, A. Slesarev, L.B. Aleany, W. Lu, J.M. Tour, Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4, 4806–4814 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1006368
M. Chen, X. Wang, Y.H. Yu, Z.L. Pei, X.D. Bai, C. Sun, R.F. Huang, L.S. Wen, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and auger electron spectroscopy studies of Al-doped ZnO films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 158, 134–140 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4332(99)00601-7
M. Fathy, A. Gomaa, F.A. Taher, M.M. EI-Fass, A.E.-H.B. Kashyout, Optimizing the preparation parameters of GO and rGO for large-scale production. J. Mater. Sci. 51, 5664–5675 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9869-8
M.K. Han, X.W. Yin, L. Kong, M. LI, W.Y. Duan, L.T. Zhang, L.F. Cheng, Graphene-wrapped ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 16403–16409 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta03033h
M.Y. Yang, L. Wang, M. Li, T.J. Hou, Y.Y. Li, Structural stability and O2 dissociation on nitrogen-doped graphene with transition metal atoms embedded: a first-principles study. AIP Adv. 5, 067136 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4922841
Y. **, J.M. Yan, Z.L. Wang, H.L. Wang, Q. Jiang, Ag0.1-Pd0.9/rGO: an efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from formic acid/sodium formate. J. Mater. Chem. A. 1, 12188–12191 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA12724A
J.Y. Cai, W.J. Liu, Z.H. Li, One-pot self-assembly of Cu2O/RGO composite aerogel for aqueous photocatalysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 358, 146–151 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.021
K.L. Zhang, Y.H. Xu, Y. Lu, Y.C. Zhu, Y.Y. Qian, D.F. Wang, J.B. Zhou, N. Lin, Y.T. Qian, A graphene oxide-wrapped bipyramidal sulfur@polyaniline core–shell structure as a cathode for Li–S batteries with enhanced electrochemical performance. J. Mater. Chem. A. 4, 6404–6410 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA01118G
Y.F. Pan, G.S. Wang, Y.H. Yue, Fabrication of Fe3O4@SiO2@RGO nanocomposites and their excellent absorption properties with low filler content. RSC Adv. 5, 71718–71723 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA13315G
M. Laroussl, J.R. Roth, Numerical calculation of the reflection, absorption, and transmission of microwaves by a nonuniform plasma slab. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 21, 366–372 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/27.234562
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B.B. Fan, W.Y. Zhao, Y.Q. Chen, R. Zhang, Facile synthesis of crumpled ZnS net-wrapped Ni walnut spheres with enhanced microwave absorption properties. RSC Adv. 5, 9806–9814 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra15411h
D.Z. Chen, G.S. Wang, S. He, J. Liu, L. Guo, M.S. Cao, Controllable fabrication of mono-dispersed RGO–hematite nanocomposites and their enhanced wave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A. 1, 5996–6003 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA10664K
H.G. Wang, F.B. Meng, F. Huang, C.F. **g, Y. Li, W. Wei, Z.W. Zhou, Interface modulating CNTs@PANi hybrids by controlled unzip** of the walls of CNTs to achieve tunable high-performance microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 12142–12153 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b01122
Y. Qin, Y. Zhang, N. Qi, Q.Z. Wang, X.J. Zhang, Y. Li, Preparation of graphene aerogel with high mechanical stability and microwave absorption ability via combining surface support of metallic-CNTs and interfacial cross-linking by magnetic nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 10409–10417 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b22382
H.S. Liang, J.L. Liu, Y. Zhang, L. Luo, H.J. Wu, Ultra-thin broccoli-like SCFs@TiO2 one-dimensional electromagnetic wave absorbing material. Compos. Part B: Eng. 178, 107507 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107507
T. Bruce, P.J. Draine, Flatau, The discrete dipole approximation for periodic targets I. Theory and tests. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 25, 2693–2703 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAA.25.002693
L.L. **ong, M. Yu, J.H. Liu, S.M. Li, B. Xue, Preparation and evaluation of the microwave absorption properties of template-free graphene foam-supported Ni nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 7, 14733–14741 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA27435H
L. Liu, N. He, T. Wu, P.B. Hu, G.X. Tong, Co/C/Fe/C hierarchical flowers with strawberry-like surface as surface plasmon for enhanced permittivity, permeability, and microwave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 355, 103–108 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.131
D. Lan, M. Qin, J.L. Liu, G.L. Wu, Y. Zhang, H.J. Wu, Novel binary cobalt nickel oxide hollowed-out spheres for electromagnetic absorption applications. Chem. Eng. J. 382, 122797 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122797
P.P. Kuzhir, A.G. Paddubskaya, M.V. Shuba, S.A. Maksimenko, A. Celzard, V. Fierro, G. Amaral-Labat, A. Pizzi, G. Valušis, J. Macutkevic, M. Ivanov, J. Banys, S. Bistarelli, A. Cataldo, M. Mastrucci, F. Micciulla, I. Sacco, E. Stefanutti, S. Bellucci, Electromagnetic shielding efficiency in Ka-band: carbon foam versus epoxy/carbon nanotube composites. J Nanophotonics 6, 061715 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JNP.6.061715
P.H. Fang, Cole–cole diagram and the distribution of relaxation times. J. Chem. Phys. 42, 3411–3413 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1695743
M. Qin, D. Lan, J.L. Liu, H.S. Liang, L.M. Zhang, H. **ng, T.T. Xu, H.J. Wu, Synthesis of single-component metal oxides with controllable multi‐shelled structure and their morphology‐related applications. Chem. Rec. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.201900017
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B.B. Fan, Y.J. **e, R. Zhang, Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption of chain-like CoNi by a hydrothermal route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 372, 195–200 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.08.018
Z.Q. Qiao, S.K. Pan, J.L. **ong, L.C. Cheng, Q.R. Yao, P.H. Lin, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of La-Nd-Fe alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 423, 197–202 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.08.093
J.J. Pan, X. Sun, T. Wang, Z.T. Zhu, Y.P. He, W. **a, J.P. He, Porous coin-like Fe@MoS2 composite with optimized impedance matching for efficient microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 457, 271–279 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.263
H.X. Jia, H.L. **ng, X.L. Ji, S.T. Gao, Synergistic effect of hexagonal flake Co3O4@PANI core–shell composites with excellent microwave-absorbing properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 3386–3395 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-00612-2
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51477002 and 51707003), and the National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of China (Grant No. 201810361075).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Q., Zhang, L., **ng, H. et al. Microwave absorption and infrared stealth performance of reduced graphene oxide-wrapped Al flake. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 3005–3016 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02844-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02844-2