Abstract
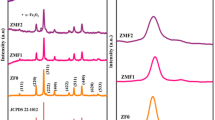
Superparamagnetic nanoparticles (NPs) have a prominent interest from researchers in the field of industrial and biomedical applications. Herein, Mg2+-substituted Mn–Zn ferrites with nominal composition Mn0.5Zn0.5−xMgxFe2O4 NPs (x = 0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.375, and 0.5) are synthesized via a facile sol–gel method. The samples after sintered at 1173 K are characterized via the X-ray diffraction technique (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, the energy-dispersive X-ray spectra (EDX), high-resolution scanning electron microscopy (SEM), ultraviolet-diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-DRS), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) technique. The XRD and FTIR patterns reveal that the formation of the cubic phase of Mn0.5Zn0.5−xMgxFe2O4 NPs. Also, small peaks associated with the phase of hematite (α-Fe2O3) are observed due to the heating of spinel ferrites. The optical band gap for Mg2+-substituted Mn–Zn ferrites ranges between 1.36 and 1.78 eV. The saturation magnetization is enhanced with increasing Mg2+ concentration. Furthermore, the M–H curves show a typical S-shaped exhibiting superparamagnetic nature for the studied samples. Also, the anisotropy constant enhances as Mg2+ content increases in Mn–Zn NPs. Overall, the results revealed that the Mn0.5Zn0.5−xMgxFe2O4 NPs presented a unique properties, and consequently, they can be candidate materials for transformer's cores, antenna, and switching applications. On other hands, antimicrobial potential of the produced ferrite NPs was estimated towards multidrug-resistant (MDR) yeast and bacteria creating urinary tract infection (UTI). All the prepared ferrite NPs showed a hopeful antimicrobial potential upon all UTI-causing pathogens. Between them, Mn0.5Mg0.5 Fe2O4 NPs at 20 µg/ml was the most promising ferrite NPs produced superior antimicrobial activity due to the narrow band gap.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Ghasemi, Particle size dependence of magnetic features for Ni0.6−xCuxZn0.4Fe2O4 spinel nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 360, 41–47 (2014)
Rani BJ, Mageswari R, Ravi G, Ganesh V, Yuvakkumar R (2017) Physico-chemical properties of pure and zinc incorporated cobalt nickel mixed ferrite (Zn x Co 0.005− x Ni 0.005 Fe 2 O 4, where x= 0, 0.002, 0.004 M) nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 28(21), 16450–16458.
S.-H. Noh, S.H. Moon, T.-H. Shin, Y. Lim, J. Cheon, Recent advances of magneto-thermal capabilities of nanoparticles: from design principles to biomedical applications. Nano Today 13, 61–76 (2017)
C. Blanco-Andujar, F.J. Teran, D. Ortega, Chapter 8—Current outlook and perspectives on nanoparticle-mediated magnetic hyperthermia, in Iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications, ed. by M. Mahmoudi, S. Laurent (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2018), pp. 197–245
Maksoud MA, Elgarahy AM, Farrell C, Rooney DW, Osman AI (2020) Insight on water remediation application using magnetic nanomaterials and biosorbents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 403:213096.
H.S. Hassan, M.A. Maksoud, L.A. Attia, Assessment of zinc ferrite nanocrystals for removal of 134Cs and 152+154Eu radionuclides from nitric acid solution. J. Mater. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02678-y
M. Angelakeris, Z.-A. Li, M. Hilgendorff, K. Simeonidis, D. Sakellari, M. Filippousi, H. Tian, G. Van Tendeloo, M. Spasova, M. Acet, M. Farle, Enhanced biomedical heat-triggered carriers via nanomagnetism tuning in ferrite-based nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 381, 179–187 (2015)
R.A. Bohara, N.D. Thorat, A.K. Chaurasia, S.H. Pawar, Cancer cell extinction through a magnetic fluid hyperthermia treatment produced by superparamagnetic Co–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 5(58), 47225–47234 (2015)
L. Khanna, N.K. Verma, S.K. Tripathi, Burgeoning tool of biomedical applications—superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J. Alloy Compd. 752, 332–353 (2018)
D. Chen, Z. Liang, J.-K. **ao, F.-H. Wei, Synthesis of Co-substituted Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles by mechanochemistry approach. J. Electroceram. 36(1), 158–164 (2016)
J.T. Seil, T.J. Webster, Antimicrobial applications of nanotechnology: methods and literature. Int. J. Nanomed. 7, 2767 (2012)
A. El-Batal, B.M. Haroun, A.A. Farrag, A. Baraka, G.S. El-Sayyad, Synthesis of silver nanoparticles and incorporation with certain antibiotic using gamma irradiation. Brit. J. Pharm. Res. 4(11), 1341 (2014)
A.F. El-Baz, A.I. El-Batal, F.M. Abomosalam, A.A. Tayel, Y.M. Shetaia, S.T. Yang, Extracellular biosynthesis of anti-Candida silver nanoparticles using Monascus purpureus. J. Basic Microbiol. 56(5), 531–540 (2016)
A.I. El-Batal, N.M. Balabel, M.S. Attia, G.S. El-Sayyad, Antibacterial and antibiofilm potential of mono-dispersed stable copper oxide nanoparticles-streptomycin nano-drug: implications for some potato plant bacterial pathogen treatment. J. Clust. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01707-4
M.A. Elkodous, G.S. El-Sayyad, I.Y. Abdelrahman, H.S. El-Bastawisy, A.E. Mohamed, F.M. Mosallam, H.A. Nasser, M. Gobara, A. Baraka, M.A. Elsayed, A.I. El-Batal, Therapeutic and diagnostic potential of nanomaterials for enhanced biomedical applications. Colloids Surf. B 180, 411–428 (2019)
Elkodous MA, El-Sayyad GS, Mohamed AE, Pal K, Asthana N, de Souza Junior FG, Mosallam FM, Gobara M, El-Batal AI (2019) Layer-by-layer preparation and characterization of recyclable nanocomposite (Co x Ni 1–x Fe 2 O 4; X= 0.9/SiO 2/TiO 2). J. Mater. Sci. 30(9), 8312–8328.
M.F. da Silva, M. Valente, Magnesium ferrite nanoparticles inserted in a glass matrix—microstructure and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132(2–3), 264–272 (2012)
P.Y. Reyes-Rodríguez, D.A. Cortés-Hernández, J.C. Escobedo-Bocardo, J.M. Almanza-Robles, H.J. Sánchez-Fuentes, A. Jasso-Terán, L.E. De León-Prado, J. Méndez-Nonell, G.F. Hurtado-López, Structural and magnetic properties of Mg–Zn ferrites (Mg1−xZnxFe2O4) prepared by sol-gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 427, 268–271 (2017)
A.H. Ashour, A.I. El-Batal, M.I.A.A. Maksoud, G.S. El-Sayyad, S. Labib, E. Abdeltwab, M.M. El-Okr, Antimicrobial activity of metal-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel technique. Particuology 40, 141–151 (2018)
M.I.A.A. Maksoud, G.S. El-Sayyad, A.H. Ashour, A.I. El-Batal, M.A. Elsayed, M. Gobara, A.M. El-Khawaga, E.K. Abdel-Khalek, M.M. El-Okr, Antibacterial, antibiofilm, and photocatalytic activities of metals-substituted spinel cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Microb. Pathog. 127, 144–158 (2019)
M.I.A. Maksoud, G.S. El-Sayyad, A.H. Ashour, A.I. El-Batal, M.S. Abd-Elmonem, H.A. Hendawy, E.K. Abdel-Khalek, S. Labib, E. Abdeltwab, M.M. El-Okr, Synthesis and characterization of metals-substituted cobalt ferrite [Mx Co(1–x) Fe2O4; (M = Zn, Cu and Mn; x = 0 and 0.5)] nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents and sensors for Anagrelide determination in biological samples. Mater. Sci. Eng. 92, 644–656 (2018)
M.I.A.A. Maksoud, A. El-ghandour, G.S. El-Sayyad, A.S. Awed, R.A. Fahim, M.M. Atta, A.H. Ashour, A.I. El-Batal, M. Gobara, E.K. Abdel-Khalek, M.M. El-Okr, Tunable structures of copper substituted cobalt nanoferrites with prospective electrical and magnetic applications. J. Mater. Sci. 30(5), 4908–4919 (2019)
M.I.A. Maksoud, A. El-ghandour, G.S. El-Sayyad, A.S. Awed, A.H. Ashour, A.I. El-Batal, M. Gobara, E.K. Abdel-Khalek, M.M. El-Okr, Incorporation of Mn2+ into cobalt ferrite via sol–gel method: insights on induced changes in the structural, thermal, dielectric, and magnetic properties. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 90(3), 631–642 (2019)
A.A. Reheem, A. Atta, M.A. Maksoud, Low energy ion beam induced changes in structural and thermal properties of polycarbonate. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 127, 269–275 (2016)
P. Belavi, G. Chavan, L. Naik, R. Somashekar, R. Kotnala, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of cadmium substituted nickel–copper ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 132(1), 138–144 (2012)
H.C. Diogo, M. Melhem, A. Sarpieri, M.C. Pires, Evaluation of the disk-diffusion method to determine the in vitro efficacy of terbinafine against subcutaneous and superficial mycoses agents. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatol. 85(3), 324–330 (2010)
A.I. El-Batal, F.M. Mosallam, G.S. El-Sayyad, Synthesis of metallic silver nanoparticles by fluconazole drug and gamma rays to inhibit the growth of multidrug-resistant microbes. J. Clust. Sci. 29(6), 1003–1015 (2018)
A.I. El-Batal, G.S. El-Sayyad, N.E. Al-Hazmi, M. Gobara, Antibiofilm and antimicrobial activities of silver boron nanoparticles synthesized by PVP polymer and gamma rays against urinary tract pathogens. J. Clust. Sci. 30(4), 947–964 (2019)
M. Isaka, A. Yangchum, S. Supothina, S. Veeranondha, S. Komwijit, S. Phongpaichit, Semisynthesis and antibacterial activities of nidulin derivatives. J. Antibiot. 72(3), 181 (2019)
L.S. Clinical, Institute, Methods for determining bactericidal activity of antimicrobial agents: approved guideline M26-A (CLSI Wayne, PA, USA, 1999)
D. Knaack, E.A. Idelevich, N. Schleimer, S. Molinaro, A. Kriegeskorte, G. Peters, K. Becker, Bactericidal activity of bacteriophage endolysin HY-133 against Staphylococcus aureus in comparison to other antibiotics as determined by minimum bactericidal concentrations and time-kill analysis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 93(4), 362–368 (2019)
K. Brownlee, Probit analysis: a statistical treatment of the sigmoid response curve (Cambridge University, New York, JSTOR, 1952)
U. Ghodake, R.C. Kambale, S. Suryavanshi, Effect of Mn2+ substitution on structural, electrical transport and dielectric properties of Mg–Zn ferrites. Ceram. Int. 43(1), 1129–1134 (2017)
E.R. Kumar, R. Jayaprakash, M.S. Seehra, T. Prakash, S. Kumar, Effect of α-Fe2O3 phase on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 74(7), 943–949 (2013)
R. Sharma, P. Thakur, M. Kumar, P.B. Barman, P. Sharma, V. Sharma, Enhancement in A-B super-exchange interaction with Mn2+ substitution in Mg–Zn ferrites as a heating source in hyperthermia applications. Ceram. Int. 43(16), 13661–13669 (2017)
M. Satalkar, S.N. Kane, A. Ghosh, N. Ghodke, G. Barrera, F. Celegato, M. Coisson, P. Tiberto, F. Vinai, Synthesis and soft magnetic properties of Zn0.8−xNixMg0.1Cu0.1Fe2O4 (x=0.0−0.8) ferrites prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. 615, S313–S316 (2014)
J. Gutiérrez-López, E. Rodriguez-Senín, J.Y. Pastor, M.A. Paris, A. Martín, B. Levenfeld, A. Várez, Microstructure, magnetic and mechanical properties of Ni–Zn ferrites prepared by powder injection moulding. Powd. Technol. 210(1), 29–35 (2011)
P. Tiwari, R. Verma, S.N. Kane, T. Tatarchuk, F. Mazaleyrat, Effect of Zn addition on structural, magnetic properties and anti-structural modeling of magnesium-nickel nano ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 229, 78–86 (2019)
R. Sharma, P. Thakur, M. Kumar, N. Thakur, N. Negi, P. Sharma, V. Sharma, Improvement in magnetic behaviour of cobalt doped magnesium zinc nano-ferrites via co-precipitation route. J. Alloy Compd. 684, 569–581 (2016)
Kakade S, Kambale R, Ramanna C, Kolekar Y (2016) Crystal strain, chemical bonding, magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of erbium (Er 3+) ion substituted cobalt-rich ferrite (Co 1.1 Fe 1.9− x Er x O 4). RSC Adv. 6(40), 33308–33317.
S. Bahhar, H. Lemziouka, A. Boutahar, H. Bioud, H. Lassri, E. Hlil, Influence of La3+ site substitution on the structural, magnetic and magnetocaloric properties of ZnFe2− xLaxO4 (x= 0.00, 0.001, 0.005 and 0.01) spinel zinc ferrites. Chem. Phys. Lett. 716, 186–191 (2019)
G. Kumar, J. Shah, R.K. Kotnala, P. Dhiman, R. Rani, V.P. Singh, G. Garg, S.E. Shirsath, K.M. Batoo, M. Singh, Self-ignited synthesis of Mg–Gd–Mn nanoferrites and impact of cation distribution on the dielectric properties. Ceram. Int. 40(9), 14509–14516 (2014)
K. Ramakanth, Basics of X-ray diffraction and its application (IK, New Delhi, 2007)
J.-M. Zhang, Y. Zhang, K.-W. Xu, V. Ji, General compliance transformation relation and applications for anisotropic hexagonal metals. Solid State Commun. 139(3), 87–91 (2006)
A.K. Zak, W.A. Majid, M.E. Abrishami, R. Yousefi, X-ray analysis of ZnO nanoparticles by Williamson-Hall and size–strain plot methods. Solid State Sci. 13(1), 251–256 (2011)
V.D. Mote, Y. Purushotham, B.N. Dole, Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 6(1), 6 (2012)
C. Murugesan, G. Chandrasekaran, Impact of Gd 3+ substitution on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 5(90), 73714–73725 (2015)
K.B. Modi, P.Y. Raval, S.J. Shah, C.R. Kathad, S.V. Dulera, M.V. Popat, K.B. Zankat, K.G. Saija, T.K. Pathak, N.H. Vasoya, V.K. Lakhani, U. Chandra, P.K. Jha, Raman and mossbauer spectroscopy and X-ray diffractometry studies on quenched copper–ferri–aluminates. Inorg. Chem. 54(4), 1543–1555 (2015)
Y. Gao, Z. Wang, J. Pei, H. Zhang, Structural, elastic, thermal and soft magnetic properties of Ni–Zn–Li ferrites. J. Alloy Compd. 774, 1233–1242 (2019)
R.S. Yadav, I. Kuřitka, J. Havlica, M. Hnatko, C. Alexander, J. Masilko, L. Kalina, M. Hajdúchová, J. Rusnak, V. Enev, Structural, magnetic, elastic, dielectric and electrical properties of hot-press sintered Co1−xZnxFe2O4 (x=0.0, 0.5) spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 447, 48–57 (2018)
C. Li, Z. Wang, Computational modelling and ab initio calculations in MAX phases—I, in Advances in Science and Technology of Mn+1AXn Phases, ed. by I.M. Low (Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, 2012), pp. 197–222
S.E. Shirsath, S.M. Patange, R. Kadam, M. Mane, K. Jadhav, Structure refinement, cation site location, spectral and elastic properties of Zn2+ substituted NiFe2O4. J. Mol. Struct. 1024, 77–83 (2012)
K.M. Srinivasamurthy, J. Angadi, S.P. Kubrin, S. Matteppanavar, D.A. Sarychev, P.M. Kumar, H.W. Azale, B. Rudraswamy, Tuning of ferrimagnetic nature and hyperfine interaction of Ni2+ doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for power transformer applications. Ceram. Int. 44(8), 9194–9203 (2018)
K. Zipare, S. Bandgar, G. Shahane, Effect of Dy-substitution on structural and magnetic properties of MnZn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Rare Earths 36(1), 86–94 (2018)
T. Dippong, I.G. Deac, O. Cadar, E.A. Levei, L. Diamandescu, G. Borodi, Effect of Zn content on structural, morphological and magnetic behavior of ZnxCo1-xFe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposites. J. Alloys Compd. 792, 432–443 (2019)
S. Banerjee, P.C. Chakraborti, S.K. Saha, An automated methodology for grain segmentation and grain size measurement from optical micrographs. Measurement 140, 142–150 (2019)
Omri A, Dhahri E, Costa B, Valente M (2019) Structural, electric and dielectric properties of Ni0. 5Zn0. 5FeCoO4 ferrite prepared by sol-gel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. Doi: 10.1155/2016/4709687.
T. Tatarchuk, N. Paliychuk, M. Bououdina, B. Al-Najar, M. Pacia, W. Macyk, A. Shyichuk, Effect of cobalt substitution on structural, elastic, magnetic and optical properties of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloy Compd. 731, 1256–1266 (2018)
J. Tauc, R. Grigorovici, A. Vancu, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Physica Status Solidi (b) 15(2), 627–637 (1966)
N. Ghazi, H.M. Chenari, F.E. Ghodsi, Rietveld refinement, morphology analysis, optical and magnetic properties of magnesium-zinc ferrite nanofibers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 468, 132–140 (2018)
A. Ashok, L.J. Kennedy, J.J. Vijaya, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Zn1-xMnxFe2O4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) spinel nano particles for transesterification of used cooking oil. J. Alloys Compd. 780, 816–828 (2019)
A. Goldman, Modern ferrite technology (Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin, 2006)
K. Nadeem, S. Rahman, M. Mumtaz, Effect of annealing on properties of Mg doped Zn-ferrite nanoparticles. Prog. Nat. Sci. 25(2), 111–116 (2015)
S. Rahman, K. Nadeem, M. Anis-ur-Rehman, M. Mumtaz, S. Naeem, I. Letofsky-Papst, Structural and magnetic properties of ZnMg-ferrite nanoparticles prepared using the co-precipitation method. Ceram. Int. 39(5), 5235–5239 (2013)
S. Hajarpour, A.H. Raouf, K. Gheisari, Structural evolution and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline magnesium–zinc soft ferrites synthesized by glycine–nitrate combustion process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 363, 21–25 (2014)
S. Khot, N. Shinde, B. Ladgaonkar, B. Kale, S. Watawe, Magnetic and structural properties of magnesium zinc ferrites synthesized at different temperature. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2(4), 460–471 (2011)
L. Kumar, M. Kar, Effect of La3+ substitution on the structural and magnetocrystalline anisotropy of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite (CoFe2−xLaxO4). Ceram. Int. 38(6), 4771–4782 (2012)
H. El Moussaoui, O. Mounkachi, R. Masrour, M. Hamedoun, E.K. Hlil, A. Benyoussef, Synthesis and super-paramagnetic properties of neodymium ferrites nanorods. J. Alloys Compd. 581, 776–781 (2013)
M.N. Akhtar, M.A. Khan, M. Ahmad, M. Nazir, M. Imran, A. Ali, A. Sattar, G. Murtaza, Evaluation of structural, morphological and magnetic properties of CuZnNi (CuxZn0. 5− xNi0. 5Fe2O4) nanocrystalline ferrites for core, switching and MLCI’s applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 421, 260–268 (2017)
A.V. Humbe, A.C. Nawle, A. Shinde, K. Jadhav, Impact of Jahn Teller ion on magnetic and semiconducting behaviour of Ni-Zn spinel ferrite synthesized by nitrate-citrate route. J. Alloy Compd. 691, 343–354 (2017)
S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, Y. Yasukawa, X. Liu, A. Morisako, Self-ignited high temperature synthesis and enhanced super-exchange interactions of Ho 3+–Mn 2+–Fe 3+–O 2− ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16(6), 2347–2357 (2014)
J. Smit, H.P.J. Wijn, Physical properties of ferrites, in Advances in Electronics and Electron Physics, ed. by L. Marton (Academic Press, Massachusetts, 1954), pp. 69–136
M.A. Elkodous, G.S. El-Sayyad, H.A. Nasser, A.A. Elshamy, M. Morsi, I.Y. Abdelrahman, A.S. Kodous, F.M. Mosallam, M. Gobara, A.I. El-Batal, Engineered nanomaterials as potential candidates for HIV treatment: between opportunities and challenges. J. Clust. Sci. 30(3), 531–540 (2019)
T. **, Y. He, Antibacterial activities of magnesium oxide (MgO) nanoparticles against foodborne pathogens. J. Nanopart Res. 13(12), 6877–6885 (2011)
Z.-X. Tang, B.-F. Lv, MgO nanoparticles as antibacterial agent: preparation and activity. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 31(3), 591–601 (2014)
M.E. Abd, G. El-Sayyad, M.M. Abdel, I. Abdelrahman, F. Mosallam, M. Gobara, A. El-Batal, Fabrication of ultra-pure anisotropic zinc oxide nanoparticles via simple and cost-effective route: implications for UTI and EAC medications. Trace Elem. Res. Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01894-1 (2019)
P. Singha, C.D. Workman, J. Pant, S.P. Hopkins, H. Handa, Zinc-oxide nanoparticles act catalytically and synergistically with nitric oxide donors to enhance antimicrobial efficacy. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 107(7), 1425–1433 (2019)
V. Stanić, S. Dimitrijević, J. Antić-Stanković, M. Mitrić, B. Jokić, I.B. Plećaš, S. Raičević, Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of copper and zinc-doped hydroxyapatite nanopowders. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(20), 6083–6089 (2010)
R.J. Lynch, Zinc in the mouth, its interactions with dental enamel and possible effects on caries; a review of the literature. Int. Dent. J. 61, 46–54 (2011)
S. Peulon, D. Lincot, Cathodic electrodeposition from aqueous solution of dense or open-structured zinc oxide films. Adv. Mater. 8(2), 166–170 (1996)
S. Pal, Y.K. Tak, J.M. Song, Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73(6), 1712–1720 (2007)
A.I. El-Batal, G.S. El-Sayyad, A. El-Ghamery, M. Gobara, Response surface methodology optimization of melanin production by Streptomyces cyaneus and synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using gamma radiation. J. Clust. Sci. 28(3), 1083–1112 (2017)
S. Xavier, H. Cleetus, P. Nimila, S. Thankachan, R. Sebastian, E. Mohammed, Structural and antibacterial properties of silver substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 5(5), 364–371 (2014)
D. Gingasu, I. Mindru, L. Patron, J.M. Calderon-Moreno, O.C. Mocioiu, S. Preda, N. Stanica, S. Nita, N. Dobre, M. Popa, Green synthesis methods of CoFe2O4 and Ag-CoFe2O4 nanoparticles using hibiscus extracts and their antimicrobial potential. J. Nanomater. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2106756
M.M. Naik, H.B. Naik, N. Kottam, M. Vinuth, G. Nagaraju, M. Prabhakara, Multifunctional properties of microwave-assisted bioengineered nickel doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 91(3), 578–595 (2019)
S. Ma, M. Tong, S. Yuan, H. Liu, Responses of the microbial community structure in Fe (II)-bearing sediments to oxygenation: the role of reactive oxygen species. ACS Earth Space Chem. 3(5), 738–747 (2019)
A. Hezma, A. Rajeh, M.A. Mannaa, An insight into the effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the structural, thermal, mechanical properties and antimicrobial activity of Cs/PVA composite. Colloids Surf. A 581, 123821 (2019)
N. Sanpo, C.C. Berndt, J. Wang, Microstructural and antibacterial properties of zinc-substituted cobalt ferrite nanopowders synthesized by sol-gel methods. J. Appl. Phys. 112(8), 084333 (2012)
G.S. El-Sayyad, H.S. El-Bastawisy, M. Gobara, A.I. El-Batal, Gentamicin-assisted mycogenic selenium nanoparticles synthesized under gamma irradiation for robust reluctance of resistant urinary tract infection-causing pathogens. Trace Elem. Res. Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01842-z(2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Materials Science Unit, Radiation Physics Department, National Center for Radiation Research and Technology, Egypt, for financing and supporting this study under the project Nanostructured Magnetic Materials. Also, the authors would like to thank Prof. Mohamed Gobara (Head of Chemical Engineering Department, Military Technical College, Egyptian Armed Forces, Cairo, Egypt), and Zeiss microscope team in Cairo for their invaluable advice during this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel Maksoud, M.I.A., El-Sayyad, G.S., Abokhadra, A. et al. Influence of Mg2+ substitution on structural, optical, magnetic, and antimicrobial properties of Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 2598–2616 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02799-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02799-4