Abstract
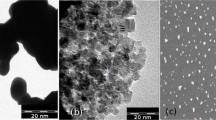
High content oxygen vacancies BiOCl consisted of thinner nanosheets was successfully synthesized assisted with ammonium sulfamate (AS) via a facile solvothermal route. X-ray powder diffractometer (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), UV–Vis diffused reflectance spectra (DRS), temperature programmed oxidation (O2-TPD), photoluminescence (PL), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and electron spin resonance (ESR) were applied to characterize the structure, morphology as well as the physicochemical properties of as-synthesized samples. The results confirm that AS and the mix solution pH have great effect on the BiOCl properties. BOC-2 (k = 0.484 min− 1) due to its high content oxygen vacancies exhibits 23 times high visible photocatalytic performance than BOC (k = 0.021 min− 1) for degradation of Rhodamine B (RhB), and enhanced photodegradation of antibiotic tetracycline hydrochloride (TC-HCl) solution. This work provides new insights on controllable synthesis of highly active BiOCl with different content oxygen vacancies.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.R. Hoffmann, S.T. Martin, W. Choi, D.W. Bahnemann, Chem. Rev. 95, 69 (1995)
M. Dresselhaus, I. Thomas, Nature 414, 332 (2001)
J. Du, X. Lai, N. Yang et al., ACS Nano 5, 590 (2010)
K. Zhang, C. Liu, F. Huang, C. Zheng, W. Wang, Appl. Catal. B 68, 125 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.08.002
Y. Wu, B. Yuan, M. Li, W.-H. Zhang, Y. Liu, C. Li, Chem. Sci. 6, 1873 (2015)
J. Li, Y. Yu, L. Zhang, Nanoscale 6, 8473 (2014)
L. Zhang, W. Wang, Nanostructured Photocatalysts, (Springer, New York, 2016)
C. Huang, J. Hu, S. Cong, Z. Zhao, X. Qiu, Appl. Catal. B 174, 105 (2015)
C.-Y. Wang, Y.-J. Zhang, W.-K. Wang et al., Appl. Catal. B 221, 320 (2018)
W.T. Li, W.Z. Huang, H. Zhou, H.Y. Yin, Y.F. Zheng, X.C. Song, J. Alloy. Compd. 638, 148 (2015)
Z. Li, Y. Qu, K. Hu, M. Humayun, S. Chen, L. **g, Appl. Catal. B 203, 355 (2017)
P. **ao, J. Lou, H. Zhang et al., Catal. Sci. Technol. 8, 201 (2018)
H. Wang, X. Yuan, Y. Wu et al., Appl. Catal. B 209, 543 (2017)
S. Weng, J. Hu, M. Lu et al., Appl. Catal. B 163, 205 (2015)
J. Di, C. Chen, S.-Z. Yang et al., J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 14144 (2017)
J. Di, J. **a, M. Ji et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 20111 (2015)
C. Hao, Y. Yang, Y. Shen et al., Mater. Des. 89, 864 (2016)
H. Li, J. Li, Z. Ai, F. Jia, L. Zhang, Angewandte Chemie. 57(1), 122–138 (2018)
S. Wu, J. **ong, J. Sun et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(19), 16620–16626 (2017)
H. Li, J. Shang, H. Zhu, Z. Yang, Z. Ai, L. Zhang, ACS Catal. 6, 8276 (2016)
L. Ye, K. Deng, F. Xu, L. Tian, T. Peng, L. Zan, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 82 (2012)
D. Cui, L. Wang, K. Xu et al., J. Mater. Chem. A 6(5), 2193–2199 (2017)
C. Hao, Y. Xu, M. Bao, X. Wang, H. Zhang, T. Li, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 3119 (2017)
C. Hao, J. Wang, Q. Cheng, Y. Bai, X. Wang, Y. Yang, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 332, 384 (2017)
L. Zhang, Z. Han, W. Wang et al., Chem. A 21, 18089 (2015)
S. Weng, Z. Fang, Z. Wang, Z. Zheng, W. Feng, P. Liu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 18423 (2014)
J. Jiang, K. Zhao, X. **ao, L. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 4473 (2012)
F. Zaera, A.J. Gellman, G.A. Somorjai, Acc. Chem. Res. 19, 24 (1986)
Y. Mi, L. Wen, Z. Wang, D. Cao, Y. Fang, Y. Lei, Appl. Catal. B 176, 331 (2015)
H. Li, T. Hu, J. Liu et al., Appl. Catal. B 182, 431 (2016)
J. Hu, W. Fan, W. Ye, C. Huang, X. Qiu, Appl. Catal. B 158, 182 (2014)
Y. Huang, H. Li, M.-S. Balogun et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 22920 (2014)
X. **, C. Lv, X. Zhou et al., Appl. Catal. B 226, 53 (2018)
Y. Cai, D. Li, J. Sun et al., Appl. Surf. Sci. (2018)
L. Ye, Y. Su, X. **, H. **e, C. Zhang, Environ. Sci. 1, 90 (2014)
L. Ding, R. Wei, H. Chen, J. Hu, J. Li, Appl. Catal. B 172, 91 (2015)
K.-L. Zhang, C.-M. Liu, F.-Q. Huang, C. Zheng, W.-D. Wang, Appl. Catal. B 68, 125 (2006)
B. Li, L. Shao, B. Zhang, R. Wang, M. Zhu, X. Gu, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 505, 653 (2017)
D.-H. Wang, G.-Q. Gao, Y.-W. Zhang, L.-S. Zhou, A.-W. Xu, W. Chen, Nanoscale 4, 7780 (2012)
F. Chang, Y. **e, J. Zhang et al., RSC Adv. 4, 28519 (2014)
D. Mao, A. Yu, S. Ding et al., Appl. Surf. Sci. 389, 742 (2016)
H. Huang, X. Han, X. Li, S. Wang, P.K. Chu, Y. Zhang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 482 (2015)
M. Zhu, Q. Liu, W. Chen et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 38832 (2017)
F. Wu, X. Wang, S. Hu, C. Hao, H. Gao, S. Zhou, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 42, 30098 (2017)
S. Ning, L. Ding, Z. Lin et al., Appl. Catal. B 185, 203 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported from the International S&T Cooperation Program of Wuhan (2017030209020255), the Creative Research Groups Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei (2017CFA026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Li, D., Cai, Y. et al. Controllable synthesis of highly active BiOCl with different content oxygen vacancies. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 12241–12250 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9335-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9335-2