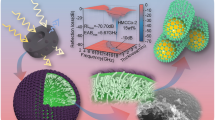
Abstract
SiC coated Ni nanocomposites were fabricated by a facile arc-discharge method. XRD, HRTEM and XPS technologies indicate that as-prepared Ni@SiC nanocomposites consist of the Ni nanoparticles core and shells composed of crystalline SiC together with a few C/SiOx. The Ni@SiC nanocomposites absorbent present excellent microwave absorption in C–Ku band. The strongest reflection loss (RL) of Ni@SiC-parrafin composites achieve −42.1 dB at 11.2 GHz with its absorption bandwidth below −10 dB covering the whole X band at a matching thickness of 2.88 mm. Moreover, the RL values of Ni@SiC nanocomposites absorbent below −10 dB are about 1.6–2.5 times of those of the Ni nanoparticles absorbent at absorbent thicknesses of 1.4–5.5 mm. Furthermore, the maximum absorption bandwidth exceeding −10 dB is about 7.2 (6.2–13.4 GHz) for Ni@SiC-paraffin composites at a relatively thin matching thickness of 3.0 mm, covering the almost half C band and the whole X band.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.W. Jiang, Z.H. Wang, D.Y. Geng, Y.M. Lin, Y. Wang, J. An, J. He, D. Li, W. Liu, Z.D. Zhang, Structure and electromagnetic properties of both regular and defective onion-like carbon nanoparticles. Carbon 95, 910–918 (2015)
X.F. Zhang, Y. Rao, J.J. Guo, G.W. Qin, Multiple-phase carbon-coated FeSn2/Sn nanocomposites for high-frequency microwave absorption. Carbon 96, 972–979 (2016)
Q. Li, X.W. Yin, W.Y. Duan, L. Kong, B.L. Hao, F. Ye, Electrical, dielectric and microwave-absorption properties of polymer derived SiC ceramics in X band. J. Alloys. Compd. 565, 66–72 (2013)
H.P. Xu, Z.M. Dang, M.J. Jiang, S.H. Yao, J. Bai, Enhanced dielectric properties and positive temperature coefficient effect in the binary polymer composites with surface modified carbon black. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 229–234 (2008)
X.L. Su, Y. Jia, J.B. Wang, J. Xu, X.H. He, C. Fu, S.T. Liu, Combustion synthesis and microwave absorption property of SiC(Fe) solid solution powder under different reaction time. J. Mater. Sci. 24, 1905–1912 (2013)
S. Agathopoulos, Influence of synthesis process on the dielectric properties of B-doped SiC powders. Ceram. Int. 38, 3309–3315 (2012)
X. Su, W. Zhou, J. Xu, J. Wang, X. He, C. Fu, Z. Li, Preparation and dielectric property of Al and N co-doped SiC powder by combustion synthesis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 1388–1393 (2012)
A. B. Kheradmand, Z. Lalegani, Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of Al/SiC composite foams. J. Mater. Sci. 26,7530–7536 (2015)
D. Li, H. **, M. Cao, T. Chen, Y. Dou, B. Wen, S. Agathopoulos, Production of Ni-doped SiC nanopowders and their dielectric properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 1523–1527 (2011)
Q.H. Liu, Q. Cao, H. Bi, C.Y. Liang, K.P. Yuan, W. She, Y.J. Yang, R.C. Che, CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 28, 486–490 (2015)
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B.B. Fan, W.Y. Zhao, Y.J. **e, R. Zhang, Facile preparation and enhanced microwave absorption properties of core–shell composite spheres composited of Ni cores and TiO2 shells. Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys. 17, 8802–8810 (2015)
X. Ding, Y. Huang, J.G. Wang, H.W. Wu, P.B. Liu, Excellent electromagnetic wave absorption property of quaternary composites consisting of reduced graphene oxide, polyaniline and FeNi3@SiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 908–914 (2015)
B. Wang, J. Zhang, T. Wang, L. Qiao, F. Li, Synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties of Ni@Ni2O3 core–shell particles. J. Alloys. Compd. 567, 21–25(2013)
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B.B. Fan, W.Y. Zhao, R. Zhang, Enhanced microwave absorption capabilities of Ni microspheres after coating with SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 26, 5393–5399(2015)
X. Liu, C. Feng, S. W. Or, Y. Sun, C. **, W. Li and Y. Lv, Investigation on microwave absorption properties of CuO/Cu2O-coated Ni nanocapsules as wide-band microwave absorbers. RSC Adv. 3, 14590–14594 (2013)
X.L. Dong, X.F. Zhang, H. Huang, F. Zuo, Enhanced microwave absorption in Ni/polyaniline nanocomposites by dual dielectric relaxations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 013127–013123 (2008)
H. Wang, H. Guo, Y. Dai, D. Geng, Z. Han, D. Li, T. Yang, S. Ma, W. Liu, Z. Zhang, Optimal electromagnetic-wave absorption by enhanced dipole polarization in Ni/C nanocapsules. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 083116–083114 (2012)
X.F. Zhang, H. Huang, X.L. Dong, Core/shell metal/heterogeneous oxide nanocapsules: the empirical formation law and tunable electromagnetic losses. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 8563–8569 (2013)
H. Wang, Y.Y. Dai, W.J. Gong, D.Y. Geng, S. Ma, D. Li, W. Liu, Z.D. Zhang, Broadband microwave absorption of CoNi@C nanocapsules enhanced by dual dielectric relaxation and multiple magnetic resonances. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 223113–223114 (2013)
G.M. Shi, Y.F. Li, L. Ai, F.N. Shi, Two step synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties of polycrystalline BaTiO3 coated Ni nanocomposites. J. Alloys. Compd. 680, 735–743 (2016)
C.D. Wagner, W.M. Riggs, L.E. Davis et al., Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (Minnesota, Perkin-Elemer Corporation and Physical Electronics Division, 1979)
N.K. Huang, B. Yang, Q. **ong, Y. G. Liu, Effect of hydrogen on SiC–C films with AES and XPS analyses. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 14, 56–59(2003)
F. Arezzo, E. Severini, N. Zacchetti, An XPS study of diamond films grown on differently pretreated silicon substrates. Surf. Interface Anal. 22, 218–223 (1994)
N.B. Hamzan, F.N.B. Nordin, S.A. Rahman et al., Effects of substrate temperature on the growth, structural and optical properties of NiSi/SiC core–shell nanowires. Appl. Surf. Sci. 343, 70–76 (2015)
Y. Saito, T. Yoshikawa, M. Okuda, Synthesis and electron-beam incision of carbon nanocapsules encaging YC2. Chem. Phys. Lett. 299, 73–76 (1993)
X.F. Zhang, X.L. Dong, H. Huang, B. Lv, X.G. Zhu, J.P. Lei, S. Ma, W. Liu, Z.D. Zhang, Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of SiO2-coated Fe nanocapsules. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 454–455, 211–215 (2007)
C.H. Gong, X.X. Wang, X.F. Zhang, X.W. Zhao, H.J. Meng, Y.S. Ji, J.W. Zhang, Z.J. Zhang, Synthesis of Ni/SiO2 nanocomposites for tunable electromagnetic absorption. Mater. Lett. 121, 81–84 (2014)
N.D. Wu, X.G. Liu, C.Y. Zhao, C.Y. Cui, A.L. **a, Effects of particle size on the magnetic and microwave absorption properties of carbon-coated nickel nanocapsules. J. Alloys Compd. 656, 628–634 (2016)
Z.H. Wang, Z. Han, D.Y. Geng, Z.D. Zhang, Synthesis, characterization and microwave absorption of carbon-coated Sn nanorods. Chem. Phys. Lett. 489, 187–190 (2010)
H.L. Lv, H.Q. Zhang, G.B. Ji, Z.C.J. Xu, Interface strategy to achieve tunable high frequency attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 6529–6538 (2016)
S. He, C. Lu, G. S. Wang, J. W. Wang, H. Y. Guo, L. Guo, Synthesis and growth mechanism of white-fungus-like nickel sulfide microspheres, and their application in polymer composites with enhanced microwave-absorption properties. Chem. Plus. Chem. 79, 569–576(2014)
X.F. Zhang, X.L. Dong, H. Huang, B. Lv, J.P. Lei, C.J. Choi, Microstructure and microwave absorption properties of carbon-coated iron nanocapsules. J. Phys. D 40, 5383–5387 (2007)
B. Lu, X.L. Dong, H. Huang, X.F. Zhang, X.G. Zhu, J.P. Lei, J.P. Sun, Microwave absorption properties of the core/shell-type iron and nickel nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 106–1111(2008)
V.B. Bregar, Advantages of ferromagnetic nanoparticle composites in microwave absorbers. IEEE Trans. Magn. 40, 1679–1684 (2004)
D.A. Dimitrov, G.M. Wysin, Magnetic properties of spherical fcc clusters with radial surface anisotropy. Phys. Rev. B 51, 11947–11950 (1995)
H. Zhang, M. Hong, P. Chen, A.J. **e, Y.H. Shen, 3D and ternary rGO/MCNTs/Fe3O4 composite hydrogels: synthesis, characterization and their electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Alloys Compd. 665, 381–387 (2016)
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B.B. Fan et al., Effect of the TiO2 amounts on microwave absorption properties of Ni/TiO2 heterostructure composites. Phys. B 454, 120–125 (2014)
A.N. Yusoff, M.H. Abdullah, S.H. Ahmad, S.F. Jusoh, A.A. Mansor, S.A.A. Hamid, Electromagnetic and absorption properties of some microwave absorbers. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 876–882 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Science technology program of Shen Yang (F14-231-1-25) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21571132).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, ZJ., Shi, GM. & Zhao, Q. Improved microwave absorption properties of core–shell type Ni@SiC nanocomposites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 5887–5897 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6262-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6262-y