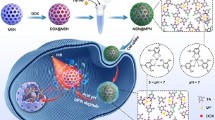
Abstract
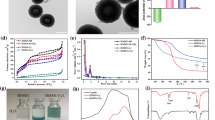
Chemotherapy combined with photothermal therapy, a promising strategy for cancer treatment, has a high potential to control drug release and improve therapeutic efficacy. Inspired by this, a pH/NIR dual-responsive drug delivery system (DOX/HMSN@PDA-HA nanoparticles, simplified as DHPH NPs) based on hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (HMSNs) was designed for targeted therapy of tumor, by self-coating polydopamine-modified hyaluronic acid (HA-PDA) layer. Doxorubicin (DOX) was loaded into HMSNs for chemotherapy, while HA-PDA coating acted as photothermal therapy agent with tumor-targeted capability. Characterizations suggest that DHPH nanoparticles have been successfully constructed with excellent drug loading capacity (36.91%) and satisfactory photothermal conversion efficiency (25.74%). Furthermore, in vitro results indicate that DHPH nanoparticles could precisely target human hepatocellular liver carcinoma cells and effectively suppress the tumor cells growth under 808 nm laser irradiation (2 W cm−2). Therefore, this study presents a feasible strategy for develo** efficient platform for tumor-targeted chemo-photothermal therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
He H, **e H, Chen Y, Li C, Han D, Xu F, Lyu J (2020) Global, regional, and national burdens of bladder cancer in 2017: estimates from the 2017 global burden of disease study. BMC Public Health 20(1):1693. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09835-7
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Wang ZY, Li ZY, Sun ZL, Wang SR, Ali Z, Zhu S, Liu S, Ren QFS, Wang B, Hou Y (2020) Visualization nanozyme based on tumor microenvironment “unlocking” for intensive combination therapy of breast cancer. Sci Adv 6(48):8733–8743. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abc8733
Song Y, Qu Z, Li J, Shi L, Zhao W, Wang H, Sun T, Jia T, Sun Y (2021) Fabrication of the biomimetic DOX/Au@Pt nanoparticles hybrid nanostructures for the combinational chemo/photothermal cancer therapy. J Alloy Compd 881:160592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160592
Yang D, Xu J, Yang G, Zhou Y, Ji H, Bi H, Gai S, He F, Yang P (2018) Metal-organic frameworks join hands to create an anti-cancer nanoplatform based on 808 nm light driving up-conversion nanoparticles. Chem Eng J 344:363–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.101
Yang G, Tian J, Chen C, Jiang D, Xue Y, Wang C, Gao Y, Zhang W (2019) An oxygen self-sufficient NIR-responsive nanosystem for enhanced PDT and chemotherapy against hypoxic tumors. Chem Sci 10(22):5766–5772. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9sc00985j
Liu X, Zhang M, Yan D, Deng G, Wang Q, Li C, Zhao L, Lu J (2020) A smart theranostic agent based on Fe-HPPy@Au/DOX for CT imaging and PTT/chemotherapy/CDT combined anticancer therapy. Biomater Sci 8(15):4067–4072. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0bm00623h
Deng Z, Fang C, Ma X, Li X, Zeng YJ, Peng X (2020) One stone two birds: Zr–Fc metal-organic framework nanosheet for synergistic photothermal and chemodynamic cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(18):20321–20330. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c06648
Meng X, Zhang B, Yi Y, Cheng H, Wang B, Liu Y, Gong T, Yang W, Yao Y, Wang H, Bu W (2020) Accurate and real-time temperature monitoring during MR imaging guided PTT. Nano Lett 20(4):2522–2529. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b05267
Wang K, Cai Z, Fan R, Yang Q, Zhu T, Jiang Z, Ma Y (2020) A tumor-microenvironment-responsive nanomaterial for cancer chemo-photothermal therapy. RSC Adv 10(37):22091–22101. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra04171h
Wang H, Williams GR, **e X, Wu M, Wu J, Zhu L-M (2020) Stealth polydopamine-based nanoparticles with red blood cell membrane for the chemo-photothermal therapy of cancer. ACS Appl Bio Mater 3(4):2350–2359. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.0c00094
Khafaji M, Zamani M, Golizadeh M, Bavi O (2019) Inorganic nanomaterials for chemo/photothermal therapy: a promising horizon on effective cancer treatment. Biophys Rev 11(3):335–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-019-00532-3
Yu D, Wang Y, Chen J, Liu S, Deng S, Liu C, McCulloch I, Yue W, Cheng D (2021) nCo-delivery of NIR-II semiconducting polymer and pH-sensitive doxorubicin-conjugated prodrug for photothermal/chemotherapy. Acta Biomater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2021.10.009
Sun H, Zhang Q, Li J, Peng S, Wang X, Cai R (2021) Near-infrared photoactivated nanomedicines for photothermal synergistic cancer therapy. Nano Today 37:101073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2020.101073
Zhang W, Cai K, Li X, Zhang J, Ma Z, Foda MF, Mu Y, Dai X, Han H (2019) Au hollow nanorods-chimeric peptide nanocarrier for NIR-II photothermal therapy and real-time apoptosis imaging for tumor theranostics. Theranostics 9(17):4971–4981. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.35560
Zheng S, Dou P, ** S, Jiao M, Wang W, ** Z, Wang Y, Li J, Xu K (2021) Tumor microenvironment/NIR-responsive carbon monoxide delivery with hollow mesoporous CuS nanoparticles for MR imaging guided synergistic therapy. Mater Des 205:109731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109731
Chen Q, He S, Zhang F, Cui F, Liu J, Wang M, Wang D, ** Z, Li C (2020) A versatile Pt–Ce6 nanoplatform as catalase nanozyme and NIR-II photothermal agent for enhanced PDT/PTT tumor therapy. Sci China Mater 64(2):510–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-020-1431-5
Chang M, Hou Z, Wang M, Yang C, Wang R, Li F, Liu D, Peng T, Li C, Lin J (2021) Single-atom Pd nanozyme for ferroptosis-boosted mild-temperature photothermal therapy. Angew Chem 60(23):12971–12979. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202101924
Chang X, Zhang M, Wang C, Zhang J, Wu H, Yang S (2020) Graphene oxide/BaHoF5/PEG nanocomposite for dual-modal imaging and heat shock protein inhibitor-sensitized tumor photothermal therapy. Carbon 158:372–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.10.105
Chen YW, Su YL, Hu SH, Chen SY (2016) Functionalized graphene nanocomposites for enhancing photothermal therapy in tumor treatment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 105(Pt B):190–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2016.05.022
Cai W, Gao H, Chu C, Wang X, Wang J, Zhang P, Lin G, Li W, Liu G, Chen X (2017) Engineering phototheranostic manoscale metal-organic frameworks for multimodal imaging-guided cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(3):2040–2051. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11579
Pu Y, Zhu Y, Qiao Z, **n N, Chen S, Sun J, ** R, Nie Y, Fan H (2021) A Gd-doped polydopamine (PDA)-based theranostic nanoplatform as a strong MR/PA dual-modal imaging agent for PTT/PDT synergistic therapy. J Mater Chem B 9(7):1846–1857. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0tb02725a
Lu J, Cai L, Dai Y, Liu Y, Zuo F, Ni C, Shi M, Li J (2021) Polydopamine-based nanoparticles for photothermal therapy/chemotherapy and their synergistic therapy with autophagy inhibitor to promote antitumor treatment. Chem Rec 21(4):781–796. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.202000170
Fan R, Chen C, Hou H, Chuan D, Mu M, Liu Z, Liang R, Guo G, Xu J (2021) Tumor acidity and near-infrared light responsive dual drug delivery polydopamine-based nanoparticles for chemo-photothermal therapy. Adv Funct Mater 31(18):2009733. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202009733
Zhu W, Chen M, Liu Y, Tian Y, Song Z, Song G, Zhang X (2019) A dual factor activated metal-organic framework hybrid nanoplatform for photoacoustic imaging and synergetic photo-chemotherapy. Nanoscale 11(43):20630–20637. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr06349h
Huang C, Zhang L, Guo Q, Zuo Y, Wang N, Wang H, Kong D, Zhu D, Zhang L (2021) Robust nanovaccine based on polydopamine-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for effective photothermal-immunotherapy against melanoma. Adv Funct Mater 31(18):2010637. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202010637
Zhang C, Wu D, Lu L, Duan X, Liu J, **e X, Shuai X, Shen J, Cao Z (2018) Multifunctional hybrid liposome as a theranostic platform for magnetic resonance imaging guided photothermal therapy. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4(7):2597–2605. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00176
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Meng X, Lu H, Chang H, Dong H, Zhang X (2018) Light-triggered theranostic liposomes for tumor diagnosis and combined photodynamic and hypoxia-activated prodrug therapy. Biomaterials 185:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.09.033
Yang L, Zhang C, Liu J, Huang F, Zhang Y, Liang XJ, Liu J (2020) ICG-conjugated and (125) I-labeled polymeric micelles with high biosafety for multimodality imaging-guidedphotothermal therapy of tumors. Adv Healthc Mater 9(5):e1901616. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201901616
Zhong S, Chen C, Yang G, Zhu Y, Cao H, Xu B, Luo Y, Gao Y, Zhang W (2019) Acid-triggered nanoexpansion polymeric micelles for enhanced photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(37):33697–33705. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b12620
Shang W, Peng L, Guo P, Hui H, Yang X, Tian J (2020) Metal-organic frameworks as a theranostic nanoplatform for combinatorial chemophotothermal therapy adapted to different administration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6(2):1008–1016. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01075
Huang L, Liu J, Gao F, Cheng Q, Lu B, Zheng H, Xu H, Xu P, Zhang X, Zeng X (2018) A dual-responsive, hyaluronic acid targeted drug delivery system based on hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy. J Mater Chem B 6(28):4618–4629. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8tb00989a
Zhou S, Zhong Q, Wang Y, Hu P, Zhong W, Huang C-B, Yu Z-Q, Ding C-D, Liu H, Fu J (2022) Chemically engineered mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based intelligent delivery systems for theranostic applications in multiple cancerous/non-cancerous diseases. Coord Chem Rev 452:214309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214309
Chen Z, Liao T, Wan L, Kuang Y, Liu C, Duan J, Xu X, Xu Z, Jiang B, Li C (2021) Dual-stimuli responsive near-infrared emissive carbon dots/hollow mesoporous silica-based integrated theranostics platform for real-time visualized drug delivery. Nano Res 14(11):4264–4273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3624-4
Yan T, He J, Liu R, Liu Z, Cheng J (2020) Chitosan capped pH-responsive hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted chemo-photo combination therapy. Carbohydr Polym 231:115706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115706
Ma G, Du X, Zhu J, Xu F, Yu H, Li J (2021) Multi-functionalized dendrimers for targeted co-delivery of sorafenib and paclitaxel in liver cancers. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 63:102493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102493
Zhou Y, Chang C, Liu Z, Zhao Q, Xu Q, Li C, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Lu B (2021) Hyaluronic acid-functionalized hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pH-sensitive nanocarriers for cancer chemo-photodynamic therapy. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 37(8):2619–2628. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c03250
Sun Q, Bi H, Wang Z, Li C, Wang X, Xu J, Zhu H, Zhao R, He F, Gai S, Yang P (2019) Hyaluronic acid-targeted and pH-responsive drug delivery system based on metal-organic frameworks for efficient antitumor therapy. Biomaterials 223:119473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119473
Chiesa E, Riva F, Dorati R, Greco A, Ricci S, Pisani S, Patrini M, Modena T, Conti B, Genta I (2020) On-chip synthesis of hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles for selective inhibition of CD44+ human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation. Pharmaceutics 12(3):260–283. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12030260
Yu F, Huang J, Yu Y, Lu Y, Chen Y, Zhang H, Zhou G, Sun Z, Liu J, Sun D, Zhang G, Zou H, Zhong Y (2016) Glutathione-responsive multilayer coated gold nanoparticles for targeted gene delivery. J Biomed Nanotechnol 12(3):503–515. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2016.2177
Chen K, Chang C, Liu Z, Zhou Y, Xu Q, Li C, Huang Z, Xu H, Xu P, Lu B (2020) Hyaluronic acid targeted and pH-responsive nanocarriers based on hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for chemo-photodynamic combination therapy. Colloids Surf B 194:111166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111166
Liu X, **e Z, Shi W, He Z, Liu Y, Su H, Sun Y, Ge D (2019) Polynorepinephrine nanoparticles: a novel photothermal nanoagent for chemo-photothermal cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(22):19763–19773. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b03458
Pu XQ, Ju XJ, Zhang L, Cai QW, Liu YQ, Peng HY, **e R, Wang W, Liu Z, Chu LY (2021) Novel multifunctional stimuli-responsive nanoparticles for synergetic chemo-photothermal therapy of tumors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(24):28802–28817. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c05330
Jiang A, Liu Y, Ma L, Mao F, Liu L, Zhai X, Zhou J (2019) Biocompatible heat-shock protein inhibitor-delivered flowerlike short-wave infrared nanoprobe for mild temperature-driven highly efficient tumor ablation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(7):6820–6828. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b21483
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51773162 and 21204071).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Dale Huber.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Chang, C., Wang, X. et al. A self-coated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticle for tumor targeting and chemo-photothermal therapy. J Mater Sci 57, 6013–6025 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07020-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07020-2