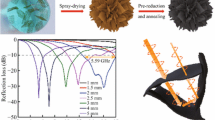
Abstract
The three-dimensional porous structure of a material can trap the propagating electromagnetic waves by multiple reflections and scatterings, thereby improving the microwave absorption properties. The highly ordered and interconnected porous NaY zeolites can serve as the templates to prepare the three-dimensional graphene (3DG). A high defect density of 13.4–23.7 × 1010 cm−2 was obtained in the 3DG due to the incomplete replication. Simultaneously, the broken asymmetry of space charges in the defect sites will lead to the separation of space charges and the formation of electric dipoles, which results in significantly enhanced dielectric performance and microwave absorption. Consequently, owing to the porous structure and high specific surface area, the effective absorption band of the 3DG attains a large width of 14.3 GHz (3.7–18 GHz) with the absorber thicknesses located in 2–5 mm. The microwave absorption performance of 3DG is much superior to that of multilayer graphene with a two-dimensional structure. Hence, this ultralight 3DG can act as a promising microwave absorption material and probably gifts other physical applications in the future.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lv HL, Yang ZH, Wang PLY, Ji GB, Song JZ, Zheng LR, Zeng HB, Xu ZCJ (2018) A voltage-boosting strategy enabling a low-frequency, flexible electromagnetic wave absorption device. Adv Mater 30:1706343
Kefeni KK, Msagati TAM, Mamba BB (2017) Ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, characterisation and applications in electronic device. Mater Sci Eng B 215:37–55
Al-Ghamdi AA, Al-Ghamdi AA, Al-Turki Y, Yakuphanoglu F, El-Tantawy F (2016) Electromagnetic shielding properties of graphene/acrylonitrile butadiene rubber nanocomposites for portable and flexible electronic devices. Compos Part B 88:212–219
Song WL, Guan XT, Fan LZ, Zhao YB, Cao WQ, Wang CY, Cao MS (2016) Strong and thermostable polymeric graphene/silica textile for lightweight practical microwave absorption composites. Carbon 100:109–117
Mo ZC, Yang RL, Lu DW, Yang LL, Hu QM, Li HB, Zhu H, Tang ZK, Gui XC (2019) Lightweight, three-dimensional carbon Nanotube@TiO2 sponge with enhanced microwave absorption performance. Carbon 144:433–439
Liu XF, Chen YX, Cui XR, Zeng M, Yu RH, Wang GS (2015) Flexible nanocomposites with enhanced microwave absorption properties based on Fe3O4/ SiO2 nanorods and polyvinylidene fluoride. J Mater Chem A 3:12197–12204
Wang FY, Sun YQ, Li DR, Zhong B, Wu ZG, Zuo SY, Yan D, Zhou RF, Feng JJ, Yan PX (2018) Microwave absorption properties of 3D cross-linked Fe/C porous nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Carbon 134:264–273
Wang XX, Ma T, Shu JC, Cao MS (2018) Confinedly tailoring Fe3O4 clusters-NG to tune electromagnetic parameters. Chem Eng J 332:321–330
Lu ZG, Ma LM, Tan JB, Wang HY, Ding XM (2016) Transparent multi-layer graphene/polyethylene terephthalate structures with excellent microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding performance and microwave absorption with broadened bandwidth. Nanoscale 8:16684–16693
Wang L, Huang Y, Sun X, Huang HJ, Liu PB, Zong M, Wang Y (2014) Synthesis and microwave absorption enhancement of graphene@Fe3O4 @SiO2 @NiO nanosheet hierarchical structures. Nanoscale 6:3157–3164
Feng W, Wang YM, Chen JC, Wang L, Guo LX, Ouyang JH, Jia DC, Zhou Y (2016) Reduced graphene oxide decorated with in-situ growing ZnO nanocrystals: facile synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 108:52–60
Chen C, ** JB, Zhou EZ, Peng L, Chen ZC, Gao C (2018) Porous graphene microflowers for high-performance microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett 10:26
Zhang Y, Huang Y, Chen HH, Huang ZY, Yang Y, **ao PS, Zhou Y, Chen YS (2016) Composition and structure control of ultralight graphene foam for high-performance microwave absorption. Carbon 105:438–447
Xu DW, Yang S, Chen P, Yu Q, **ong XH, Wang J (2019) 3D nitrogen-doped porous magnetic graphene foam-supported Ni nanocomposites with superior microwave absorption properties. J Alloy Compd 782:600–610
Xu HL, Yin XW, Zhu M, Li MH, Zhang H, Wei HJ, Zhang LT, Cheng LF (2019) Constructing hollow graphene nano-spheres confined in porous amorphous carbon particles for achieving full X band microwave absorption. Carbon 142:346–353
Hu CG, Mou ZY, Lu GW, Chen N, Dong ZL, Hu MJ, Qu LT (2013) 3D graphene-Fe3O4 nanocomposites with high-performance microwave absorption. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:13038
Ji HM, Li JH, Zhang JJ, Yan Y (2019) Remarkable microwave absorption performance of ultralight graphene-polyethylene glycol composite aerogels with a very low loading ratio of graphene. Compos Part A 123:158–169
Wang L, **ng HL, Gao ST, Ji XL, Shen ZY (2017) Porous flower-like NiO @graphene composites with superior microwave absorption properties. J Mater Chem C 5:2005–2014
Song CQ, Yin XW, Han MK, Li XL, Hou ZX, Zhang LT, Cheng LF (2017) Three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide foam modified with ZnO nanowires for enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 116:50–58
Wang ZC, Wei RB, Gu JW, Liu H, Liu CT, Luo CJ, Kong J, Shao Q, Wang N, Guo ZH, Liu XB (2018) Ultralight, highly compressible and fire-retardant graphene aerogel with self-adjustable electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 139:1126–1135
Zheng YW, Wang XX, Wei S, Zhang BQ, Yu MX, Zhao W, Liu JQ (2017) Fabrication of porous graphene-Fe3O4 hybrid composites with outstanding microwave absorption performance. Compos Part A 95:237–247
Stadie NP, Wang ST, Kravchyk KV, Kovalenk MV (2017) Zeolite-templated carbon as an ordered microporous electrode for aluminum batteries. ACS Nano 11:1911–1919
Kim K, Lee T, Kwon Y, Seo Y, Song JC, Park JK, Lee H, Park JY, Ihee H, Cho SJ, Ryoo R (2016) Lanthanum-catalysed synthesis of microporous 3D graphene-like carbons in a zeolite template. Nature 535:131–135
Nueangnoraj K, Nishihara H, Imai K, Itoi H, Ishii T, Kiguchi M, Sato Y, Terauchi M, Kyotani T (2013) Formation of crosslinked-fullerene-like framework as negative replica of zeolite Y. Carbon 62:455–464
Voiry D, Yang J, Kupferberg J, Fullon R, Lee C, Jeong HY, Shin HS, Chhowalla M (2016) High-quality graphene via microwave reduction of solution-exfoliated graphene oxide. Science 353:1413–1416
Ferrari AC, Meyer JC, Scardaci V, Casiraghi C, Lazzeri M, Mauri F, Piscanec S, Jiang D, Novoselov KS, Roth S, Geim AK (2006) Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys Rev Lett 97:187401
Cançado LG, Jorio A, E. Ferreira HM, Stavale F, Achete CA, Capaz RB, Moutinho MVO, Lombardo A, Kulmala TS, Ferrari AC, (2011) Quantifying defects in graphene via Raman spectroscopy at different excitation energies. Nano Lett 11:3190–3196
Zafar Z, Ni ZH, Wu X, Shi ZX, Nan HY, Bai J, Sun LT (2013) Evolution of Raman spectra in nitrogen doped graphene. Carbon 61:57–62
Ammar MR, Galy N, Rouzaud JN, Toulhoat N, Vaudey CE, Simon P, Moncoffre N (2015) Characterizing various types of defects in nuclear graphite using Raman scattering: heat treatment, ion irradiation and polishing. Carbon 95:364–373
Nanda SS, Kim MJ, Yeom KS, An SSA, Ju H, Yi DK (2016) Raman spectrum of graphene with its versatile future perspectives. Trend Anal Chem 80:125–131
Viinikanoja A, Kauppila J, Damlin P, Suominena M, Kvarnstrom C (2015) In situ FTIR and Raman spectroelectrochemical characterization of graphene oxide upon electrochemical reduction in organic solvents. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:12115–12123
Tu ZQ, Wu SF, Yang F, Li YF, Zhang LQ, Liu HW, Ding H, Richard P (2015) Synthesis of three-dimensional nanoporous graphene for use as surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate. Mater Lett 152:264–267
Kim TH, Lee KB, Choi JW (2013) 3D graphene oxide-encapsulated gold nanoparticles to detect neural stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials 34:8660–8670
Pierlot AP, Woodhead AL, Church JS (2014) Thermal annealing effects on multi-walled carbon nanotube yarns probed by Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A 117:598–603
Cividanes LS, Brunelli DD, Antunes EF, Corat EJ, Sakane KK, Thim GP (2013) Cure study of epoxy resin reinforced with multiwalled carbon nanotubes by Raman and luminescence spectroscopy. J Appl Polym Sci 127:544–553
Lemos V, Guerini S, Lala SM, Montoro LA, Rosolen JM (2005) Li-inserted carbon nanotube Raman scattering. Microelectr J 36:1020–1022
Monteiro FH, Larrude DG, Maia da Costa MEH, Freire FL (2013) Estimating the boron do** level on single wall carbon nanotubes using Raman spectroscopy. Mater Lett 92:224–226
He N, Yang XF, Shi LX, Yang XC, Lu Y, Tong GX, Wu WH (2020) Chemical conversion of Cu2O/PPy core-shell nanowires (CSNWs): A surface/interface adjustment method for high-quality Cu/Fe/C and Cu/ Fe3O4/C CSNWs with superior microwave absorption capabilities. Carbon 166:205–217
Wu B, Tuncer HM, Katsounaros A, Wu WP, Cole MT, Ying K, Zhang LH, Milne WI, Hao Y (2014) Microwave absorption and radiation from large-area multilayer CVD graphene. Carbon 77:814–822
Batrakov K, Kuzhir P, Maksimenko S, Voronovich N, Paddubskaya A, Valusis G, Kaplas T, Svirko Yu, Lambin Ph (2016) Enhanced microwave-to-terahertz absorption in graphene. Appl Phys Lett 108:123101
Liu L, He N, Wu T, Hu PB, Tong GX (2019) Co/C/Fe/C hierarchical flowers with strawberry-like surface as surface plasmon for enhanced permittivity, permeability and microwave absorption properties. Chem Eng J 355:103–108
Lv HL, Ji GB, Liu W, Zhang HQ, Du YW (2015) Achieving hierarchical hollow carbon@Fe@Fe3O4 nanospheres with superior microwave absorption properties and lightweight features. J Mater Chem C 3:10232–10241
He N, Liu MM, Qi JY, Tong JY, Sao W, Yang XC, Shi LX, Tong GX (2019) Plasmon resonance strategy to enhance permittivity and microwave absorbing performance of Cu/C core-shell nanowires. Chem Eng J 378:122160
He N, He ZD, Liu L, Lu Y, Wang FQ, Wu WH, Tong GX (2020) Ni2+ guided phase/structure evolution and ultra-wide bandwidth microwave absorption of CoxNi1-x alloy hollow microspheres. Chem Eng J 381:122743
Vázquez E, Prato M (2009) Carbon nanotubes and microwaves: Interactions, responses and applications. ACS Nano 3:3819–3824
Paredes JI, Rodil SV, Alonso AM, Tascon JMD (2008) Graphene oxide dispersions in organic solvents. Langmuir 24:10560–10564
Zhang XF, Guan PF, Guo JJ (2013) Dumbbell-like Fe3O4-Au nanoparticles for ultrabroadband electromagnetic losses by heterogeneous interfacial polarizations. Part Part Syst Charact 30:842–846
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1704253, 51471045, 51471048 and 51401049), the Zhejiang provincial natural science foundation of China (LR18E010001), the fundamental research funds for the Central universities (N160208001) and the basic research program of key laboratory of Liaoning province (LZ2015035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Annela M. Seddon.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Liao, Y., Wang, Z. et al. Highly ordered, ultralight three-dimensional graphene-like carbon for high-frequency electromagnetic absorption. J Mater Sci 56, 4305–4315 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05533-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-05533-2