Abstract
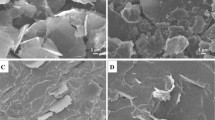
Graphene platelets (GnPs) were surface modified with a long-chain surfactant B200, and then compounded with polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). B200 provided an anchor into GnPs and a bridge into the matrix, thus creating molecular entanglement between matrix and GnPs. The interface modification promoted the dispersion of GnPs, as no aggregates of GnPs were observed on the fracture surface of the modified composites, in sharp contrast with the unmodified composites. Although GnPs formed clusters in the matrix, bilayer graphene was readily observed under TEM in randomly selected regions; it showed high structural integrity under diffraction pattern. The addition of 2.7 vol% m-GnPs produced 32.8 % improvement in the flexural modulus of PMMA as compared to 9.0 % by unmodified GnPs. At 1.1 vol%, the interface-modified composite showed a 19.6 % improvement in the absorption resistance to ethanol, in comparison with 3.8 % for the unmodified composites. The addition of 2.7 vol% m-GnPs improved fracture toughness of PMMA by 79.2 %, while GnPs enhanced it by 23.9 %.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV et al (2004) Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306:666–669. doi:10.1126/science.1102896
Cheng C, Li D (2013) Solvated graphenes: an emerging class of functional soft materials. Adv Mater 25:13–30. doi:10.1002/adma.201203567
Polyakova EY, Rim KT, Eom D et al (2011) Scanning tunneling microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy studies of graphene films prepared by sonication-assisted dispersion. ACS Nano 5:6102–6108. doi:10.1021/nn1009352
Chang L, Wu S, Chen S, Li X (2011) Preparation of graphene oxide-molecularly imprinted polymer composites via atom transfer radical polymerization. J Mater Sci 46:2024–2029. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-5033-z
Han Y, Wu Y, Shen M, Huang X, Zhu J, Zhang X (2013) Preparation and properties of polystyrene nanocomposites with graphite oxide and graphene as flame retardants. J Mater Sci 48:4214–4222. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7234-8
Imran S, Kim Y, Shao G, Hussain M, Choa Y-h, Kim H (2014) Enhancement of electroconductivity of polyaniline/graphene oxide nanocomposites through in situ emulsion polymerization. J Mater Sci 49:1328–1335. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7816-5
Kim J, Im H, Kim J-m, Kim J (2012) Thermal and electrical conductivity of Al(OH)3 covered graphene oxide nanosheet/epoxy composites. J Mater Sci 47:1418–1426. doi:10.1007/s10853-011-5922-9
Ma W-S, Wu L, Yang F, Wang S-F (2014) Non-covalently modified reduced graphene oxide/polyurethane nanocomposites with good mechanical and thermal properties. J Mater Sci 49:562–571. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7736-4
Wang Y, Tang Y, Chen Y et al (2013) Reduced graphene oxide-based photocatalysts containing Ag nanoparticles on a TiO2 nanotube array. J Mater Sci 48:6203–6211. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7417-3
Zhang Y, Pan C (2011) TiO2/graphene composite from thermal reaction of graphene oxide and its photocatalytic activity in visible light. J Mater Sci 46:2622–2626. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-5116-x
Zaman I, Kuan H-C, Meng Q et al (2012) A facile approach to chemically modified graphene and its polymer nanocomposites. Adv Funct Mater 22:2735–2743. doi:10.1002/adfm.201103041
Zaman I, Kuan HC, Dai J et al (2012) From carbon nanotubes and silicate layers to graphene platelets for polymer nanocomposites. Nanoscale 4:4578–4586. doi:10.1039/c2nr30837a
Zhao B, Liu P, Jiang Y et al (2012) Supercapacitor performances of thermally reduced graphene oxide. J Power Sources 198:423–427. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.09.074
Van Landuyt KL, Snauwaert J, De Munck J et al (2007) Systematic review of the chemical composition of contemporary dental adhesives. Biomaterials 28:3757–3785
Frankenberger R, Sindel J, Krämer N, Petschelt A (1999) Dentin bond strength and marginal adaptation: direct composite resins vs ceramic inlays. Oper Dent 24:147
Blond D, Barron V, Ruether M et al (2006) Enhancement of modulus, strength, and toughness in poly(methyl methacrylate)-based composites by the incorporation of poly(methyl methacrylate)-functionalized nanotubes. Adv Funct Mater 16:1608–1614. doi:10.1002/adfm.200500855
Kuljanin-Jakovljević J, Stojanović Z, Nedeljković JM (2006) Influence of cds-filler on the thermal properties of poly(methyl methacrylate). J Mater Sci 41:5014–5016. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-0111-y
Park JH, Jana SC (2003) The relationship between nano- and micro-structures and mechanical properties in Pmma-epoxy-nanoclay composites. Polymer 44:2091–2100. doi:10.1016/s0032-3861(03)00075-2
Young RJ, Kinloch IA, Gong L, Novoselov KS (2012) The mechanics of graphene nanocomposites: a review. Compos Sci Technol 72:1459–1476. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2012.05.005
Li B, Yuan H, Zhang Y (2013) Transparent Pmma-based nanocomposite using electrospun graphene-incorporated Pa-6 nanofibers as the reinforcement. Compos Sci Technol 89:134–141. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.09.022
Yang J, Yan X, Wu M, Chen F, Fei Z, Zhong M (2012) Self-assembly between graphene sheets and cationic poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) particles: preparation and characterization of PMMA/graphene composites. J Nanopart Res 14:1–9. doi:10.1007/s11051-011-0717-0
Li Y-L, Kuan C-F, Chen C-H et al (2012) Preparation, thermal stability and electrical properties of PMMA/functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets composites. Mater Chem Phys 134:677–685
Tripathi SN, Saini P, Gupta D, Choudhary V (2013) Electrical and mechanical properties of PMMA/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites prepared via in situ polymerization. J Mater Sci 48:6223–6232. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7420-8
Zeng X, Yang J, Yuan W (2012) Preparation of a poly (methyl methacrylate)-reduced graphene oxide composite with enhanced properties by a solution blending method. Eur Polym J 48:1674–1682
Zhang H-B, Zheng W-G, Yan Q, Jiang Z-G, Yu Z–Z (2012) The effect of surface chemistry of graphene on rheological and electrical properties of polymethylmethacrylate composites. Carbon 50:5117–5125
Jiang SH, Gui Z, Bao C et al (2013) Preparation of functionalized graphene by simultaneous reduction and surface modification and its polymethyl methacrylate composites through latex technology and melt blending. Chem Eng J 226:326–335. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.068
Ma J, La LTB, Zaman I et al (2011) Fabrication, structure and properties of epoxy/metal nanocomposites. Macromol Mater Eng 296:465–474. doi:10.1002/mame.201000409
Ma J, Qi Q, Bayley J, Du X-S, Mo M-S, Zhang L-Q (2007) Development of senb toughness measurement for thermoset resins. Polym Test 26:445–450. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2006.12.011
Meng Q, Zaman I, Hannam JR et al (2011) Improvement of adhesive toughness measurement. Polym Test 30:243–250. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2011.01.001
Araby S, Meng Q, Zhang L et al (2014) Electrically and thermally conductive elastomer/graphene nanocomposites by solution mixing. Polymer 55:201–210. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2013.11.032
Araby S, Zaman I, Meng Q et al (2013) Melt compounding with graphene to develop functional, high-performance elastomers. Nanotechnology 24:165601. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/24/16/165601
Meng Q, Araby S, Saber N et al (2014) Toughening polymer adhesives using nanosized elastomeric particles. J Mater Res 29:665–674. doi:10.1557/jmr.2014.34
Ezrin M (1996) Plastics failure guide: causes and prevention. Hanser, Cincinnati
Ma J, Mo MS, Du XS, Rosso P, Friedrich K, Kuan HC (2008) Effect of inorganic nanoparticles on mechanical property, fracture toughness and toughening mechanism of two epoxy systems. Polymer 49:3510–3523. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2008.05.043
Kuan H-C, Dai J-B, Ma J (2010) A reactive polymer for toughening epoxy resin. J Appl Polym Sci 115:3265–3272. doi:10.1002/app.31001
Wan Y-J, Tang L-C, Yan D et al (2013) Improved dispersion and interface in the graphene/epoxy composites via a facile surfactant-assisted process. Compos Sci Technol 82:60–68. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.04.009
Sun L, Gibson RF, Gordaninejad F, Suhr J (2009) Energy absorption capability of nanocomposites: a review. Compos Sci Technol 69:2392–2409. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.06.020
Bortz DR, Heras EG, Martin-Gullon I (2012) Impressive fatigue life and fracture toughness improvements in graphene oxide/epoxy composites. Macromolecules 45:238–245. doi:10.1021/ma201563k
Ma J, Meng QS, Zaman I et al (2014) Development of polymer composites using modified, high-structural integrity graphene platelets. Compos Sci Technol 91:82–90. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.11.017
Dai J-B, Kuan H-C, Du X-S, Dai S-C, Ma J (2009) Development of a novel toughener for epoxy resins. Polym Int 58:838–845. doi:10.1002/pi.2604
Hull D (1999) Fractography: observing, measuring and interpreting fracture surface topography. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Le Q-H, Kuan H-C, Dai J-B, Zaman I, Luong L, Ma J (2010) Structure–property relations of 55 nm particle-toughened epoxy. Polymer 51:4867–4879. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2010.08.038
Hernandez Y, Nicolosi V, Lotya M et al (2008) High-yield production of graphene by liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite. Nat Nanotechnol 3:563–568. doi:10.1038/nnano.2008.215
Meng QS, ** J, Wang RY et al (2014) Processable 3-nm thick graphene platelets of high electrical conductivity and their epoxy composites. Nanotechnology 25:125707. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/25/12/125707
Vallés C, Drummond C, Saadaoui H et al (2008) Solutions of negatively charged graphene sheets and ribbons. J Am Chem Soc 130:15802–15804. doi:10.1021/ja808001a
Yu S, Hu H, Ma J, Yin J (2008) Tribological properties of epoxy/rubber nanocomposites. Tribol Int 41:1205–1211. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2008.03.001
Ribeiro H, Silva W, Rodrigues M-T et al (2013) Glass transition improvement in epoxy/graphene composites. J Mater Sci 48:7883–7892. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7478-3
Putz KW, Palmeri MJ, Cohn RB, Andrews R, Brinson LC (2008) Effect of cross-link density on interphase creation in polymer nanocomposites. Macromolecules 41:6752–6756. doi:10.1021/ma800830p
Grossiord N, Loos J, Regev O, Koning CE (2006) Toolbox for dispersing carbon nanotubes into polymers to get conductive nanocomposites. Chem Mater 18:1089–1099. doi:10.1021/cm051881h
Ma P-A, Siddiqui NA, Marom G, Marom G, Kim J-K (2010) Dispersion and functionalization of carbon nanotubes for polymer-based nanocomposites: a review. Compos Part A: Appl Sci Manuf 41:1345–1367. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2010.07.003
Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Dommett GH et al (2006) Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 442:282–286. doi:10.1038/nature04969
Du FP, Wang JJ, Tang CY et al (2012) Water-soluble graphene grafted by poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) for enhancement of electric capacitance. Nanotechnology 23:475704. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/23/47/475704
Ma J, Meng Q, Michelmore A et al (2013) Covalently bonded interfaces for polymer/graphene composites. J Mater Chem A 1:4255. doi:10.1039/c3ta01277h
Shen J, Hu Y, Shi M et al (2009) Fast and facile preparation of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide nanoplatelets. Chem Mater 21:3514–3520. doi:10.1021/cm901247t
Acknowledgement
JM and QM appreciate assistance and help from Matt Zoina and also thank Animesh Basak, Angus Netting and John Terlet for technical support at Adelaide Microscopy. CW would like to acknowledge the support by an Australian Research Council Discovery project (DP140100778).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Q., Kuan, HC., Araby, S. et al. Effect of interface modification on PMMA/graphene nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 49, 5838–5849 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8278-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8278-0