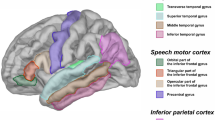
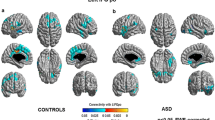
Abstract
A significant number of individuals with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) exhibit language difficulties. Here, we examined the language-related brain morphometry in 59 participants (7 participants with TSC and comorbid autism spectrum disorder (ASD) (TSC + ASD), 13 with TSC but no ASD (TSC-ASD), 10 with ASD-only (ASD), and 29 typically develo** (TD) controls). A hemispheric asymmetry was noted in surface area and gray matter volume of several cortical language areas in TD, ASD, and TSC-ASD groups, but not in TSC + ASD group. TSC + ASD group demonstrated increased cortical thickness and curvature values in multiple language regions for both hemispheres, compared to other groups. After controlling for tuber load in the TSC groups, within-group differences stayed the same but the differences between TSC-ASD and TSC + ASD were no longer statistically significant. These preliminary findings suggest that comorbid ASD in TSC as well as tuber load in TSC is associated with changes in the morphometry of language regions. Future studies with larger sample sizes will be needed to confirm these findings.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
01 February 2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-023-06098-0
References
Acheson, D. J., & Hagoort, P. (2013). Stimulating the Brain’s Language Network: Syntactic ambiguity resolution after TMS to the Inferior Frontal Gyrus and middle temporal Gyrus. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00430
American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition: DSM-IV-TR®. American Psychiatric Association.
Au, K. S., Williams, A. T., Roach, E. S., Batchelor, L., Sparagana, S. P., Delgado, M. R., et al. (2007). Genotype/phenotype correlation in 325 individuals referred for a diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis complex in the United States. Genetics in medicine: official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics, 9(2), 88–100.
Baskin, H. J., Jr. (2008). The pathogenesis and imaging of the tuberous sclerosis complex. Pediatric radiology, 38(9), 936–952.
Baumer, F. M., Peters, J. M., Clancy, S., Prohl, A. K., Prabhu, S. P., Scherrer, B., et al. (2018). Corpus Callosum White Matter Diffusivity reflects cumulative neurological comorbidity in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Cerebral cortex, 28(10), 3665–3672.
Belyk, M., Brown, S., & Kotz, S. A. (2017). Demonstration and validation of Kernel Density Estimation for spatial meta-analyses in cognitive neuroscience using simulated data. Data in brief, 13, 346–352.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false Discovery rate: A practical and powerful Approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x
Binder, J. R., Frost, J. A., Hammeke, T. A., Cox, R. W., Rao, S. M., & Prieto, T. (1997). Human brain language areas identified by functional magnetic resonance imaging. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 17(1), 353–362.
Bogousslavsky, J., Miklossy, J., Deruaz, J. P., Assal, G., & Regli, F. (1987). Lingual and fusiform gyri in visual processing: A clinico-pathologic study of superior altitudinal hemianopia. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry, 50(5), 607–614.
Bolton, P. F., & Griffiths, P. D. (1997). Association of tuberous sclerosis of temporal lobes with autism and atypical autism. The Lancet, 349(9049), 392–395.
Burton, M. W., Small, S. L., & Blumstein, S. E. (2000). The role of segmentation in phonological processing: An fMRI investigation. Journal of cognitive neuroscience, 12(4), 679–690.
Cohen, A. L., Mulder, B. P. F., Prohl, A. K., Soussand, L., Davis, P., Kroeck, M. R., et al. (2021a). Tuber locations Associated with Infantile Spasms Map to a common Brain Network. Annals of neurology, 89(4), 726–739.
Cohen, R., Genizi, J., & Korenrich, L. (2021b). Behavioral symptoms may correlate with the load and spatial location of tubers and with Radial Migration Lines in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Frontiers in neurology, 12, 673583.
Crino, P. B. (2013). Evolving neurobiology of tuberous sclerosis complex. Acta neuropathologica, 125(3), 317–332.
Crino, P. B. (2015). mTOR signaling in epilepsy: Insights from malformations of cortical development. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine, 5(4). https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a022442
Curatolo, P., & Bombardieri, R. (2008). Tuberous sclerosis. Handbook of clinical neurology, 87, 129–151.
Curatolo, P., Verdecchia, M., & Bombardieri, R. (2002). Tuberous sclerosis complex: A review of neurological aspects. European journal of paediatric neurology: EJPN: official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society, 6(1), 15–23.
Dale, A. M., & Sereno, M. I. (1993). Improved localization of cortical activity by combining EEG and MEG with MRI cortical Surface Reconstruction: A Linear Approach. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.1993.5.2.162
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical Surface-Based Analysis. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1998.0395
Dapretto, M., & Bookheimer, S. Y. (1999). Form and content: Dissociating syntax and semantics in sentence comprehension. Neuron, 24(2), 427–432.
Davis, P. E., Peters, J. M., Krueger, D. A., & Sahin, M. (2015). Tuberous sclerosis: A New Frontier in targeted treatment of Autism. Neurotherapeutics: the journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics, 12(3), 572–583.
DiMario F.J. (2004). Brain abnormalities in tuberous sclerosis complex. J Child Neurol 2004 Sep;19(9):650-7. https://doi.org/10.1177/08830738040190090401. PMID: 15563010.
Docampo, J., Cabrini, M., Bruno, C., & Morales, C. (2013). Tuberous sclerosis: Evaluation of intracranial lesions. Revista Argentina de Radiologia, 77(4), 275–283.
Eklöf, E., Mårtensson, G. E., Ådén, U., & Padilla, N. (2019). Reduced structural brain asymmetry during neonatal life is potentially related to autism spectrum disorders in children born extremely preterm. Autism research: official journal of the International Society for Autism Research, 12(9), 1334–1343.
Fischl, B., & Dale, A. M. (2000). Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(20), 11050–11055.
Fischl, B., Sereno, M. I., & Dale, A. M. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. II: Inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage, 9(2), 195–207.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., et al. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: Automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355.
Fischl, B., van der Kouwe, A., Destrieux, C., Halgren, E., Ségonne, F., Salat, D. H., et al. (2004). Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cerebral cortex, 14(1), 11–22.
Gallagher A., Grant E.P., Madan N., Jarrett D.Y., Lyczkowski D.A., Thiele E.A. (2010). MRI findings reveal three different types of tubers in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. J Neurol. 257(8):1373–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-010-5535-2.
Gallagher, A., Tanaka, N., Suzuki, N., Liu, H., Thiele, E. A., & Stufflebeam, S. M. (2012). Decreased language laterality in tuberous sclerosis complex: A relationship between language dominance and tuber location as well as history of epilepsy. Epilepsy & behavior: E&B, 25(1), 36–41.
Gallagher, A., Tanaka, N., Suzuki, N., Liu, H., Thiele, E. A., & Stufflebeam, S. M. (2013). Diffuse cerebral language representation in tuberous sclerosis complex. Epilepsy research, 104(1–2), 125–133.
Genovese, C. R., Lazar, N. A., & Nichols, T. (2002). Thresholding of statistical maps in functional neuroimaging using the false discovery rate. NeuroImage, 15(4), 870–878.
Geranmayeh, F., Brownsett, S. L. E., Leech, R., Beckmann, C. F., Woodhead, Z., & Wise, R. J. S. (2012). The contribution of the inferior parietal cortex to spoken language production. Brain and language, 121(1), 47–57.
Geranmayeh, F., Leech, R., & Wise, R. J. S. (2015). Semantic retrieval during overt picture description: Left anterior temporal or the parietal lobe? Neuropsychologia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.12.012
Hallett, L., Foster, T., Liu, Z., Blieden, M., & Valentim, J. (2011). Burden of disease and unmet needs in tuberous sclerosis complex with neurological manifestations: Systematic review. Current medical research and opinion, 27(8), 1571–1583.
Hartwigsen, G., Baumgaertner, A., Price, C. J., Koehnke, M., Ulmer, S., & Siebner, H. R. (2010). Phonological decisions require both the left and right supramarginal gyri. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(38), 16494–16499.
Hullett, P. W., Hamilton, L. S., Mesgarani, N., Schreiner, C. E., & Chang, E. F. (2016). Human Superior temporal Gyrus Organization of Spectrotemporal Modulation tuning derived from Speech Stimuli. The Journal of Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1779-15.
Hulshof H.M., Benova B., Krsek P., Kyncl M., Lequin M.H., Belohlavkova A., Jezdik P., Braun K.P.J., Jansen F.E. (2021). The epileptogenic zone in children with tuberous sclerosis complex is characterized by prominent features of focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsia Open. 6(4):663–671. https://doi.org/10.1002/epi4.12529.
Im, K., Ahtam, B., Haehn, D., Peters, J. M., Warfield, S. K., Sahin, M., & Ellen Grant, P. (2016). Altered structural brain networks in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Cerebral cortex, 26(5), 2046–2058.
Jobard, G., Crivello, F., & Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. (2003). Evaluation of the dual route theory of reading: a metanalysis of 35 neuroimaging studies. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1053-8119(03)00343-4
Just, M. A., Cherkassky, V. L., Keller, T. A., & Minshew, N. J. (2004). Cortical activation and synchronization during sentence comprehension in high-functioning autism: Evidence of underconnectivity. Brain: a journal of neurology, 127(Pt 8), 1811–1821.
Kiernan, J. A. (2012). Anatomy of the temporal lobe. Epilepsy research and treatment, 2012, 176157.
Klapwijk, E. T., van de Kamp, F., van der Meulen, M., Peters, S., & Wierenga, L. M. (2019). Qoala-T: A supervised-learning tool for quality control of FreeSurfer segmented MRI data. NeuroImage, 189, 116–129.
Knecht, S. (2000). Handedness and hemispheric language dominance in healthy humans. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/123.12.2512
Kotz, S. A., Cappa, S. F., von Cramon, D. Y., & Friederici, A. D. (2002). Modulation of the lexical-semantic network by auditory semantic priming: An event-related functional MRI study. NeuroImage, 17(4), 1761–1772.
Levitin, D. and Menon, V. (2003). Musical structure is processed in “language” areas of the brain: A possible role for Brodmann Area 47 in temporal coherence. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.08.016
Lewis, W. W., Sahin, M., Scherrer, B., Peters, J. M., Suarez, R. O., Vogel-Farley, V. K., et al. (2013). Impaired language pathways in tuberous sclerosis complex patients with autism spectrum disorders. Cerebral cortex, 23(7), 1526–1532.
Lord, C., Risi, S., Lambrecht, L., Cook, E. H., Jr, Leventhal, B. L., DiLavore, P. C., et al. (2000). The autism diagnostic observation schedule-generic: A standard measure of social and communication deficits associated with the spectrum of autism. Journal of autism and developmental disorders, 30(3), 205–223.
Marie, D., Maingault, S., Crivello, F., Mazoyer, B., & Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. (2016). Surface-based morphometry of cortical thickness and Surface Area Associated with Heschl’s Gyri Duplications in 430 healthy volunteers. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00069
Markou, P., Ahtam, B., & Papadatou-Pastou, M. (2017). Elevated levels of atypical handedness in Autism: Meta-Analyses. Neuropsychology review, 27(3), 258–283.
Mechelli, A., Humphreys, G. W., Mayall, K., Olson, A., & Price, C. J. (2000). Differential effects of word length and visual contrast in the fusiform and lingual gyri during reading. Proceedings. Biological sciences / The Royal Society, 267(1455), 1909–1913.
Metwellay, K. A., Farghaly, H. S., Darweesh, A.E.M., Hamed, S.A. (2012). Cognitive delay in children with tuberous sclerosis in a develo** country: Clinical correlations. Journal of Pediatric Epilepsy, 1(4), 221–228.
Morosan, P., Schleicher, A., Amunts, K., & Zilles, K. (2005). Multimodal architectonic map** of human superior temporal gyrus. Anatomy and embryology, 210(5–6), 401–406.
Motulsky, H.M. and Brown, R.E. (2006). Detecting outliers when fitting data with nonlinear regression – a new method based on robust nonlinear regression and the false discovery rate. BMC Bioinformatics, 7:123.
Müller, R.-A., Rothermel, R. D., Behen, M. E., Muzik, O., Mangner, T. J., & Chugani, H. T. (1997). Receptive and expressive language activations for sentences. NeuroReport. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-199712010-00022
Murtha, S., Chertkow, H., Beauregard, M., & Evans, A. (1999). The neural substrate of picture naming. Journal of cognitive neuroscience, 11(4), 399–423.
Naeser, M. A., Martin, P. I., Theoret, H., Kobayashi, M., Fregni, F., Nicholas, M., et al. (2011). TMS suppression of right pars triangularis, but not pars opercularis, improves naming in aphasia. Brain and Language. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2011.07.005
Numis, A. L., Major, P., Montenegro, M. A., Muzykewicz, D. A., Pulsifer, M. B., & Thiele, E. A. (2011). Identification of risk factors for autism spectrum disorders in tuberous sclerosis complex. Neurology, 76(11), 981–987.
Ocak, P. E., & Kocaelı, H. (2017). Investigation of topographical anatomy of Broca’s area: An anatomic cadaveric study. Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1748-0
Onitsuka, T., Shenton, M. E., Salisbury, D. F., Dickey, C. C., Kasai, K., Toner, S. K., et al. (2004). Middle and inferior temporal gyrus gray matter volume abnormalities in chronic schizophrenia: An MRI study. The American journal of psychiatry, 161(9), 1603–1611.
Osborne, J. P., Fryer, A., & Webb, D. (1991). Epidemiology of tuberous sclerosis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 615, 125–127.
Palejwala, A. H., Dadario, N. B., Young, I. M., O’Connor, K., Briggs, R. G., Conner, A. K., et al. (2021). Anatomy and White Matter connections of the Lingual Gyrus and Cuneus. World neurosurgery, 151, e426–e437.
Palmen, S. J. M. C., & van Engeland, H. (2004). Review on structural neuroimaging findings in autism. Journal of neural transmission, 111(7), 903–929.
Park, B.S., Yoo, M.J., Kim, I.H., Park, J.H., Park, S.H., Lee, Y.J., Park, K.M. (2020). Alterations of gray matter volumes and connectivity in patients with tuberous sclerosis complex. J Clin Neurosci. 72:360–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2019.12.046.
Paulesu, E., Goldacre, B., Scifo, P., Cappa, S. F., Gilardi, M. C., Castiglioni, I., et al. (1997). Functional heterogeneity of left inferior frontal cortex as revealed by fMRI. Neuroreport, 8(8), 2011–2017.
Pereira, A. M., Campos, B. M., Coan, A. C., Pegoraro, L. F., de Rezende, T. J. R., Obeso, I., et al. (2018). Differences in cortical structure and functional MRI connectivity in high Functioning Autism. Frontiers in Neurology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00539
Peters, J. M., Sahin, M., Vogel-Farley, V. K., Jeste, S. S., Nelson, C. A., 3rd, Gregas, M. C., et al. (2012). Loss of white matter microstructural integrity is associated with adverse neurological outcome in tuberous sclerosis complex. Academic radiology, 19(1), 17–25.
Peters, J. M., Taquet, M., Vega, C., Jeste, S. S., Fernández, I. S., Tan, J., et al. (2013). Brain functional networks in syndromic and non-syndromic autism: A graph theoretical study of EEG connectivity. BMC Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-54
Petrides, M., Tomaiuolo, F., Yeterian, E. H., & Pandya, D. N. (2012). The prefrontal cortex: Comparative architectonic organization in the human and the macaque monkey brains. Cortex; a journal devoted to the study of the nervous system and behavior, 48(1), 46–57.
Pienaar, R., Fischl, B., Caviness, V., Makris, N., & Grant, P. E. (2008). A methodology for analyzing curvature in the develo** brain from preterm to adult. International journal of imaging systems and technology, 18(1), 42–68.
Prather, P., & de Vries, P. J. (2004). Behavioral and cognitive aspects of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Journal of Child Neurology. https://doi.org/10.1177/08830738040190090601
Prather, P. A., Morgan, A., Hickory, M., & Thiele, E. (2002). New Perspectives in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Research. Neuropsychological profiles of children with tuberous sclerosis complex: Implications for clinical guidelines and interventions, abstract. Chantillly, VA.
Pujol, J., Deus, J., Losilla, J. M., & Capdevila, A. (1999). Cerebral lateralization of language in normal left-handed people studied by functional MRI. Neurology, 52(5), 1038–1043.
Qin, W., Kozlowski, P., Taillon, B. E., Bouffard, P., Holmes, A. J., Janne, P., et al. (2010). Ultra deep sequencing detects a low rate of mosaic mutations in tuberous sclerosis complex. Human genetics, 127(5), 573–582.
Raznahan, A., Toro, R., Daly, E., Robertson, D., Murphy, C., Deeley, Q., et al. (2010). Cortical anatomy in autism spectrum disorder: An in vivo MRI study on the effect of age. Cerebral cortex, 20(6), 1332–1340.
Rojas, D. C., Bawn, S. D., Benkers, T. L., Reite, M. L., & Rogers, S. J. (2002). Smaller left hemisphere planum temporale in adults with autistic disorder. Neuroscience letters, 328(3), 237–240.
Rojas, D. C., Camou, S. L., Reite, M. L., & Rogers, S. J. (2005). Planum temporale volume in children and adolescents with autism. Journal of autism and developmental disorders, 35(4), 479–486.
Scherrer, B., Prohl, A.K., Taquet, M., Kapur, K., Peters, J.M., Tomas-Fernandez, X., Davis, P.E., Bebin, E.M., Krueger, D.A., Northrup, H., Wu J.Y., Sahin, M., Warfield, S.K. (2020). The Connectivity Fingerprint of the Fusiform Gyrus Captures the Risk of Develo** Autism in Infants with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Cereb Cortex. 14;30(4):2199–2214. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhz233.
Segonne, F., Dale, A. M., Busa, E., Glessner, M., Salat, D., Hahn, H. K., & Fischl, B. (2001). A hybrid approach to the Skull Strip** problem in MRI. NeuroImage. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1053-8119(01)91584-8
Segonne, F., Pacheco, J., & Fischl, B. (2007). Geometrically accurate topology-correction of cortical Surfaces using nonseparating loops. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2006.887364
Simao, G., Raybaud, C., Chuang, S., Go, C., Snead, O. C., & Widjaja, E. (2010). Diffusion tensor imaging of commissural and projection white matter in tuberous sclerosis complex and correlation with tuber load. AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology, 31(7), 1273–1277.
Sled, J. G., Zijdenbos, A. P., & Evans, A. C. (1998). A nonparametric method for automatic correction of intensity nonuniformity in MRI data. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 17(1), 87–97.
Springer, J. A., Binder, J. R., Hammeke, T. A., Swanson, S. J., Frost, J. A., Bellgowan, P. S. F., et al. (1999). Language dominance in neurologically normal and epilepsy subjects. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/122.11.2033
Staley, B. A., Vail, E. A., & Thiele, E. A. (2011). Tuberous sclerosis complex: Diagnostic challenges, presenting symptoms, and commonly missed signs. Pediatrics, 127(1), e117–25.
Stoeckel, C., Gough, P. M., Watkins, K. E., & Devlin, J. T. (2009). Supramarginal gyrus involvement in visual word recognition. Cortex; a journal devoted to the study of the nervous system and behavior, 45(9), 1091–1096.
Strand, F., Forssberg, H., Klingberg, T., & Norrelgen, F. (2008). Phonological working memory with auditory presentation of pseudo-words -- an event related fMRI study. Brain research, 1212, 48–54.
Szaflarski, J. P., Binder, J. R., Possing, E. T., McKiernan, K. A., Ward, B. D., & Hammeke, T. A. (2002). Language lateralization in left-handed and ambidextrous people: fMRI data. Neurology, 59(2), 238–244.
Szaflarski, J. P., Rajagopal, A., Altaye, M., Byars, A. W., Jacola, L., Schmithorst, V. J., et al. (2012). Left-handedness and language lateralization in children. Brain research, 1433, 85–97.
Vingerhoets, G. (2014). Contribution of the posterior parietal cortex in reaching, gras**, and using objects and tools. Frontiers in psychology, 5, 151.
Vries, P. J. D., De Vries, P. J., & Bolton, P. F. (2002). Tuberous sclerosis. Outcomes in Neurodevelopmental and Genetic Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511543876.012
Walz, N. C., Byars, A. W., Egelhoff, J. C., & Franz, D. N. (2002). Supratentorial tuber location and autism in tuberous sclerosis complex. Journal of child neurology, 17(11), 830–832.
Warrier, C., Wong, P., Penhune, V., Zatorre, R., Parrish, T., Abrams, D., & Kraus, N. (2009). Relating structure to function: Heschl’s Gyrus and Acoustic Processing. Journal of Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3489-08.2009
White, T., Su, S., Schmidt, M., Kao, C.-Y., & Sapiro, G. (2010). The development of gyrification in childhood and adolescence. Brain and cognition, 72(1), 36–45.
Wilke, M., Pieper, T., Lindner, K., Dushe, T., Holthausen, H., & Krägeloh-Mann, I. (2010). Why one task is not enough: Functional MRI for atypical language organization in two children. European journal of paediatric neurology: EJPN: official journal of the European Paediatric Neurology Society, 14(6), 474–478.
Wiznitzer, M. (2004). Autism and tuberous sclerosis. Journal of child neurology, 19(9), 675–679.
Xu, J., Wang, J., Fan, L., Li, H., Zhang, W., Hu, Q., & Jiang, T. (2015). Tractography-based parcellation of the human middle temporal Gyrus. Scientific reports, 5, 18883.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahtam, B., Yun, H.J., Vyas, R. et al. Morphological Features of Language Regions in Individuals with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. J Autism Dev Disord (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-023-06004-8
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-023-06004-8